Abstract
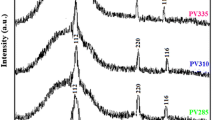
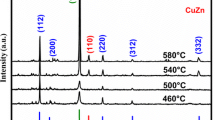
Investigations into the influence of the substrate type (a glass substrate with a molybdenum sublayer, tantalum and molybdenum foils) on the surface morphology of Cu2ZnSnSe4 thin films obtained by selenization of electrochemically deposited and preliminary annealed metallic precursors are presented. Metal foils are attractive for use as substrates of solar cells in both ground and space objects due to their light weight, flexibility, and the possibility of using the commercial roll-to-roll technology of film fabrication, leading to a reduction in the cost. At different stages of Cu2ZnSnSe4 film preparation, their surface morphology is studied by atomic-force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy in combination with energy-dispersive spectrometry. The metal substrate morphology is demonstrated to have an insignificant effect on the surface morphology of Cu2ZnSnSe4 films, indicating that flexible-foil substrates are promising for the production of thin-film solar cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Semiconductor Materials for Solar Photovoltaic Cells Ed. by M. P. Paranthaman, W. Wong-Ng, and R. N. Bhattacharya, Vol. 218 of Springer Series in Material Science (Springer, 2016).
M. A. Green, K. Emery, Y. Hishikawa, et al., Prog. Photovoltaics. 24, 905 (2016). doi 10.1002/pip.2788
M. A. Green, Prog. Photovoltaics. 17, 347 (2009). doi 10.1002/pip.899
P. D. Moskowitz and V. M. Fthenakis, Sol. Cells 29, 63 (1990).
W. Shockley and H. J. Queisser, J. Appl. Phys. 32, 510 (1961). doi 10.1063/1.1736034
J. Lee, S. C. Nam, and Y. Tak, Korean J. Chem. Eng. 22, 161 (2005). doi 10.1007/BF02701479
L. Guo, Y. Zhu, O. Gunawan, et al., Prog. Photovoltaics. 22, 58 (2012). doi 10.1002/pip.2332
M. Pagliaro, G. Palmisano, and R. Ciriminna, Flexible Solar Cells (Wiley, Weinheim, 2008).
F. Kessler and D. Rudmann, Sol. Energy 77, 685 (2004). doi 10.1016/j.solener.2004.04.010
A. V. Stanchik, S. A. Bashkirov, Y. S. Yakovenko, et al., Fiz. Obraz. VUZakh 22 (1), 106C (2016).
A. V. Stanchik, S. M. Barajshuk, S. A. Bashkirov, et al., Vestsi Nats. Akad. Nauk Belarusi., Ser. Fiz.-Mat. Nauk, No. 4, 67 (2016).
H. Chia-Ho and W. Dong-Cherng, Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 568648 (2014). doi 10.1155/2014/568648
I. S. Tashlykov and S. M. Baraishuk, Russ. J. Non-Ferrous Met. 49, 303 (2008). doi 10.3103/S1067821208040172
I. Tashlykov, S. Baraishuk, O. Mikkalkovich, and I. Antonovich, Przegl. Elektrotech. 84 (3), 111 (2008).
R. Kondrotas, A. Juskenas, A. Naujokaitis, et al., Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 132, 21 (2015). doi 10.1016/j.solmat.2014.08.010
A. Redinger, K. Hönes, X. Fontané, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 101907 (2011). doi 10.1063/1.3558706
A. H. Pinto, S. W. Shin, E. S. Aydil, and R. L. Penn, Green Chem. 18, 5814 (2016). doi 10.1039/c6gc01287f
C. Xue, D. Papadimitriou, Y. S. Raptis, et al., J. Appl. Phys. 96, 1963 (2004). doi 10.1063/1.1772885
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was performed in the context of scientific research according to the grant of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus, by the State program of scientific studies “Physical Material Science, New Materials and Technologies” (МАТТЕХ 1.0.6), and was supported by the Belarusian Republican Foundation for Fundamental Research (project no. F17PM-089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by S. Rodikov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baraishuk, S.M., Tkachenko, T.M., Stanchik, A.V. et al. Influence of the Substrate Type on the Surface Morphology of Cu2ZnSnSe4 Thin Films. J. Surf. Investig. 12, 1077–1081 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1027451018050415
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1027451018050415