Abstract
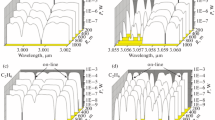
A differential absorption lidar (DIAL) system based on optical parametric oscillators (OPO) with nonlinear KTA and KTP crystals is designed. The crystals allow laser radiation tuning in the IR wavelength region. A series of experiments on remote monitoring of methane along a horizontal surface sounding path in the 3300–3430 nm spectral range was carried out. Based on the experimental results, the CH4 concentrations are retrieved along a surface 800-m path in the spectral range under study with a spatial resolution of 100 m.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. T. Reghunath, P. Malhotra, Y. Kumar, and B. Bhushan, “Design of a tunable mid-IR OPO source for DIAL detection of trace gases,” Proc. SPIE—Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 6409, 64091 (2006).
K. O. Douglass, S. E. Maxwell, D. F. Plusquellic, J. T. Hodges, R. D. van Zee, D. V. Samarov, and J. R. Whetstone, “Construction of a high power OPO laser system for differential absorption LIDAR,” Proc. SPIE—Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 8159, 81590 (2011).
J. Barrientos-Barria, J. Dherbecourt, M. Raybaut, A. Godard, J. M. Melkonian, M. H. Lefebvre, B. Faure, and G. Souhaite, “3.3–3.7 μm nested cavity OPO pumped by an amplified micro-laser for portable DIA-L,” in 2013 Conference on Lasers & Electro-Optics & International Quantum Electronics Conference CLEO EUROPE/IQEC (IEEE, 2014), p. 978-1-4799-0594-2. https://doi.org/10.1109/CLEOE-IQEC.2013.6800859
S. Amoruso, A. Amodeo, M. Armenante, A. Boselli, L. Mona, M. Pandolfi, G. Pappalardo, R. Velotta, N. Spinelli, and X. Wang, “Development of a tunable IR lidar system,” Opt. Laser Eng. 37 (5), 521–532 (2002).
V. S. Airapetyan, ”Measurement of atmospheric methane absorption spectra by lidar station with tunable emission wavelength in 1.41–4.24 μm range,” Zh. Prikl. Spektrosk. 76 (2), 285–290 (2009).
V. S. Airapetyan, ”Continuously and (or) discretely tunable optical parametric oscillator,” Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 21 (10), 791–794 (2008).
A. Amediek, A. Fix, M. Wirth, and G. Ehret, “Development of an OPO system at 1.57 μm for integrated path DIAL measurement of atmospheric carbon dioxide,” Appl. Phys. B 92 (2), 295–302 (2008).
J. Barrientos-Barria, A. A. Dobroc, H. Coudert-Alteirac, M. Raybaut, N. Cezard, J.-P. Dherbecourt, B. Faure, G. Souhaite, J.-M. Melkonian, A. Godard, M. Lefebvre, and J. Pelon, “3.3–3.7 μm OPO/OPA optical source for multi-species 200 m range integrated path differential absorption lidar,” in Applications of Lasers for Sensing and Free Space Communications (Opt. Soc. Am, 2013).
D. Mammez, E. Cadiou, J.-P. Dherbecourt, M. Raybaut, J.-M. Melkonian, A. Godard, G. Gorju, J. Pelon, and M. Lefebvre, “Multispecies transmitter for DIAL sensing of atmospheric water vapour, methane and carbon dioxide in the 2 μm region,” Proc. SPIE—Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 9645, 964507–1 (2015).
I. Robinson, J. W. Jack, C. F. Rae, and J. B. Moncrieff, “Development of a laser for differential absorption lidar measurement of atmospheric carbon dioxide,” Proc. SPIE—Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 9246, 92460 (2014).
I. Robinson, J. W. Jack, C. F. Rae, and J. B. Moncrieff, “A robust optical parametric oscillator and receiver telescope for differential absorption lidar of greenhouse gases,” Proc. SPIE—Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 9645, 96450 (2015).
V. Mitev, S. Babichenko, R. Borelli, L. Fiorani, I. Grigorov, M. Nuvoli, A. Palucci, M. Pistilli, Ad. Puiu, O. Rebane, and S. Santoro, “Lidar extinction measurement in the mid-infrared,” Proc. SPIE—Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 9292, 92923 (2014).
A. R. Geiger, US Patent No. 5 250 810 (5 October 1993).
H. M. Kalayeh, US Patent No. 7411196 (22 October 2007).
J. Liu, US Patent No. 8 541 744 (24 September 2013).
R. Foltynowicz, US Patent No. 8 837 538 (31 January 2013).
V. S. Airapetyan, “Laser based remote sensing of explosives by the method of differential absorption and scattering,” Zh. Prikl. Spektrosk. 84 (6), 987–992 (2017).
V. S. Ayrapetyan and P. A. Fomin, “Laser detection of explosives based on differential absorption and scattering,” Opt. Laser Technol. 106, 202–208 (2018).
S. Veerabuthiran, A. K. Razdan, M. K. Jindal, R. K. Sharma, and Vikas Sagar, “Development of 3.0–3.45 μm OPO laser based range resolved and hard-target differential absorption lidar for sensing of atmospheric methane,” Opt. Laser Technol. 73, 1–5 (2015).
V. Mitev, S. Babichenko, J. Bennes, R. Borelli, A. Dolfi-Bouteyre, L. Fiorani, L. Hespel, T. Huet, A. Palucci, M. Pistilli, A. Puiu, O. Rebane, and I. Sobolev, “Mid-IR DIAL for high-resolution mapping of explosive precursors,” Proc. SPIE—Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 8894, 88940 (2013).
E. Cadiou, D. Mammez, J.-B. Dherbecourt, G. Gorju, J. Pelon, J.-M. Melkonian, A. Godard, and M. Raybaut, “Atmospheric boundary layer CO2 remote sensing with a direct detection LIDAR instrument based on a widely tunable optical parametric source,” Opt. Lett. 42 (5), 4044–4047 (2017).
Y. Shibata, C. Nagasawa, and M. Abo, “Development of 1.6 μm DIAL using an OPG/OPA transmitter for measuring atmospheric CO2 concentration profiles,” Appl. Opt. 56 (4), 1194–1201 (2017).
O. A. Romanovskii, S. A. Sadovnikov, O. V. Kharchenko, and S. V. Yakovlev, “Broadband IR lidar for gas analysis of the atmosphere,” J. Appl. Spectrosc. 85 (3), 457–461 (2018).
G. G. Matvienko, O. A. Romanovskii, S. A. Sadovnikov, A. Ya. Sukhanov, O. V. Kharchenko, and S. V. Yakovlev, “Optical parametric oscillator in lidar sensing of atmospheric gases in the 3–4 μm spectral range,” Opt. Atmos. Okeana. 30 (7), 598–604 (2017).
G. G. Matvienko, O. A. Romanovskii, S. A. Sadovnikov, A. Ya. Sukhanov, O. V. Kharchenko, and S. V. Yakovlev, “Study of the possibility of using a parametric-light-generator-based laser system for lidar probing of the composition of the atmosphere,” J. Opt. Technol. 84 (6), 408–414 (2017).
O. A. Romanovskii, S. A. Sadovnikov, O. V. Kharchenko, and S. V. Yakovlev, “Development of near/mid IR differential absorption OPO lidar system for sensing of atmospheric gases,” Opt. Laser Technol. 116, 43–47 (2019).
O. A. Romanovskii, S. A. Sadovnikov, O. V. Kharchenko, and S. V. Yakovlev, “Near/mid-IR OPO lidar system for gas analysis of the atmosphere: Simulation and measurement results,” Optical Memory & Neural Networks 28 (1), 1–10 (2019).
I. E. Gordon, L. S. Rothman, C. Hill, R. V. Kochanov, Y. Tan, P. F. Bernath, M. Birk, V. Boudon, A. Campargue, K. V. Chance, B. J. Drouin, J.-M. Flaud, R. R. Gamache, J. T. Hodges, D. Jacquemart, V. I. Perevalov, A. Perrin, K. P. Shine, M.-A. H. Smith, J. Tennyson, G. C. Toon, H. Tran, V. G. Tyuterev, A. Barbe, A. G. Csaszar, V. M. Devi, T. Furtenbacher, J. J. Harrison, J.-M. Hartmann, A. Jolly, T. J. Johnson, T. Karman, I. Kleiner, A. A. Kyuberis, J. Loos, O. M. Lyulin, S. T. Massie, S. N. Mikhailenko, N. Moazzen-Ahmadi, H. S. P. Muller, O. V. Naumenko, A. V. Nikitin, O. L. Polyansky, M. Rey, M. Rotger, S. W. Sharpe, K. Sung, E. Starikova, S. A. Tashkun, J. Auwera, Wagner G. Vander, J. Wilzewski, P. Wcislo, S. Yu, and E. J. Zak, “The HITR-AN2016 molecular spectroscopic database,” J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 203, 3–69 (2017).
http://lop.iao.ru/EN/tor/gas/. Cited February 1, 2019.
D. K. Davydov, B. D. Belan, P. N. Antokhin, O. Yu. Antokhina, V. V. Antonovich, V. G. Arshinova, M. Yu. Arshinov, A. Yu. Akhlestin, S. B. Belan, N. V. Dudorova, G. A. Ivlev, A. V. Kozlov, D. A. Pestunov, T. M. Rasskazchikova, D. E. Savkin, D. V. Simonenkov, T. K. Sklyadneva, G. N. Tolmachev, A. Z. Fazliev, and A. V. Fofonov, “Monitoring of atmospheric parameters: 25 years of the tropospheric ozone research station of the Institute of Atmospheric Optics, Siberian Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences,” Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 32 (2), 180–192 (2019).
Funding
The work was financially supported by the President of the Russian Federation (grant no. MK-932.2019.8) in the part of the design of the lidar system for methane concentration measurements in the real atmosphere and by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (grant no. 19-45-700 003) regarding laboratory measurements of OPO laser radiation absorption by methane in the informative sounding range.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by O. Ponomareva
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romanovskii, O.A., Sadovnikov, S.A., Kharchenko, O.V. et al. Remote Analysis of Methane Concentration in the Atmosphere with an IR Lidar System in the 3300–3430 nm Spectral Range. Atmos Ocean Opt 33, 188–194 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1024856020020074
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1024856020020074