Abstract
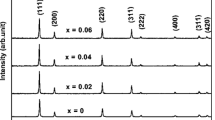
To study the effect of chromium oxide on the electric properties of Ce0.9Gd0.1O2, a solid-oxide fuel cell electrolyte, two approaches were used: (a) the studying of electrochemical properties of the Ce0.9Gd0.1O2- electrolyte after the spontaneous adsorption of chromium-containing molecules from a gas phase and (b) the analyzing of transport properties of the Ce0.9Gd0.1O2-based chromium-containing compositions obtained by the mixing of solid-oxide electrolyte with chromium(III) oxide. It was found that the chromium reduction at the electrolyte surface dominates when chromium is adsorbed from gas phase. Both approaches allow concluding that the chromium presence in Ce0.9Gd0.1O2 deteriorates the electrolyte transport properties at temperatures above 735°С. This is caused by the chromium incorporation into the electrolyte’s fluorite structure, as well as surface microheterogeneity induced by the chromium presence at the Ce0.9Gd0.1O2 surface and the cerium and gadolinium cation redistribution between the grains’ bulk and surface. At intermediate temperatures (below 735°С) the electric conductivity of the Ce0.9Gd0.1O2-based chromium-containing composition exceeds that of the initial solid-oxide electrolyte, which can be due to changes in transport properties of the chromium-containing phases formed at the Ce0.9Gd0.1O2 surface and grain boundaries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bredikhin, S.I., Golodnitskii, A.E., Drozhzhin, O.A., Istomin, C.Ya., Kovalevskii, V.P., and Filippov, S.P., Statsionarnye energeticheskie ustanovki s toplivnymi elementami: materially, tekhnologii, rynki (Fuel Cell-based Stationary Power Plants: Materials, Technologies, Markets), Moscow: NTF “Energoprogress,” the “EEEK” Corp., 2017.
Quadakkers, W.J., Piron-Abellan, J., Shemet, V., and Singheiser, L., Metallic interconnectors for solid oxide fuel cells—a review, Mater. High Temperatures, 2003, vol. 20, no. 2, p. 115.
Hilpert, K., Quadakkers, W.J., and Singheiser, L., Interconnects, in Handbook of Fuel Cells †Fundamentals, Technology and Applications, Vielstich, W., Gasteiger, H.A., and Lamm, A., Eds, New York: Wiley, 2003, vol. 3, p. 1037.
Hilpert, K., Das, D., Miller, M., Peck, D.H., and Weiss, R., Chromium vapor species over solid oxide fuel cell interconnect materials and their potential for degradation processes, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, vol. 143, no. 11, p. 3642.
Jiang, S.P., Zhang, J.P., Apateanu, L., and Foger, K., Deposition of chromium species at Sr-doped LaMnO3 electrodes in solid oxide fuel cells. II. Effect on O2 reduction reaction, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2000, vol. 147, no. 9, p. 3195.
Konysheva, E., Penkalla, H., Wessel, E., Mertens, J., Seeling, U., Singheiser, L., and Hilpert, K., Chromium poisoning of perovskite cathodes by the ODS alloy Cr5Fe1Y2O3 and the high chromium ferritic steel Crofer22APU, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2006, vol. 153, no. 4, p. A765.
Krumpelt, M., Cruse, T.A., Ingram, B.J., Routbort, J.L., Wang, S.L., Salvador, P.A., and Chen, G., The effect of chromium oxyhydroxide on solid oxide fuel cells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2010, vol. 157, no. 2, p. B228.
Konysheva, E., Mertens, J., Penkalla, H., Singheiser, L., and Hilpert, K., Chromium poisoning of the porous composite cathode. Effect of cathode thickness and current density, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2007, vol. 154, no. 12, p. B1252.
Stodolny, M.K., Boukamp, B.A., Blank, D.H.A., and van Berkel, F.P.F., La(Ni,Fe)O3 stability in the presence of chromia—a solid-state reactivity study, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2011, vol. 158, no. 2, p. B112.
Stodolny, M.K., Boukamp, B.A., Blank, D.H.A., and van Berkel, F.P.F., Impact of Cr-poisoning on the conductivity of LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3, J. Power Sources, 2011, vol. 196, p. 9290.
Huang, B., Zhu, X.J., Ren, R.X., Hu, Y.X., Ding, X.Y., Liu, Y.B., and Liu, Z.Y., Chromium poisoning and degradation at Gd0.2Ce0.8O2-impregnated LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3-δ cathode for solid oxide fuel cell, J. Power Sources, 2012, vol. 216, p. 89.
Yuan, M., Wang, X., Huang, B., Li, Y., Zhang, Z., Liu, Z., Tang, X., and Zhu, X., Performance of chromium-poisoning resistance of Gd0.2Ce0.8O2-impregnated LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3 †δ cathode materials, Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2014, vol. 31, no. 6, p. 1635.
Jiang, S.P., A comparison of O2 reduction reactions on porous (La,Sr)MnO3 and (La,Sr)(Co,Fe)O3 electrodes, Solid State Ionics, 2002, vol. 146, nos. 1–2, p. 1.
Tucker, M.C., Kurokawa, H., Jacobson, C.P., De Jonghe, L.C., and Visco S.J., A fundamental study of chromium deposition on solid oxide fuel cell cathode materials, J. Power Sources, 2006, vol. 160, no. 1, p. 130.
Arregui, A., Rodriguez-Martinez, L.M., Modena, S., Bertoldi, M., and Sglavo, V.M., Ferritic cathodes degradation by potassium/chromium poisoning and air humidification, Fuel Cells, 2013, vol. 13, no. 5, p. 720.
Menzler, N.H., Sebold, D., and Wessel, E., Interaction of La0.58Sr0.40Co0.20Fe0.80O3 †δ cathode with volatile Cr in a stack test—Scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy investigations, J. Power Sources, 2014, vol. 254, p. 148.
Konysheva, E. Yu., Effect of current density on poisoning rate of Co-containing fuel cell cathodes by chromium, Russ. J. Electrochem., 2014, vol. 50, no. 7, p. 630.
Zhao, L., Zhang, J., Becker, T., and Jiang, S.P., Raman spectroscopy study of chromium deposition on La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3 †δ cathode of solid oxide fuel cells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2014, vol. 161, no. 6, p. F687.
Matsuzaki, Y. and Yasuda, I., Dependence of SOFC cathode degradation by chromium-containing alloy on compositions of electrodes and electrolytes, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2001, vol. 148, no. 2, p. A126.
Perfil’ev, M.V., Demin, A.K., Kuzin, B.L., and Lipilin, A.S., Vysokotemperaturnyi elektroliz gazov (High-Temperature Electrolysis of Gases), Moscow: Nauka, 1988.
De Guire, M.R., Shingler, M.J., and Dincer, E., Point defect analysis and microstructural effects in pure and donor-doped ceria, Solid State Ionics, 1992, vol. 52, nos. 1–3, p. 155.
Eguchi, K., Setoguchi, T., Inoue, T., and Arai, H., Electrical properties of ceria-based oxides and their application to solid oxide fuel cells, Solid State Ionics, 1992, vol. 52, no. 1, p. 165.
Pound, B.G., The characterization of doped CeO2 electrodes in solid oxide fuel cells, Solid State Ionics, 1992, vol. 52, nos. 1–3, p. 183.
Morris, B.C., Flavell, W.R., Mackrodt, W.C., and Morris, M.A., Lattice parameter changes in the mixedoxide system Ce1 †xLaxO2 †δ: a combined experimental and theoretical study, J. Mater. Chem., 1993, vol. 3, no. 10, p. 1007.
Mogensen, M., Lindegaard, T., Hansen, U.R., and Mogensen, G., Physical properties of mixed conductor solid oxide fuel cell anodes of doped CeO2, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1994, vol. 141, no. 8, p. 2122.
Dikmen, S., Shuk, P., and Greenblatt, M., Hydrothermal synthesis and properties of Ce1 †xLaxO2 †δ solid solutions, Solid State Ionics, 1999, vol. 126, no. 1, p. 89.
Jud, E. and Gauckler, L.J., The effect of cobalt oxide addition on the conductivity of Ce0.9Gd0.1O1.95, J. Electroceram., 2005, vol. 15, no. 2, p. 159.
Konysheva, E. and Irvine, J.T.S., Transport properties of multi-cations doped cerium oxide, Solid State Ionics, 2011, vol. 184, no. 1, p. 27.
Steele, B.C.H. and Heinzel, A., Materials for fuel–cell technologies, Nature, 2001, vol. 414, p. 345.
Fergus, J.W., Electrolytes for solid oxide fuel–cells, J. Power Sources, 2006, vol. 162, no. 1, p. 30.
Jacobson, A.J., Materials for solid oxide fuel–cells, Chem. Mater., 2010, vol. 22, no. 3, p. 660.
Dalslet, B., Blennow, P., Hendriksen, P.V., Bonanos, N., Lybye, D., and Mogensen M., Assessment of doped ceria as electrolyte, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2006, vol. 10, no. 8, p. 547.
Pikalova, E.Yu., Bogdanovich, N.M., Kolchugin, A.A., Osinkin, D.A., and Bronin, D.I., Electrical and electrochemical properties of La2NiO4 + δ-based cathodes in contact with Ce0.8Sm0.2O2 †δ electrolyte, Procedia Eng., 2014, vol. 98, p. 105.
Hou, Y., Wu, J., and Konysheva, E.Yu., Quantitative characterization of Cr–adsorption on CeO2, pure and doped BaCeO3 and its impact on the electrochemical performance of Ce containing complex oxides, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, vol. 41, no. 6, p. 3994.
Zhao, L., Cui, Y., Gui, L., Li., G., and He, B., A comparison study of chromium deposition and poisoning on La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.8Mg0.2O3 − δ and Gd0.1Ce0.9O2 − δ electrolytes of solid oxide fuel cells, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, vol. 688, p. 376.
Ishibashi, D., Taniguchi, S., Inoue, Y., Chou J.T., and Sasaki, K., Deposition, agglomeration and vaporization of chromium oxide by cathode polarization change in SOFC cathodes, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2016, vol. 163, no. 7, p. F596.
Ebbinghaus, B.B., Thermodynamics of gas phase chromium species: the chromium oxides, the chromium oxyhydroxides, and volatility calculations in waste incineration processes, Combust. Flame, 1993, vol. 93, nos. 1–2, p. 119.
Jacobson, N., Myers, D., Opila, E., and Coplan, E., Interactions of water vapor with oxides at elevated temperatures, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2005, vol. 66, nos. 2–4, p. 471.
MacDonald, J. R., Zplot for Windows, Version 2.2, fitting program, LEVM 6.0.
Fleig, J., The grain boundary impedance of random microstructures: numerical simulations and implications for the analysis of experimental data, Solid State Ionics, 2002, vol. 150, nos. 1–2, p. 181.
NIST XPS database, http://srdata.nist.gov/xps/index.htm
Konysheva, E.Yu. and Francis, S.M., Identification of surface composition and chemical states in composites comprised of phases with fluorite and perovskite structures by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, vol. 268, p. 278.
Shannon, R.D., Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chaleogenides, Acta Crystallogr. A, 1976, vol. 32, p. 751.
Holt, A. and Kofstad, P., Electrical conductivity and defect structure of Cr2O3. II. Reduced temperatures (<1000°C), Solid State Ionics, 1994, vol. 69, no. 2, p. 137.
Zhu, W.Z. and Deevi, S.C., Development of interconnect materials for solid oxide fuel cells, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, vol. 348, p. 227.
Liu, H., Stack, M.M., and Lyon, S.B., Reactive element effects on the ionic transport processes in Cr2O3 scales, Solid State Ionics, 1998, vol. 109, nos. 3–4, p. 247.
Gray, C., Lei, Y., and Wang, G., Charged vacancy diffusion in chromium oxide crystal: DFT and DFT+U predictions, J. Appl. Phys., 2016, vol. 120, no. 21, article no. 215101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.Yu. Konysheva, 2018, published in Elektrokhimiya, 2018, Vol. 54, No. 6, pp. 544–553.
Presented at the IV All-Russian Conference “Fuel Cells and Fuel Cell based Power Plants” (with international participation) June 25‒29, 2017, Suzdal, Vladimir region.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konysheva, E.Y. The Effect of Chromium Oxide on the Conductivity of Ce0.9Gd0.1O2, a Solid-Oxide Fuel Cell Electrolyte. Russ J Electrochem 54, 471–480 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193518060095
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193518060095