Abstract
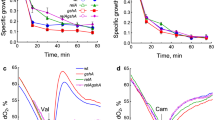
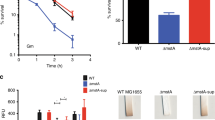
The paradoxical effect of deletion of the Escherichia coli genes cysK and cysM encoding cysteine synthase enzymes has been studied: such cysteine auxotrophs actively degrade the excess of cysteine transported from the medium to form H2S. We have shown that deletions of any of the known genes controlling the degradation of exogenous cysteine, including the genes aspC, mstA, cysK, cysM, tnaA, metC, and malY, as well as the newly discovered genes yciW, cyuA, cyuP, and cyuR, do not deprive the cysteine auxotrophs ΔcysK ΔcysM of the ability to degrade cysteine. Cysteine degradation in the ΔcysK ΔcysM mutant is positively regulated by the products of the cysB and cysE genes. It is significant that the ΔcysK ΔcysM mutant shows an increased transcription of the genes opposing the oxidative stress (sodA, catG, arcA, and cydD). We assume that oxidative stress in cells of the ΔcysK ΔcysM mutant is provoked by restriction of cysteine resynthesis, while cysB-dependent degradation of exogenous cysteine and generated H2S provide protection against oxidative stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Shatalin, K., Shatalina, E., Mironov, A., and Nudler, E., H2S: a universal defense against antibiotics in bacteria, Science, 2011, vol. 334, pp. 986-990.
Mironov, A., Seregina, T., Nagornykh, M., et al., A mechanism of H2S-mediated protection against oxidative stress in E. coli, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2017, vol. 114, pp. 6022-6027.
Kredich, N.M. and Tomkins, G.M., The enzymic synthesis of L-cysteine in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, J. Biol. Chem., 1966, vol. 241, pp. 4955-4965.
Awano, N., Wada, M., Mori, H., et al., Identification and functional analysis of Escherichia coli cysteine desulfhydrases, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 71, pp. 4149-4152.
Kawano, Y., Ohtsu, I., Takumi, K., et al., Enhancement of L-cysteine production by disruption of yciW in Escherichia coli, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2015, vol. 119, pp. 176-179.
Kawano, Y., Ohtsu, I., Tamakoshi, A., et al., Involvement of the yciW gene in l-cysteine and l-methionine metabolism in Escherichia coli, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2015, vol. 119, pp. 310-313.
Shimada, T., Tanaka, K., and Ishihama, A., Transcription factor DecR (YbaO) controls detoxification of L‑cysteine in Escherichia coli, Microbiology, 2016, vol. 162, pp. 1698-1707.
Nonaka, G. and Takumi, K., Cysteine degradation gene yhaM, encoding cysteine desulfidase, serves as a genetic engineering target to improve cysteine production in Escherichia coli, AMB Exp., 2017, vol. 7, p. 90.
Loddeke, M., Schneider, B., Oguri, T., et al., Anaerobic cysteine degradation and potential metabolic coordination in Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli, J. Bacteriol., 2018, vol. 199. e00117-17
Baba, T., Ara, T., Hasegawa, M., et al., Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: the Keio collection, Mol. Syst. Biol., 2006, vol. 2, pp. 2006-2008.
Miller, J.H., Experiments in Molecular Genetics, Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Lab., 1972.
Colnaghi, R., Cassinelli, G., Drummond, M., et al., Properties of the Escherichia coli rhodanese-like protein SseA: contribution of the active-site residue Ser240 to sulfur donor recognition, FEBS Lett., 2001, vol. 500, pp. 153-156.
Gelfand, D.H. and Steinberg, R.A., Escherichia coli mutants deficient in the aspartate and aromatic amino acid aminotransferases, J. Bacteriol., 1977, vol. 130, pp. 429-440.
Kredich, N.M., The molecular basis for positive regulation of cys promoters in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli, Mol. Microbiol., 1992, vol. 6, pp. 2747-2753.
Ostrowski, J. and Kredich, N.M., Molecular characterization of the cysJIH promoters of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: regulation by cysB protein and N-acetyl-L-serine, J. Bacteriol., 1989, vol. 171, pp. 130-140.
Ohtsu, I., Wiriyathanawudhiwong, N., Morigasaki, S., et al., The L-cysteine/L-cystine shuttle system provides reducing equivalents to the periplasm in Escherichia coli, J. Biol. Chem., 2010, vol. 285, pp. 17479-17487.
Ohtsu, I., Kawano, Y., Suzuki, M., et al., Uptake of L‑cystine via an ABC transporter contributes defense of oxidative stress in the L-cystine export-dependent manner in Escherichia coli, PLoS One, 2015, vol. 10. e0120619.
Imlay, K.R., Korshunov, S., and Imlay, J.A., Physiological roles and adverse effects of the two cystine importers of Escherichia coli, J. Bacteriol., 2015, vol. 197, pp. 3629-3644.
Walkup, L.K.B. and Kogoma, T., Escherichia coli proteins inducible by oxidative stress mediated by the superoxide radical, J. Bacteriol., 1989, vol. 171, pp. 1476-1484.
Pomposiello, P.J., Bennik, M.H., and Demple, B., Genome-wide transcriptional profiling of the Escherichia coli responses to superoxide stress and sodium salicylate, J. Bacteriol., 2001, vol. 183, pp. 3890-3902.
Christman, M.F., Storz, G., and Ames, B.N., OxyR, a positive regulator of hydrogen peroxide-inducible genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, is homologous to a family of bacterial regulatory proteins, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1989, vol. 86, pp. 3484-3488.
Rolfe, M.D., Beek, T.A., Graham, A.I., et al., Transcript profiling and inference of Escherichia coli K-12 ArcA activity across the range of physiologically relevant oxygen concentrations, J. Biol. Chem., 2011, vol. 286, pp. 10147-10154.
Park, D.M., Akhtar, M.S., Ansari, A.Z., et al., The bacterial response regulator ArcA uses a diverse binding site architecture to regulate carbon oxidation globally, PLoS Genet., 2013, vol. 9. e1003839.
Delaney, J.M., Wall, D., and Georgopoulos, C., Molecular characterization of the Escherichia coli htrD gene: cloning, sequence, regulation, and involvement with cytochrome d oxidase, J. Bacteriol., 1993, vol. 175, pp. 166-175.
Cook, G.M., Membrillo-Hernandes, J., and Poole, R.K., Transcriptional regulation of the cydDC operon, encoding a heterodimeric ABC transporter required for assembly of cytochromes c and bd in Escherichia coli K-12: regulation by oxygen and alternative electron acceptors, J. Bacteriol., 1997, vol. 179, pp. 6525-6530.
Frávega, J., Álvarez, R., Díaz, F., et al., Salmonella typhimurium exhibits fluoroquinolone resistance mediated by the accumulation of the antioxidant molecule H2S in a CysK-dependent manner, J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 2016, vol. 71, pp. 3409-3415.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to E.A. Nudler for valuable comments in discussing the results of this work.
The results of the studies presented in Figs. 2 and 3 were obtained in the framework of the Program of Fundamental Research of the State Academies of Sciences for 2013–2020 (topic no. 01201363822). The results of the studies presented in Figs. 4–8 were obtained using funds of the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 17-74-30030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by K. Lazarev
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seregina, T.A., Nagornykh, M.O., Lobanov, K.V. et al. The New Role of СysB Transcription Factor in Cysteine Degradation and Production of Hydrogen Sulfide in E. coli. Russ J Genet 54, 1259–1265 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795418110145
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795418110145