Abstract
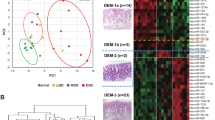
Applying the method of multiple parallel sequencing on the MiSeq platform (Illumina, United States), a comparative analysis of miRNA expression in tumor and normal colon tissue cells was performed. Forty miRNAs aberrantly expressed in cancer were detected. Among them, 15 and 25 miRNAs showed increased and decreased expression, respectively, for all or most of the cases. Sixteen miRNA clusters were identified, which showed a coordinated or incompletely coordinated aberrant expression in colorectal cancer cells. In two (miR-183/182 and miR-106b/25) and four (miR-143/145, miR-497/195, miR-30e/30c-1, and miR-30a/30c-2) miRNA clusters, respectively, a statistically significant coordinated increase or decrease in expression was registered for all miRNAs within the corresponding cluster. Three aberrantly expressed well-known miRNAs (miR-100-5p, miR-30d-5p, and miR-204-5p) were identified, which, however, had never before been associated with colorectal cancer. The obtained results demonstrate the potential and promising application of 6 miRNA clusters with coordinated aberrant expression as markers for colorectal cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolff, M.S. and Weston, A., Breast cancer risk and environmental exposures, Environ. Health Perspect., 1997, vol. 105,suppl. 4, pp. 891–896.
Vogelstein, B. and Kinzler, K.W., The multistep nature of cancer, Trends Genet., 1993, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 138–141.
Sherr, C.J., Principles of tumor suppression, Cell, 2004, vol. 116, no. 2, pp. 235–246.
Jones, P.A. and Baylin, S.B., The epigenomics of cancer, Cell, 2007, vol. 128, no. 4, pp. 683–692.
Ehrlich, M., DNA hypomethylation in cancer cells, Epigenomics, 2009, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 239–259.
Zardo, G., Ciolfi, A., Vian, L., et al., Polycombs and microRNA-223 regulate human granulopoiesis by transcriptional control of target gene expression, Blood, 2012, vol. 119, no. 17, pp. 4034–4046.
Benhamed, M., Herbig, U., Ye, T., et al., Senescence is an endogenous trigger for microRNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in human cells, Nat. Cell Biol., 2012, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 266–275.
Griffiths-Jones, S., Hui, J.H., Marco, A., and Ronshaugen, M., MicroRNA evolution by arm switching, EMBO Rep., 2011, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 172–177.
Calin, G.A., Dumitru, C.D., Shimizu, M., et al., Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2002, vol. 99, no. 24, pp. 15524–15529.
Chomczynski, P. and Sacchi, N., Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanatephenol-chloroform extraction, Anal. Biochem., 1987, vol. 162, pp. 156–159.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F., and Sambrook, J., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, 1982.
Robinson, M.D., McCarthy, D.J., and Smyth, G.K., edgeR: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data, Bioinformatics, 2010, vol. 26, pp. 139–140.
Robinson, M.D. and Oshlack, A., A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data, Genome Biol., 2010, vol. 11, p. R25.
McCarthy, D.J., Chen, Y., and Smyth, G.K., Differential expression analysis of multifactor RNA-seq experiments with respect to biological variation, Nucleic Acids Res., 2012, vol. 40, pp. 4288–4297.
Robinson, M.D. and Smyth, G.K., Small sample estimation of negative binomial dispersion, with applications to SAGE data, Biostatistics, 2008, vol. 9, pp. 321–332.
Benjamini, Y. and Hochberg, Y., Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing, J. R. Stat. Soc., 1995, vol. 57, no. 1, pp. 289–300.
Kozomara, A. and Griffiths-Jones, S., MiRBase: integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data, Nucleic Acids Res., 2011, vol. 39, pp. D152–D157.
Papagiannakopoulos, T., Shapiro, A., and Kosik, K.S., MicroRNA-21 targets a network of key tumor-suppressive pathways in glioblastoma cells, Cancer Res., 2008, vol. 68, no. 19, pp. 8164–8172.
Wang, F.E., Zhang, C., Maminishkis, A., et al., MicroRNA-204/211 alters epithelial physiology, FASEB J., 2010, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 1552–1571.
Abdelmohsen, K., Hutchison, E.R., Lee, E.K., et al., MiR-375 inhibits differentiation of neurites by lowering HuD levels, Mol. Cell Biol., 2010, vol. 30, no. 17, pp. 4197–4210.
Mohamed, J.S., Lopez, M.A., and Boriek, A.M., Mechanical stretch up-regulates microRNA-26a and induces human airway smooth muscle hypertrophy by suppressing glycogen synthase kinase-3β, J. Biol. Chem., 2010, vol. 285, no. 38, pp. 29336–29347.
Zhang, X., Li, M., and Zuo, K., et al., Upregulated miR-155 in papillary thyroid carcinoma promotes tumor growth by targeting APC and activating WNT/β-catenin signaling, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 2013, vol. 98, no. 8, pp. E1305–E1313.
Nagel, R., le Sage, C., Diosdado, B., et al., Regulation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene by the miR-135 family in colorectal cancer, Cancer Res., 2008, vol. 68, no. 14, pp. 5795–5802.
Dong, J., Zhao, Y.P., Zhou, L., et al., Bcl-2 upregulation induced by miR-21 via a direct interaction is associated with apoptosis and chemoresistance in MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells, Arch. Med. Res., 2011, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 8–14.
Song, J., Liu, P., Yang, Z., et al., MiR-155 negatively regulates c-Jun expression at the post-transcriptional level in human dermal fibroblasts in vitro: implications in UVA irradiation-induced photoaging, Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 2012, vol. 29, nos. 3–4, pp. 331–340.
Valeri, N., Gasparini, P., Fabbri, M., et al., Modulation of mismatch repair and genomic stability by miR-155, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2010, vol. 107, no. 15, pp. 6982–6987.
Valeri, N., Gasparini, P., Braconi, C., et al., MicroRNA-21 induces resistance to 5-fluorouracil by down-regulating human DNA MutS homolog 2 (hMSH2), Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2010, vol. 107, no. 49, pp. 21098–21103.
Zhang, Z., Florez, S., Gutierrez-Hartmann, A., et al., MicroRNAs regulate pituitary development, and microRNA 26b specifically targets lymphoid enhancer factor 1 (Lef-1), which modulates pituitary transcription factor 1 (Pit-1) expression, J. Biol. Chem., 2010, vol. 285, no. 45, pp. 34718–34728.
Calin, G.A., Cimmino, A., Fabbri, M., et al., MiR-15a and miR-16-1 cluster functions in human leukemia, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2008, vol. 105, no. 13, pp. 5166–5171.
He, L., Thomson, J.M., Hemann, M.T., et al., A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene, Nature, 2005, vol. 435, no. 7043, pp. 828–833.
Valladares-Ayerbes, M., Blanco, M., Haz, M., et al., Prognostic impact of disseminated tumor cells and microRNA-17-92 cluster deregulation in gastrointestinal cancer, Int. J. Oncol., 2011, vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 1253–1264.
Hayashita, Y., Osada, H., Tatematsu, Y., et al., A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation, Cancer Res., 2005, vol. 65, no. 21, pp. 9628–9632.
Conkrite, K., Sundby, M., Mukai, S., et al., MiR-17∼92 cooperates with RB pathway mutations to promote retinoblastoma, Genes Dev., 2011, vol. 25, no. 16, pp. 1734–1745.
Li, J., Fu, H., Xu, C., et al., MiR-183 inhibits TGF-beta1-induced apoptosis by downregulation of PDCD4 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells, BMC Cancer, 2010, vol. 10, p. 354.
Yu, S., Lu, Z., Liu, C., et al., MiRNA-96 suppresses KRAS and functions as a tumor suppressor gene in pancreatic cancer, Cancer Res., 2010, vol. 70, no. 14, pp. 6015–6025.
Hirata, H., Ueno, K., Shahryari, V., et al., Oncogenic miRNA-182-5p targets Smad4 and RECK in human bladder cancer, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, no. 11. e51056
Yan, D., Dong, X.D., Chen, X., et al., Role of microRNA-182 in posterior uveal melanoma: regulation of tumor development through MITF, Bcl2 and cyclin D2, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, no. 7. e40967
Smith, A.L., Iwanaga, R., Drasin, D.J., et al., The miR-106b-25 cluster targets Smad7, activates TGF-β signaling, and induces EMT and tumor initiating cell characteristics downstream of Six1 in human breast cancer, Oncogene, 2012, vol. 31, no. 50, pp. 5162–5171.
Petrocca, F., Visone, R., Onelli, M.R., et al., E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer, Cancer Cell, 2008, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 272–286.
Fang, L., Du, W.W., Yang, W., et al., MiR-93 enhances angiogenesis and metastasis by targeting LATS2, Cell Cycle, 2012, vol. 11, no. 23, pp. 4352–4365.
Kim, Y.K., Yu, J., Han, T.S., et al., Functional links between clustered microRNAs: suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer, Nucleic Acids Res., 2009, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 1672–1681.
Lin, T., Dong, W., Huang, J., et al., MicroRNA-143 as a tumor suppressor for bladder cancer, J. Urol., 2009, vol. 181, no. 3, pp. 1372–1380.
Noguchi, S., Yasui, Y., Iwasaki, J., et al., Replacement treatment with microRNA-143 and -145 induces synergistic inhibition of the growth of human bladder cancer cells by regulating PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways, Cancer Lett., 2013, vol. 328, no. 2, pp. 353–361.
Zhang, J., Guo, H., Zhang, H., et al., Putative tumor suppressor miR-145 inhibits colon cancer cell growth by targeting oncogene friend leukemia virus integration 1 gene, Cancer, 2011, vol. 117, no. 1, pp. 86–95.
Chen, Z., Zeng, H., Guo, Y., et al., MiRNA-145 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation by targeting c-Myc, J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res., 2010, vol. 29, p. 151.
Gregersen, L.H., Jacobsen, A.B., Frankel, L.B., et al., MicroRNA-145 targets YES and STAT1 in colon cancer cells, PLoS One, 2010, vol. 5, no. 1. e8836
Luo, M., Shen, D., Zhou, X., et al., MicroRNA-497 is a potential prognostic marker in human cervical cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor, Surgery, 2013, vol. 153, no. 6, pp. 836–847.
Zheng, D., Radziszewska, A., and Woo, P., MicroRNA 497 modulates interleukin 1 signalling via the MAPK/ERK pathway, FEBS Lett., 2012, vol. 586, no. 23, pp. 4165–4172.
Li, D., Zhao, Y., Liu, C., et al., Analysis of miR-195 and miR-497 expression, regulation and role in breast cancer, Clin. Cancer Res., 2011, vol. 17, no. 7, pp. 1722–1730.
Hui, W., Yuntao, L., Lun, L., et al., MicroRNA-195 inhibits the proliferation of human glioma cells by directly targeting cyclin D1 and cyclin E1, PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, no. 1. e54932
Zhang, Q.Q., Xu, H., Huang, M.B., et al., MicroRNA-195 plays a tumor-suppressor role in human glioblastoma cells by targeting signaling pathways involved in cellular proliferation and invasion, Neurooncol., 2012, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 278–287.
Liu, L., Chen, L., Xu, Y., et al., MicroRNA-195 promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity of human colorectal cancer cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2010, vol. 400, no. 2, pp. 236–240.
Esposito, F., Tornincasa, M., Pallante, P., et al., Downregulation of the miR-25 and miR-30d contributes to the development of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma targeting the polycomb protein EZH2, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 2012, vol. 97, no. 5, pp. E710–E718.
Xia, Y., Chen, Q., Zhong, Z., et al., Down-regulation of miR-30c promotes the invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting MTA1, Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 2013, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 476–485.
Zhong, M., Bian, Z., and Wu, Z., MiR-30a suppresses cell migration and invasion through downregulation of PIK3CD in colorectal carcinoma, Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 2013, vol. 31, nos. 2–3, pp. 209–218.
Hsu, S.D., Lin, F.M., Wu, W.Y., et al., MiRTarBase: a database curates experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions, Nucleic Acids Res., 2011, vol. 39, pp. D163–D169.
Chhabra, R., Dubey, R., and Saini, N., Cooperative and individualistic functions of the microRNAs in the mir-23a∼27a∼24-2 cluster and its implication in human diseases, Mol. Cancer, 2010, vol. 9, p. 232.
Buck, A.H., Perot, J., Chisholm, M.A., et al., Post-transcriptional regulation of miR-27 in murine cytomegalovirus infection, RNA, 2010, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 307–315.
Shi, B., Zhu, M., Liu, S., and Zhang, M., Highly ordered architecture of microRNA cluster, Biomed. Res. Int., 2013, vol. 2013, p. 463168.
Chaulk, S.G., Thede, G.L., Kent, O.A., et al., Role of pri-miRNA tertiary structure in miR-17∼92 miRNA biogenesis, RNA Biol., 2011, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 1105–1114.
Monteys, A.M., Spengler, R.M., Wan, J., et al., Structure and activity of putative intronic miRNA promoters, RNA, 2010, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 495–505.
Petrocca, F., Vecchione, A., and Croce, C.M., Emerging role of miR-106b-25/miR-17-92 clusters in the control of transforming growth factor beta signaling, Cancer Res., 2008, vol. 68, no. 20, pp. 8191–8194.
Yin, G., Chen, R., Alvero, A.B., et al., Twisting stemness, inflammation and proliferation of epithelial ovarian cancer cells through MIR199A2/214, Oncogene, 2010, vol. 29, no. 24, pp. 3545–3553.
Kumar, P., Luo, Y., Tudela, C., et al., The c-Myc-regulated microRNA-17∼92 (miR-17⊃92) and miR-106a∼363 clusters target hCYP19A1 and hGCM1 to inhibit human trophoblast differentiation, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2013, vol. 33, no. 9, pp. 1782–1796.
Bui, T.V. and Mendell, J.T., Myc: maestro of microRNAs, Genes Cancer, 2010, vol. 1, no. 6, pp. 568–575.
Zhao, Y. and Westphal, H., Homeobox genes and human genetic disorders, Curr. Mol. Med., 2002, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 13–23.
Sato, F., Hatano, E., Kitamura, K., et al., MicroRNA profile predicts recurrence after resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria, PLoS One, 2011, vol. 6, no. 1. e16435
Lu, Y., Govindan, R., Wang, L., et al., MicroRNA profiling and prediction of recurrence/relapse-free survival in stage I lung cancer, Carcinogenesis, 2012, vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 1046–1054.
Ma, X., Kumar, M., Choudhury, S.N., et al., Loss of the miR-21 allele elevates the expression of its target genes and reduces tumorigenesis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2011, vol. 108, no. 25, pp. 10144–10149.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.A. Tarasov, D.G. Matishov, E.F. Shin, N.V. Boyko, N.N. Timoshkina, M.A. Makhotkin, A.M. Lomonosov, A.A. Kirpiy, O.I. Kit, A.Yu. Maximov, 2014, published in Genetika, 2014, Vol. 50, No. 10, pp. 1232–1244.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarasov, V.A., Matishov, D.G., Shin, E.F. et al. Coordinated aberrant expression of miRNAs in colon cancer. Russ J Genet 50, 1090–1101 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795414080109
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795414080109