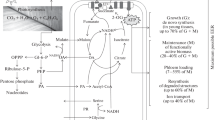
Abstract
The review discusses up-to-date concepts of interrelations between photosynthesis and respiration. It considers the quantitative ratio of the processes in the leaf and that in the whole plant reported by Russian and other researches. Special attention is paid to performance of dark respiration in the light and to the methods of its exploration, which employ classical gas exchange, chlorophyll fluorescence, and carbon isotopes. Possible causes of conservatism and variability in the total respiration to gross photosynthesis ratio under stationary and stress conditions are also discussed along with prospects in further investigations.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Smith, N. and Dukes, J., Plant respiration and photosynthesis in global-scale models: incorporating acclimation to temperature and CO2, Global Change Biol., 2013, vol. 19, pp. 45–63.
Van Oijen, M., Schapendonk, A., and Höglind, M., On the relative magnitudes of photosynthesis, respiration, growth and carbon storage in vegetation, Ann. Bot., 2010, vol. 105, pp. 793–797.
Von Gaemmerer, S., Steady-state models of photosynthesis, Plant Cell Environ., 2013, vol. 36, pp. 1617–1630.
Penning de Vries, F.W.T., The cost of maintenance processes in plant cells, Ann. Bot., 1975, vol. 39, pp. 77–92.
Tcherkez, G., Gauthier, P., Buckley, T.N., Busch, F.A., Barbour, M.M., Bruhn, D., Heskel, M.A., Gong, X.Y., Crous, K., Griffin, K.L., Way, D., Turnbull, M., Adams, M.A., Atkin, O.K., Farquhar, G.D., et al., Leaf day respiration: low CO2 flux but high significance for metabolism and carbon balance, New Phytol., 2017, vol. 216, pp. 986–1001. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14816
Atkin, O.K., Bloomfield, K.J., Reich, P.B., Tjoelker, M.G., Asner, G.P., Bonal, D., Bönisch, G., Bradford, M.G., Cernusak, L.A., Cosio, E.G., Creek, D., Crous, K.Y., Domingues, T.F., Dukes, J.S., Egerton, J.J., et al., Global variability in leaf respiration in relation to climate, plant functional types and leaf traits, New Phytol., 2015, vol. 206, pp. 614–636. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13253
Atkin, O.K., Scheurwater, I., and Pons, T.L., Respiration as a percentage of daily photosynthesis in whole plants is homeostatic at moderate, but not high, growth temperatures, New Phytol., 2007, vol. 174, pp. 367–380.
Campbell, C., Atkinson, L., Zaragoza-Castells, J., Lundmark, M., Atkin, O., and Hurry, V., Acclimation of photosynthesis and respiration is asynchronous in response to changes in temperature regardless of plant functional group, New Phytol., 2007, vol. 176, pp. 375–389. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02183.x
Huntingford, C., Atkin, O.K., Martinez-de la Torre, A., Mercado, L.M., Heskel, M.A., Harper, A.B., Bloomfield, K.J., O’Sullivan, O.S., Reich, P.B., Wythers, K.R., Butler, E.E., Chen, M., Griffin, K.L., Meir, P., Tjoelker, M.G., et al., Implications of improved representations of plant respiration in a changing climate, Nat. Commun., 2017, vol. 8, pp. 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01774-z
Wullschleger, S.D., Warren, J.M., and Thornton, P.E., Leaf respiration (GlobResp)—global trait database supports Earth System Models, New Phytol., 2015, vol. 206, pp. 483–485.
Araújo, W.L., Nunes-Nesi, A., and Fernie, A.R., On the role of plant mitochondrial metabolism and its impact on photosynthesis in both optimal and sub-optimal growth conditions, Photosynth. Res., 2014, vol. 119, pp. 141–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9807-4
Raghavendra, A.S. and Padmasree, K., Beneficial interactions of mitochondrial metabolism with photosynthetic carbon assimilation, Trends Plant Sci., 2003, vol. 8, pp. 546–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2003.09.015
Carrari, F., Nunes-Nesi, A., Gibon, Y., Lytovchenko, A., Loureiro, M.E., and Fernie, A.R., Reduced expression of aconitase results in an enhanced rate of photosynthesis and marked shifts in carbon partitioning in illuminated leaves of wild species tomato, Plant Physiol., 2003, vol. 133, pp. 1322–1335. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.026716
Hurry, V., Keerberg, O., Parnik, T., Oquist, G., and Gardestrom, P., Effect of cold hardening on the components of respiratory decarboxylation in the light and in the dark in leaves of winter rye, Plant Physiol., 1996, vol. 111, pp. 713–719.
Gifford, R.M., Plant respiration in productivity models: conceptualization, representation and issues for global terrestrial carbon-cycle research, Funct. Plant Biol., 2003, vol. 30, pp. 171–186.
Cannell, M.G.R. and Thornley, J.H.M., Modelling the components of plant respiration: some guiding principles, Ann. Bot., 2000, vol. 85, pp. 45–54.
Thornley, J.H.M. and Cannell, M.G.R., Modelling the components of plant respiration: representation and realism, Ann. Bot., 2000, vol. 85, pp. 55–67.
McCree, K.J., An equation for the rate of respiration of white clover plants grown under controlled conditions, in Prediction and Measurement of Photosynthetic Productivity, Setliik, I., Ed., Wageningen: Centre for Agricultural Publishing and Documentation, 1970, pp. 221–229.
Thornley, J.H.M., Plant growth and respiration re-visited: maintenance respiration defined—it is an emergent property of, not a separate process within, the system—and why the respiration: photosynthesis ratio is conservative, Ann. Bot., 2011, vol. 108, pp. 1365–1380. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcr238
Amthor, J.S., The McCree-de Wit-Penning de Vries-Thornley respiration paradigms: 30 years later, Ann. Bot., 2000, vol. 86, pp. 1–20.
Murrey, I.A., Components of productive respiration in photosynthetic plant tissues, Sov. Plant Physiol., 1985, vol. 32, pp. 61–69.
Murrey, I.A. and Rakhmankulova, Z.F., The ratio of photosynthesis and respiratory components in sugar beet plants during vegetative growth phase, Sov. Plant Physiol., 1990, vol. 37, pp. 462–467.
Rakhmankulova, Z.F., The relationship of photosynthesis and respiration of the whole plant under normal and stressful conditions, Zh. Obshch. Biol., 2002, vol. 63, pp. 44–53.
Nunes-Nesi, A., Sweetlove, L.J., and Fernie, A.R., Operation and function of the tricarboxylic acid cycle in the illuminated leaf, Physiol. Plant., 2007, vol. 129, pp. 45–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00778.x
Noguchi, K. and Yoshida, K., Interaction between photosynthesis and respiration in illuminated leaves, Mitochondrion, 2008, vol. 8, pp. 87–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2007.09.003
Nunes-Nesi, A., Araújo, W.L., and Fernie, A.R., Targeting mitochondrial metabolism and machinery as a means to enhance photosynthesis, Plant Physiol., 2011, vol. 155, pp. 101–107. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.163816
Bauwe, H., Hagemann, M., Kern, R., and Timm, S., Photorespiration has a dual origin and manifold links to central metabolism, Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2012, vol. 15, pp. 269–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2012.01.008
Foyer, C.H., Noctor, G., and Hodges, M., Respiration and nitrogen assimilation: targeting mitochondria-associated metabolism as a means to enhance nitrogen use efficiency, J. Exp. Bot., 2011, vol. 62, pp. 1467–1482. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq453
Gimeno, T.E., Sommerville, K.E., Valladares, F., and Atkin, O.K., Homeostasis of respiration under drought and its important consequences for foliar carbon balance in a drier climate: insights from two contrasting Acacia species, Funct. Plant Biol., 2010, vol. 37, pp. 323–333.
Metcalfe, D.B., Lobo-do-Vale, R., Chaves, M.M., Maroco, J.P., Aragao, L., Malhi, Y., da Costa, A.L., Braga, A.P., Goncalves, P.L., de Athaydes, J., da Costa, M., Almeida, S.S., Campbell, C., Hurry, V., Williams, M., et al., Impacts of experimentally imposed drought on leaf respiration and morphology in an Amazon rain forest, Funct. Ecol., 2010, vol. 24, pp. 524–533.
Nunes-Nesi, A., Fernie, A.R., and Stitt, M., Metabolic and signaling aspects underpinning the regulation of plant carbon nitrogen interactions, Mol. Plant, 2010, vol. 3, pp. 973–996. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssq049
Ghashghaie, J. and Badeck, F.W., Opposite carbon isotope discrimination during dark respiration in leaves versus roots—a review, New Phytol., 2013, vol. 201, pp. 751–769.
Bidwell, R.G.S., Krotkov, G., and Reed, G.B., The influence of light and darkness on the metabolism of radioactive glucose and glutamine in wheat leaves, Can. J. Bot., 1955, vol. 33, pp. 189–196.
Tovar-Mendez, A., Miernyk, J.A., and Randall, D.D., Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity in plant cells, Eur. J. Biochem., 2003, vol. 270, pp. 1043–1049.
Tcherkez, G., Cornic, G., Bligny, R., Gout, E., and Ghashghaie, J., In vivo respiratory metabolism of illuminated leaves, Plant Physiol., 2005, vol. 138, pp. 1596–1606.
Tcherkez, G., Bligny, R., Gout, E., Mahe, A., Hodges, M., and Cornic, G., Respiratory metabolism of illuminated leaves depends on CO2 and O2 conditions, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2008, vol. 105, pp. 797–802.
Gessler, A., Tcherkez, G., Karyanto, O., Keitel, C., Ferrio, J.P., Ghashghaie, J., Kreuzwieser, J., and Farquhar, G.D., On the metabolic origin of the carbon isotope composition of CO2 evolved from darkened light-acclimated leaves in Ricinus communis, New Phytol., 2009, vol. 181, pp. 374–386.
Hurry, V., Igamberdiev, A.U., Keerberg, O., Pärnik, T., Atkin, O.K., Zaragoza-Castells, J., and Gardestrom, P., Respiration in photosynthetic cells: gas exchange components, interactions with photorespiration and the operation of mitochondria in the light, in Plant R-espiration, Lambers, H. and Ribas-Carbo, M., Eds., Berlin-Heidelberg: Springer Germany, 2005, pp. 43–61.
Farquhar, G.D. and Busch, F., Changes in the chloroplastic CO2 concentration explain much of the observed Kok effect: a model, New Phytol., 2017, vol. 214, pp. 570–584.
Gong, X.Y., Tcherkez, G., Wenig, J., Schäufele, R., and Schnyder, H., Atmospheric CO2 mole fraction affects stand-scale carbon use efficiency of sunflower by stimulating respiration in light, Plant Cell Environ., 2017, vol. 40, pp. 401–412.
Gong, X.Y., Tcherkez, G., Wenig, J., Schäufele, R., and Schnyder, H., Measurement of leaf day respiration using a new isotopic disequilibrium method compared with the Laisk method, bioRxiv, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1101/201038
Kok, B., A critical consideration of the quantum yield of Chlorella photosynthesis, Enzymologia, 1948, vol. 13, pp. 1–56.
Kok, B., On the interrelation of respiration and photosynthesis in green plants, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1949, vol. 3, pp. 625–631.
Laisk, A.Kh., Kinetika fotosinteza i fotodykhaniya C 3 ‑rastenii (Kinetics of Photosynthesis and Photorespiration of C3 Plants), Moscow: Nauka, 1977.
Atkin, O.K., Millar, A.H., Gardestrom, P., and Day, D.A., Photosynthesis, carbohydrate metabolism and respiration in leaves of higher plants, in P-hotosynthesis: Physiology and Metabolism. Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration, Leegood, R., Sharkey, T., and Caemmerer, S., Eds., London: Kluwer, 2000, vol. 9, pp. 53–175.
Cornic, G., Etude de l’inhibition de la respiration pars la lumiere chez la moutarde blanche (Sinapis alba L.), Physiol. Veg., 1973, vol. 11, pp. 663–679.
Pärnik, T. and Keerberg, O., Advanced radiogasometric method for the determination of the rates of photorespiratory and respiratory decarboxilations of primary and stored photosynthates under steady-state photosynthesis, Physiol. Plant., 2007, vol. 129, pp. 34–44.
Loreto, F., Velikova, V., and Di Marco, G., Respiration in the light measured by 12CO2 emission in 13CO2 atmosphere in maize leaves, Funct. Plant Biol., 2001, vol. 28, pp. 1103–1108.
Gong, X.Y., Schaufele, R., Feneis, W., and Schnyder, H., 13CO2/12CO2 exchange fluxes in a clamp-on leaf cuvette: disentangling artefacts and flux components, Plant Cell Environ., 2015, vol. 38, pp. 2417–2432.
Keerberg, O., Ivanova, H., Keerberg, H., and Pärnik, T., CO2 exchange of potato transformants with reduced activities of glycine decarboxylase, in Phytosfere'99—Hi-ghlights in European Plant Biotechnology, De Vries, G.E. and Metzlaff, K., Eds., Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1999, pp. 215–219.
Pärnik, T. and Keerberg, O., Decarboxylation of primary and end products of photosynthesis at different oxygen concentrations, J. Exp. Bot., 1995, vol. 46, pp. 1439–1440.
Sweetlove, L.J., Beard, K.F.M., Nunes-Nesi, A., Fernie, A.R., and Ratcliffe, R.G., Not just a circle: flux modes in the plant TCA cycle, Trends Plant Sci., 2010, vol. 15, pp. 462–470.
Garmash, E.V., Mitochondrial respiration of the photosynthesizing cell, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2016, vol. 63, pp. 13–25.
Huntingford, C., Harris, P.P., Gedney, N., Cox, P.M., Betts, R.A., Marengo, J.A., and Gash, J.H.C., Using a GCM analogue model to investigate the potential for Amazonian forest dieback, Theor. Appl. Climatol., 2004, vol. 78, pp. 177–185.
Gifford, R.M., Whole plant respiration and photosynthesis of wheat under increased CO2 concentration and temperature: long-term vs short-term distinctions for modeling, Global Change Biol., 1995, vol. 1, pp. 385–396.
Ryan, M.G., Hubbard, R.M., Pongracic, S., Raison, R.J., and McMurtrie, R.E., Foliage, fine-root, woody-tissue and stand respiration in Pinus radiata in relation to nitrogen status, Tree Physiol., 1996, vol. 16, pp. 333–343.
Goetz, S.J. and Prince, S.D., Variability in carbon exchange and light utilization among boreal forest stands: implications for remote sensing of net primary production, Can. J. For. Res., 1998, vol. 28, pp. 375–389.
Winzeler, H., Hunt, L.A., and Mahon, J.D., Ontogenetic changes in respiration and photosynthesis in a uniculm barley, Crop Sci., 1976, vol. 16, pp. 786–790.
Keith, H., Raison, R.J., and Jacobsen, K.L., Allocation of carbon in a mature eucalypt forest and some effects of soil phosphorus availability, Plant Soil, 1997, vol. 196, pp. 81–99.
Monje, O. and Bugbee, B., Adaptation to high CO2 concentration in an optimal environment: radiation capture, canopy quantum yield and carbon use efficiency, Plant Cell Environ., 1998, vol. 21, pp. 315–324.
Malhi, Y., Baldocchi, D.D., and Jarvis, P.G., The carbon balance of tropical, temperate and boreal forests, Plant Cell Environ., 1999, vol. 22, pp. 715–740.
Atkin, O.K., Bruhn, D., Hurry, V.M., and Tjoelker, M.G., The hot and the cold: unravelling the variable response of plant respiration to temperature, Funct. Plant Biol., 2005, vol. 32, pp. 87–105.
Murrey, I.A. and Shul’gin, I.A., Physiological analysis of incoming PAR to the plant, Bot. Zh., 1978, vol. 63, pp. 962–973.
Golovko, T.K., Dykhanie rastenii (fiziologicheskie aspekty) (Plant Respiration: Physiological Aspects), St. Petersburg: Nauka, 1999.
Mokronosov, A.T., Ontogeneticheskii aspekt fotosinteza (Ontogenetic Aspect of Photosynthesis), Moscow: Nauka, 1981.
Semikhatova, O.A., Ivanova, T.I., and Kirpichnikova, O.V., Respiration rate of Arctic plants as related to the production process, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2009, vol. 56, pp. 306–315.
Semikhatova, O.A. and Zalenskii, O.V., Conjugacy of photosynthesis and respiration, in Fiziologiya fotosinteza (Physiology of Photosynthesis), Nichiporovich, A.A., Ed., Moscow: Nauka, 1982.
Murrey, I.A., Kinetics of photosynthesis and respiration of Zea mays plant after the dark period, Sov. Plant Physiol., 1984, vol. 31, pp. 433–438.
Murrey, I.A. and Velichkov, D.K., The rate of visible photosynthesis and respiration in sunflower and maize, Sov. Plant Physiol., 1981, vol. 28, pp. 1109–1118.
Murrey, I.A. and Velichkov, D.K., Analysis of productive respiration in photosynthetic tissues of the whole plant, Sov. Plant Physiol., 1983, vol. 30, pp. 1126–1133.
Murrey, I.A., Parameters of integral pools of assimilates in photosynthetic plant tissues, Sov. Plant Physiol., 1984, vol. 31, pp. 1049–1055.
Murrey, I.A. and Rakhmankulova, Z.F., The relationship between photosynthesis and dark modified respiration in the light of maize, Sov. Plant Physiol., 1990, vol. 37, pp. 468–475.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 17-04-00853a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by A. Aver’yanov
Abbreviations:
A—apparent photosynthesis; Ci—CO2 concentration in intracellular space; CUE—carbon use efficiency; GEC—growth efficiency coefficient; GMRP—growth respiration/maintenance respiration paradigm; Pg—gross photosynthesis; R—dark (mitochondrial) respiration; Rd—respiration in the dark; Rl—respiration in the light.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakhmankulova, Z.F. Physiological Aspects of Photosynthesis–Respiration Interrelations. Russ J Plant Physiol 66, 365–374 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443719030117
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443719030117