Abstract
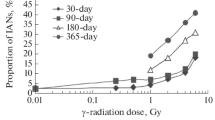
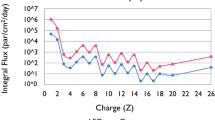
The authors present a review of new experimental data on the relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of the impact on the body of fast neutrons and accelerated multicharged ions (AMIs) in small, absorbed doses of 0.01–0.5 Gy, which are allowed by modern radiation safety standards for the career of astronauts to limit the risk of delayed adverse effects. According to new radiobiological data for low doses and their rates, the literature presents higher (2–3 times) maximum values of the RBE coefficients for cytogenetic disorders that persist in the long-term period; malignant transformation of cells and the risk of developing tumors of different tissues; reduction in life expectancy; disorders of neurons in the cerebral cortex and damage to individual organs; and the degree of clouding of the lens and the formation of cataracts. Based on the analysis performed, a new dependence of quality factors on linear energy transfer is presented, from which it follows that the estimated values of equivalent doses in relation to the effects of galactic cosmic rays and fast neutrons, as well as the calculated values of the total radiation risk during the life of astronauts, will increase significantly.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
GOST 25 645.201-83: bezopasnost’ radiatsionnaya ekipazha kosmicheskogo apparata v kosmicheskom polete: terminy i opredeleniya (State Standard 25645.201-83: Radiation Safety of the Spacecraft Crew during Space Flight. Terms and Definitions), Moscow: Gosstandart SSSR, 1983.
Shafirkin, A.V. and Grigoriev, Yu.G., Mezhplanetnye i orbital’nye polety: radiatsionnyi risk dlya kosmonavtov: radiobiologicheskoe obosnovanie (Interplanetary and Orbital Flights: Radiation Risk for Cosmonauts: Radiobiological Justification), Moscow, 2009.
Grigoriev, Yu.G., Ushakov, I.B., Krasavin, E.A., et al., Kosmicheskaya radiobiologiya za 55 let (k 50-letiyu GNTs RF—IMBP RAN) (Space Radiobiology for 55 years (to 50-years State Research Center Institute of Biomedical Problems)), Moscow: Russ. Akad. Nauk, 2013.
Grigoriev, Yu.G., Ushakov, I.B., and Shafirkin, A.V., Coordinated approaches and persisting differences in radiation regulation in the USSR (Russia) and the U.S.A. in relation to long-term manned space flights, Gig. Sanit., 2017, vol. 96, no. 9, p. 861.
Mitrikas, V.G., Evaluation of effective and average tissue doses on the ISS, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2008, vol. 42, no. 4, p. 50.
Mitrikas, V.G., Estimation of effective doses of ionizing radiation among the crews of the international space station by computational modeling, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2015, vol. 49, no. 3, p. 5.
GOST 25 645.218-90: bezopasnost’ radiatsionnaya ekipazha kosmicheskogo apparata v kosmicheskom polete: zavisimost’ koeffitsienta kachestva kosmicheskikh izluchenii ot lineinoi energii (State Standard 25645.218-90: Space Crew Radiation Safety during Space Flight: Dependence of the Cosmic Radiation Quality on Linear Energy), Moscow, 1991.
Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection 1990, Publications nos. 60—61: The Annual Limits of Radionuclides’ Intake by Bodies of Working People, Moscow, 1994.
GOST 25 645.219-90 BREKAKP: Model’ ucheta vliyaniya prostranstvennoi neravnomernosti radiatsionnogo vozdeistviya na obobshchennyi radiobiologicheskii effekt (State Standard 25 645.219-90: Model for Inventory the Influence of Spatial Irregularity of Irradiation on the Generalized Radiobiological Effect), Moscow, 1991.
Geard, C.R., Jenkins-Baker, G., Grabham, P., et al., Human endothelial cells in 2D- and 3D-system: noncancer effects and space-related radiations, Proceedings of 4th International Workshop on Space Radiation Research and 17th Annual NASA Space Radiation Health Investigators Workshop, Dubna, 2006, p. 34.
Little, M.P., Azizova, T.V., Bazika, D., et al., Systematic review and metaanalysis of circulatory disease from exposure to low-level ionizing radiation and estimate of potential population mortality risks, Environ. Health Perspect., 2012, vol. 120, no. 11, p. 1503.
Methodical Instructions MI 2.6.1. 44-03-2004: Irradiation Exposure Limits for Cosmonauts during Orbital Cosmic Flights (LECDSF-2004), Moscow: Federal. Kosm. Agent., 2004.
GOST 25 645.215-85: normy bezopasnosti pri prodolzhitel’nosti poletov do 3 let (State Standart 25 645.215-85: Regulations for Space Crew Radiation Safety during Space Flight Durations up to Three Years), Moscow: Gosstandart USSR, 1986.
Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation, UNSCEAR 2000 Report, Moscow, vol. 1, 2002.
Keirim-Markus, I.B., Savinsky, A.K., and Chernova, O.N., Koeffitsient kachestva ioniziruyushchikh izluchenii (Quality Factor of Ionizing Radiation), Moscow, 1992.
Worgul, B.V., Merriam, G.R., Medvedovsky, C., and Brenner, D.J., Accelerated heavy particles and the lens: III. Cataract enhancement by dose fractionation, Radiat. Res., 1989, vol. 118, no. 1, p. 93.
Brenner, D.J., Medvedovsky, C., Huang, Y., and Worgul, B.V., Accelerated heavy particles and the lens: VIII. Comparison between the effects of acute low doses of iron ions (190 keV/μm) and argon ions (88 keV/μm), Radiat. Res., 1993, vol. 133, no. 2, p. 198.
Worgul, B.V., Medvedovsky, C., Huang, Y., et al., Quantitative assessment of the cataractogenic potential of very low doses of neutrons, Radiat. Res., 1996, vol. 145, no. 3, p. 343.
Fedorenko, B.S., Kabitsina, R.A., Krivitskaya, G.N., et al., Study of the frequency of morphological changes in neurons of the cerebral cortex of rats under the influence of accelerated carbon ions, Kosm. Biol. Med., 1987, vol. 21, no. 1, p. 51.
Vorozhtsova, S.V., Shafirkin, A.V., and Fedoren-ko, B.S., Relative biological efficiency of accelerated heavy ions and fast neutrons based on the study of the frequency of aberrant mitoses of the corneal epithelium., Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2006, vol. 40, no. 3, p. 42.
Abrosimova, A.N. (Kabachenko), Cataractogenic efficiency of protons of various energies, Cand. Sci. (Biol.) Dissertation, Moscow, 1974.
Fedorenko, B.S., Radiobiologicheskie effekty korpuskulyarnykh izluchenii: radiatsionnaya bezopasnost’ kosmicheskikh poletov (Radiobiological Effects of Corpuscular Radiation: Radiation Safety of Space Flights), Moscow, 2006.
Fedorenko, B.S., Abrosimova, A.N., and Smirnova, O.A., Influence of accelerated charged particles of high and relativistic energies on the eye lens of experimental animals, Fiz. Elem. Chastits At. Yadra, 1995, vol. 26, no 5, p. 1373.
Cucinotta, F.A., A new approach to reduce uncertainties in space radiation cancer risk prediction, PLoS One, 2015, vol. 10, no. 3, p. e0120717. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120717
Shafirkin, A.V., Grigoriev, Yu.G., and Ushakov, I.B., Elaboration of the relative biological effectiveness of fast neutrons and accelerated multi-charged ions at low doses for estimation of the risk of brain neurons and lens injury, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 2019, vol. 53, no. 1, p. 23.
Problemy radiatsionnoi bezopasnosti kosmicheskikh poletov: fizicheskie i biologicheskie issledovaniya s protonami bol’shikh energii (Challenges in Radiation Safety of Space Flights: Physical and Biological Studies with High-Energy Protons), Nefedov, Yu.G., Ed., Moscow, 1964.
Biologicheskoe deistvie protonov vysokikh energii (Biological Action of High Energy Protons), Moscow, 1967.
Darenskaya, N.G., Koznova, L.B., Akoev, I.G., and Nevskaya, G.F., Otnositel’naya biologicheskaya effektivnost’ izluchenii: faktor vremeni oblucheniya (Relative Biological Efficiency of Radiation: Irradiation Time Factor), Moscow, 1968.
Saksonov, P.P., Antipov, V.V., and Davydov, B.I., Ocherki kosmicheskoi radiobiologii (Essays on Space Radiobiology), vol. 9 of Problemy kosmicheskoi biologii (Problems of Space Biology), Moscow, 1968.
Voprosy biologicheskogo deistviya i dozimetrii tyazhelykh zaryazhennykh chastits i andronov vysokikh energii: sbornik (Issues in Biological Action and Dosimetry of Heavy Charged Particles and High-Energy Andirons: Collection of Papers), Pushchino, 1984.
Biofizicheskie osnovy deistviya kosmicheskoi radiatsii i izluchenii uskoritelei (Biophysical Bases of the Action of Space Radiation and Radiation from Accelerators), vol. 60 of Problemy kosmicheskoi biologii (Problems of Space Biology), 1989.
Ryzhov, N.I. Biological action of accelerated heavy charged particles, Doctoral (Med.) Dissertation, Moscow, 1982.
Krasavin, E.A., Mechanisms of action of ionizing radiation with different linear energy transfer on cells, Doctoral (Biol.) Dissertation, 1985.
Krasavin, E.A., Problema OBE i reparatsiya DNK (RBE Problem and DNA Repair), Moscow, 1989.
Shafirkin, A.V. and Fedorenko, B.S., Substantiation of the dependence of radiation quality coefficients on LET in application to the assessment of early radiobiological effects, Aviakosm. Ekol. Med., 1998, vol. 32, no. 2, p. 4.
Antipov, V.V., Konoplyannikov, A.G., Kudrya-shov, Yu.B., and Tarusov, B.N., Relative biological effectiveness and the picture of radiation injury under the action of ionizing radiation with different linear energy loss, in Problemy kosmicheskoi biologii (Problems of Space Biology), Moscow, 1967, vol. 6, p. 381.
Clapp, N.K., Darden, E.D., and Jerningan, M.C., Relative effects of whole-body sublethal doses of 60-MeV protons and 300-kVp X-rays on disease incidences in RF mice, Radiat. Res., 1974, vol. 57, no. 1, p. 158.
Sverdlov, A.G., Biologicheskoe deistvie neitronov i khimicheskaya zashchita (Biological Action of Neutrons and the Chemical Protection), Leningrad, 1974.
Konoplyannikov, A.G., Radiobiologiya stvolovykh kletok (Stem Cell Radiobiology), Moscow, 1984.
Avetisov, G.M., Gubin, A.T., Keirim-Markus, I.B., et al., The dependence of the quality factor from LET for new “Radiation safety standards”, Gig. Sanit., 1988, vol. 67, no. 10, p. 32.
Lioyd, D.C., Purrott, R.J., Dolphin, G.W., et al., Chromosome aberrations induced in human lymphocytes by neutron irradiation, Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 1976, vol. 29, no. 2, p. 169.
Lioyd, D.C. and Edwards, A.A., Chromosome aberrations in human lymphocytes effect of radiation quality, dose and dose-rate, in Progress and Topics in Cytogenetics, vol. 4: Radiation Induced Chromosome Damage in Man, New York, 1983, p. 23.
Lioyd, D.C., Edwards, A.A., Prosser, J.S., et al., A collaborative exercise on cytogenetic dosimetry for simulated whole and partial body accidental irradiation, Mutat. Res., 1987, vol. 179, no. 2, p. 19.
Vulpis, N., Tognacci, L., and Scarpa, G., Chromosome aberrations as a dosimetric technique for fission neutrons over the dose range 0.2–0.5 rad, Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 1978, vol. 33, p. 301.
Scott, D. Batchelor, A.L., et al., Radiation-induced chromosome aberrations in human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro: 1. RBE and dose rate studies with fast neutrons, Mutat. Res., 1969, vol. 8, no. 2, p. 367.
Biola, M.T., Le Go, R., Vacca, G., et al., Efficacite relative de divers rayonnements mixtes gamma, neutrons pour l’induction in vitro d’anomalies chromosomiques dans les lymphocytes humains, Biological Effects of Neutron Irradiation (Proc. Symp., Neuherberg, Munich, 1973), Vienna, 1974, p. 221.
Zhang, X.Z., Jin, C.Z., Lenge, R.P., Oiao, F., and Yang, J., Chromosome aberrations induced in human lymphocytes after irradiation with neutron sources 252Cf and 241Am – Be, Proceedings of the First Academic Session, Chinese Society for Radiation Protection, Beijing, 1982, p. 255.
Sasaki, M.S., Radiation-induced chromosome aberrations in lymphocytes: possible biological dosimeter in man, in Biological Aspects of Radiation Protection, Berlin, 1971, p. 81.
Covelli, V., Di Majo, V., Bassani, B., et al., Longevity and tumor incidence in mice exposed to fast neutrons at different ages, in Biological Effects of Low Level Radiation, Vienna, 1983, p. 531.
Barendsen, G.W., RBE—LET relations of reproductive death and chromosome aberrations in mammalian cells, Radiat. Res., 1985, vol. 104, no. 2, p. 158.
ICRU, The Quality Factor in Radiation Protection, Rep. 40, Washington: ICRU, 1986.
Hill, C.K., Carnes, B.A., Han, A., et al., Neoplastic transformation is enhanced by multiple low doses of fission-spectrum neutrons, Radiat. Res., 1985, vol. 102, p. 404.
Dennis, J.A. and Dunster, H.J., Radiation quality and radiation protection implications of changes in quality factors, Radiat. Protect. Dosim., 1985, vol. 13, nos. 1—4, p. 327.
Yang, T.C.-H. and Tobias, C.A., Neoplastic cell transformation by heavy ions and its modification with chemical agents, Adv. Space Res., 1984, vol. 4, no. 10, p. 207.
Ullrich, R.L., Jernigan, M.C., Cosgrove, G.E., et al., The influence of dose and dose rate on the incidence of neoplastic disease in RFM mice after neutron irradiation, Radiat. Res., 1976, vol. 68, no. 1, p. 115.
Ullrich, R.L. and Storer, J.B., Influence of dose, dose rate on radiation carcinogenesis and life shortening in RFM and BALB/c mice, in Late Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation, Vienna, 1978, vol. II, p. 95.
Ullrich, R.L., Jernigan, M.C., and Adams, L.M., Induction of lung tumors in RFM mice after localized exposure to X-rays or neutrons, Radiat. Res., 1979, vol. 80, p. 464.
Ullrich, R.L., Tumor induction in BALB/C female mice after fission neutrons or γ-irradiation, Radiat. Res., 1983, vol. 93, p. 506.
Fry, R.J.M., Powers-Risius, P., and Alpen, E.L., High-LET radiation carcinogenesis, Adv. Space Res., 1983, vol. 3, no. 2, p. 241.
Fry, R.J.M., Radiation effects in space, Adv. Space Res., 1986, vol. 6, no. 11, p. 188.
Upton, A.C., Christenberry, K.W., Melville, G.S., et al., The RBE of neutrons, X-rays and gamma-rays for production of lens opacities: observations on mice, rats, guinea pigs and rabbits, Radiology, 1956, vol. 57, no. 5, p. 686.
Upton, A.C., Randolph, M.L., Darden, E.B., et al., RBE of fast neutrons for late somatic effects in mice, in Biological Effects of Neutron and Proton Irradiation, Vienna, 1964, vol. II, p. 337.
Bateman, J.L., Bond, V.P., Rossi, H.H., et al., Lens opacification in mice exposed to monoenergetic fast neutrons, Biological Effects of Neutron and Proton Irradiation, Vienna, 1964, vol. II, p. 321.
Merriam, G.R., Bjavati, B.J., Bateman, J.L., et al., The dependence of RBE on the energy of fast neutrons: IV. Induction of lens opacities in mice, Radiat. Res., 1965, vol. 25, no. 1, p. 123.
Paola, M., Bianchi, M., and Baarli, J., Lens opacification in mice exposed to 14-MeV neutrons, Radiat. Res., 1978, vol. 73, no. 2, p. 340.
Medvedovskaya, Ts.P., Cataractogenic effect and RBE of neutrons 2 MeV, Med. Radiol., 1977, vol. 22, no. 10, p. 84.
Parking, C.S., Fowler, J.F., Maughan, R.L., et al., Repair in mouse lung for up 20 fractions of X-rays or neutrons, Brit. J. Radiol., 1985, vol. 58, no. 2, p. 225.
Evans, T.C., Richards, R.J., and Riley, E.F., Histologic studies of neutron- and X-irradiated mouse lenses, Radiat. Res., 1960, vol. 13, no. 4, p. 737.
Baarly, J., Bianchi, M., Sullivan, A.H., et al., Biological effects of hadrons at very low doses, in Biological and Environmental Effects of Low-Level Radiation, Vienna, 1976, vol. I, p. 195.
Funding
The study was carried out within the program of fundamental research of the State Scientific Center of the Russian Federation, Institute of Biomedical Problems, Russian Academy of Sciences, topic 65.2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by A. Deryabina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafirkin, A.V., Grigoriev, Y.G., Ushakov, I.B. et al. Biological Effectiveness of Fast Neutrons and Accelerated Multicharged Ions for Derivation of a New Dependence of Space Radiation Quality Coefficients on Linear Energy Transfer. Hum Physiol 48, 871–880 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119722070180
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119722070180