Abstract
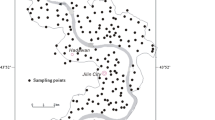
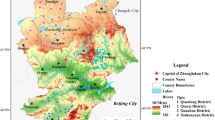
In mining areas, coal production, agriculture, and drinking use had increased the demand for fresh groundwater. It was essential to obtain a deeper understanding of the groundwater evolution processes and the water quality for domestic and irrigation uses in Sulin mining area in the northern Anhui province, China. Thirty-two shallow groundwater (SG), eighteen mid-layer groundwater (MG), and three surface water (SW) samples were analyzed for conventional hydrogeochemical and hydrogen oxygen stable isotopes. Geochemical characterization showed that the predominant ions in both SG and MG were Na+ and \({\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - }\). In addition, they probably originated from atmospheric precipitation. The ionic milliequivalent ratios demonstrated that the shallow and mid-layer groundwater circulation was mainly controlled by natural processes: rock weathering, silicates dissolution, and ion exchange were the major hydrogeochemical processes occurring. Besides, total dissolved solids, \({\text{SO}}_{4}^{{2 - }}\), Cl–, Na+, and \({\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - }\) of SG and total dissolved solids, \({\text{SO}}_{4}^{{2 - }}\), Cl–, Na+ and F– of MG were higher than the values of Chinese Standards for Drinking Water Quality and the guidelines of the World Health Organization for drinking water quality. According to some indices and the classification diagrams of water quality, most SG was suitable for irrigation, while MG with high sodium and salinity hazards was not suitable for irrigation.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Awaleh, M.O., Baudron, P., Soubaneh, Y.D., Boschetti, T., and Hoch, F.B., Recharge, groundwater flow pattern and contamination processes in an arid volcanic area: Insights from isotopic and geochemical tracers, J.Geochem. Explor., 2017, vol. 175, pp. 82−98.
Chen, L.W., Yin, X.X., and Chen, Y.P., Hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope tracing of deep groundwater circulation under mining-induced disturbance in mining district, Geograph. Geo-Inf. Sci., 2013, vol. 29, pp. 85−90.
Craig, H., Isotopic variations in meteoric waters, Science, 1961, vol. 133, pp. 1702−1703.
Ehya, F. and Mosleh, A., Hydrochemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in Basht Plain, Kohgiluyeh-Va-Boyer Ahmad Province, SW Iran, Environ. Earth Sci., 2018, vol. 77, pp. 164.
Guan, L.S., Gui, H.R., Kang, Z.Y., Zhao, H.H., and Li, J., Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment in goaf water of Kouguangou mining area in Datong, Shanxi, China, Fresen. Environ. Bull., 2018, vol. 27, pp. 9315−9324.
Gui, H.R. and Chen, S., Isotopic geochemical characteristics of groundwater and its geological significance in Sunan mining area, Earth Sci. Frontiers, 2016, vol. 23, pp. 133−139.
Hao, C.M., Huang, Y., He, P.Y., and Sun, W., Isotope drift characteristics in Ordovician Limestone Karst water caused by coal mining in Northern China, Mine Water Environ., 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-019-00606-4
Huang, D.W., Gui, H.R., Lin, M.L., and Peng, W.H., Chemical speciation distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soil from Sunan mining area, Anhui Province, China, Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess., 2018, vol. 24, pp. 1694−1709.
Huang, X.J., Wang, G.C., Liang, X.Y., Cui, L.F., Ma, L., and Xu, Q.Y., Hydrochemical and stable isotope (δD and δ18O) characteristics of groundwater and hydrogeochemical processes in the Ningtiaota coalfield, Northwest China, Mine Water Environ., 2017, vol. 37, pp. 119−136.
Jiang, Y.Q., Gui, H.R., Yu, H., Wang, M.C., Fang, H.X., Wang, C.L., Chen, C., Zhang, Y.R., and Huang, Y.H., Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of rivers in different regions of cities: a case study of Suzhou city in northern Anhui province, China, Water, 2020, vol. 12, pp. 950.
Li, P., Tian, R., and Liu, R., Solute geochemistry and multivariate analysis of water quality in the Guohua phosphorite mine, Guizhou Province, China, Expos. Health, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0277-y
Liu, J., Jin, D.W., Wang, T.T., Gao, M., Yang, J., and Wang, Q.M., Hydrogeochemical processes and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in Chenqi coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China, Environ. Earth Sci., 2019, vol. 78, pp. 347.
Ministry of Health of the P.R. China, Standardization Administration of the P. R. China, Standards for Drinking Water Quality (GB5749-2006), Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
Murkute, Y.A., Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater around Umrer coal mine area Nagpur District, Maharashtra, India, Environ. Earth Sci., 2014, vol. 72, pp. 4059−4073.
Nurtazin, S., Pureppke, S., Ospan, T., Mukhitdinov, A., and Elebessov, T., Quality of drinking water in the Balkhash District of Kazakhstan’s Almaty Region, Water, 2020, vol. 12, pp. 392.
Qiu, H.L., Gui, H.R., Cui, L., Pan, Z.G., and Lu, B., Hydrogeochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of shallow groundwater: a case study from Linhuan coal-mining district in northern Anhui Province, China, Water Sci. Tech.-W. Sup., 2019, vol. 19, pp. 1572−1578.
Richards, L.A., Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline Alkaline Soils, US Department of Agriculture, HandBook, 1954.
Sun, L.H. and Gui, H.R., Establishment of water source discrimination model in coal mine by using hydrogeochemistry and statistical analysis: a case study from Renlou Coal Mine in northern Anhui Province, China, J. Coal Sci. Eng., 2012, vol. 18, pp. 385−389.
USSL (United States Salinity Laboratory), Diagnosis and Iimprovement of Saline and Alkali Soils, US Dept of Agriculture (USDA), Agriculture Handbook 60, Washington, 1954.
Utom, A.U., Odoh, B.I., and Egboka, B.C.E., Assessment of hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater quality in the vicinity of Okpara coal and Obwetti fireclay mines, near Enugu town, Nigeria, Appl. Water Sci., 2013, vol. 3, pp. 271−283.
Wang, L.H., Dong, Y.H., Xu, Z.F., and Qiao, X.J., Hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in the northeastern Tennger Desert, northern China, Hydrogeol. J., 2017, vol. 25, pp. 2363.
WHO, Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum, World Health Organization, Geneva, 2017.
Wilcox, L.V., Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters, USDA, Circ 969, Washington, DC, USA, 1955.
Xiao, J., Jin, Z.D., and Wang, J., Assessment of the hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality of the Tarim river basin in an extreme arid region, NW China, Environ. Manage., 2014, vol. 53, pp. 135−146.
Xie, Q., Zhang, Z., Hou, T., Jin, Z.L., and Santosh, M., Geochemistry and oxygen isotope composition of magnetite from the Zhangmatun deposit, north China Craton: implications for the magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of Cornwall-type iron mineralization, Ore Geol. Rev., 2017, vol. 88, pp. 57−70.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors sincerely appreciate manuscript handling Editor and anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments that helped to greatly improve this paper.
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (41 773 100 and 41 373 095), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (2008085QD192), Key project of excellent talents support program in colleges and universities (gxyqZD2020048), Doctoral research initiation fund project (2020BS010). Key research and development projects in Anhui province (202004b11020023 and 202004a06020045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, H., Gui, H., Cui, L. et al. Hydrogeochemical Processes and Quality Assessment of Groundwater in Sulin Mining Area, Northern Anhui Province, China. Water Resour 48, 991–1000 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807821060154
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807821060154