Abstract
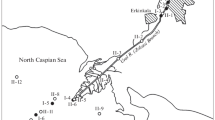
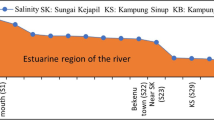
Ions of major salt composition and dissolved forms of some microelements (F, B, Sr, Rb, Cs, V, As, Mo, U) at the mouth of the Serebryanka R. (Sikhote Alin Reserve) are shown to feature conservative behavior in July 2009. The distribution of dissolved mineral phosphorus is shown to be controlled mostly by chemical processes (desorption from river suspension), even during vegetation period, while the role of biological consumption is secondary. The behavior of dissolved organic phosphorus and silicon is nearly conservative. A considerable amount of barium (up to 46% of its concentration in river water) is shown to be removed from solution, maybe because of its sorption on particulate matter of continental runoff. Ittrium and rare-earth elements (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Dy, Ho) show an abrupt decrease in the concentrations of their dissolved forms at the initial stages of river water penetration into the sea. This decrease is supposedly due to coagulation and flocculation of organic and organic-mineral colloids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anikiev, V.V., Lobanov, A.A., Starodubtsev, E.G., and Shumilin, E.N., Behavior of heavy metals at river and sea water mixing. The effect of plankton on metal migration in the marine part of Razdol’naya R. estuary, Amur Bay, Geokhimiya, 1987, no. 12, pp. 1760–1766.
Voloshina, I.V., Sikhote Alin Reserve, Izv. DVO RAN, 1996, no. 1, pp. 79–85.
Gordeev, V.V., Rechnoi stok v okean i cherty ego geokhimii (River Runoff into the Ocean and Its Geochemical Features), Moscow: Nauka, 1983.
Gordeev, V.V., Geokhimiya sistemy reka-more (Geochemistry of River-Sea System), Moscow, 2012.
Gordeev, V.V., Chudaeva, V.A., and Shul’kin, V.M., Behavior of metals in the mouth zones of two small rivers of the Eastern Sikhote Alin, Litol. Polezn. Iskop., 1983, no. 2, pp. 99–109.
Zvalinskii, V.I., Nedashkovskii, A.P., Sagalaev, S.G., et al., Nutrients and primary production in the estuary of the Razdol’naya River (Amur Bay, Sea of Japan), Russ. J. Mar. Biol., 2005, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 91–101.
Zvalinskii, V.I., Tishchenko, P.P., Tishchenko, P.Ya., et al., Results of surveying hydrochemical and production characteristics in Amur Bay water area during a flood in the Razdol’naya R. in August 2005, in Sovremennoe sostoyanie i tendentsii izmeneniya prirodnoi sredy zaliva Petra Velikogo Yaponskogo morya (Current State and Trends in the Changes in the Environment of Peter the Great Gulf of the Sea of Japan), Moscow: GEOS, 2008, pp. 199–229.
Lur’e, Yu.Yu., Unifitsirovannye metody analiza vod (Unified Methods of Water Analysis), Moscow: Khimiya, 1971.
Smirnov, E.N., Podushko, M.V., and Vasil’ev, N.G., Sikhote Alin Reserve, Priroda (Moscow), 1981, no. 3, pp. 32–45.
Sovremennoe sostoyanie i tendentsii izmeneniya prirodnoi sredy zaliva Petra Velikogo Yaponskogo morya (Current State and Trends in the Changes in the Environment of Peter the Great Gulf of the Sea of Japan), Moscow: GEOS, 2008.
Sostoyanie morskikh ekosistem, nakhodyashchikhsya pod vliyaniem rechnogo stoka (The State of Marine Ecosystems Subject to the Effect of River Runoff), Vladivostok: Dal’nauka, 2005.
Tishchenko, P.Ya., Zvalinskii, V.I., and Shevtsova, O.V., Hydrochemical studies of Razdol’naya R. estuary, Amur Bay, in Sostoyanie morskikh ekosistem, nakhodyashchikhsya pod vliyaniem rechnogo stoka (The State of Marine Ecosystems Subject to the Effect of River Runoff), Vladivostok: Dal’nauka, 2005, pp. 53–88.
Chudaeva, V.A., Migratsiya khimicheskikh elementov v vodakh Dal’nego Vostoka (Migration of Chemical Elements in Far East Waters), Vladivostok: Dal’nauka, 2002.
Shul’kin, V.M., Metally v ekosistemakh morskikh melkovodii (Metals in Ecosystems of Marine Shallows), Vladivostok: Dal’nauka, 2004.
Shul’kin, V.M., Heavy metals in riverine and marine coastal ecosystems, Doctoral (Geogr.) Dissertation, Vladivostok: PIG FEB RAS, 2007.
Ekologicheskoe sostoyanie i biota yugo-zapadnoi chasti zaliva Petra Velikogo i ust’ya reki Tumannoi (Environmental State and Biota of the Southwestern Peter the Great Gulf and Tumannaya R. Mouth), Vladivostok: Dal’nauka, 2001, vol. 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Savenko, O.S. Pokrovsky, 2014, published in Vodnye Resursy, 2014, Vol. 41, No. 6, pp. 579–584.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savenko, A.V., Pokrovsky, O.S. Migration of dissolved matter at Serebryanka R. Mouth, the basin of the Sea of Japan (Sikhote Alin Reserve). Water Resour 41, 671–676 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807814060189
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807814060189