Abstract
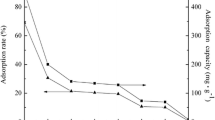
The possibility of using sorption by sulfocationite in order to extract zirconium from nitrate and sulfuric acidic solutions has been shown. The sorption of zirconium from sulfuric solutions is much more effective than from nitrate solutions. Zirconium can be desorbed by concentrated solutions of ammonium salts; at the same time, ammonium sulfate is a more effective desorbing solution when compared with ammonium nitrate. The acidification of desorbate based on ammonium nitrate decreases the efficiency of the desorption of zirconium.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Litvinova, T.E., Production of compounds of individual rare-earth metals and coproducts in processing low-quality rare-metal raw materials, Doctoral (Eng.) Dissertation, St. Petersburg: National Mineral Mining Univ., 2014.
Matveev, V.A., Kalinnikov, V.T., Maiorov, D.V., and Krasikov S.A., RF Patent 2522074, Izobret., Polezn. Modeli, 2014, no. 20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by K. Gumerov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lokshin, E.P., Tareeva, O.A. Sorption of Zirconium from Nitrate and Sulfate Solutions. Theor Found Chem Eng 53, 688–692 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579519040122
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579519040122