Abstract
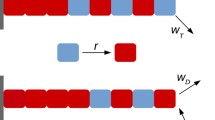
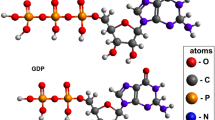
Microtubules are demonstrated as straight macromolecules including the linear chains of tubulin subunits in the length. It’s important to know the functions inside microtubule growth and the control of microtubule processes. An important item that determines the status of a microtubule, whether it is growing or shrinking, is the length of the GTP tubulin microtubule cap in view point of thermodynamic properties. Monte Carlo simulation has been applied to study dynamic instability of the microtubule length. In this model, one-dimensional microtubule is fixed at one of the two and is simulated while the opposite end is allowed for growing in random situation. By a Monte Carlo model of the assembly and disassembly of microtubules, the thermodynamic parameters helped us to explain suitable mechanism and also we take into account the contribution of water to the entropy of the microtubule systems. We compared the result of the model from published experimental data using the GTP tubulin dimer attachment rate and the lateral and longitudinal binding energies of GTP and GDP tubulin dimers at both ends. By this study at each step, one tubulin has been added to the length for growing microtubule length. Computationally, this can be done through generating a uniform random number between 0 and 1. It has been calculated a correct dimension around 10–6 m of microtubules length including around 1650 tubulin dimers. Microtubule growth rate is related to the soluble tubulin dimer concentration and for all results shown here, simulation of any single condition was run 5–10 times. For each simulation it has been recorded values number, average length and free tubulin concentration.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. Ringhoff and L. Cassimeris, Mol. Biol Cell. 20, 3451 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E09-02-0140
M. J. Clément, I. Jourdain, S. Lachkar, et al., Biochemistry 44 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0512492
B. K. Garvalov, B. Zuber, C. B. Marquis, et al., J. Cell Biol. 174, 759 (2006).
G. I. Brouhard and L. M. Rice, J. Cell Biol. 207, 323 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201407095
A. Akhmanova and M. O. Steinmetz, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 16, 711 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm4084
Y. Chen and W. O. Hancock, Nat. Commun. 6, 8160 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9160
S. Sahu, S. Ghosh, B. Ghosh, et al., Biosens. Bioelectron. 47, 141 (2013).
A. Guesdon, F. Bazile, R. M. Buey, et al., Nat. Cell Biol. 18, 1102 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3412
K. K. Gupta, E. O. Alberico, I. S. Näthke, and H. V. Goodson, Bio Essays 36, 818 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201400029
P. K. Hepler, Plant Physiol. 170, 3 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.0150626722019
P. R. Burton, J. Cell. Biol. 99, 520 (1984).
D. C. Rowlands, A. Williams, N. A. Jones, et al., Lab Invest. 72, 100 (1995).
S. Ozon, A. Maucuer, and A. Sobel, Eur. J. Biochem. 248, 794 (1997).
E. Charbaut, P. A. Curmi, S. Ozon, et al., J. Biol. Chem. 276, 16146 (2001).
S. M. Hanash, J. R. Strahler, R. Kuick, et al., J. Biol. Chem. 263, 12813 (1988).
P. A. Curmi, C. Nogues, S. Lachkar, et al., Br. J. Cancer 82, 142 (2000).
D. K. Price, J. R. Ball, Z. Bahrani-Mostafavi, et al., Cell 84, 623 (1996).
L. D. Belmont and T. J. Mitchison, Cell 84, 623–631 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81037-5.
N. Hirokawa, Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 279, 519 (1998).
R. D. Vale, Cell 112, 467 (2003).
R. H. Wade, D. Chrétien, and. D. Job, J. Mol. Biol. 212, 775 (1990).
E. Nogales, S. Wolf, and K. H. Downing, Nature (London, U.K.) 391, 199 (1998).
R. B. G. Ravelli, B. Gigant, P. A. Curmi, et al., Nature (London, U.K.) 428, 198 (2004).
B. Mallik, A. Masunov, and T. Lazaridis, J. Comput. Chem. 23, 1090 (2002).
Y. Duan, C. Wu, S. Chowdhury, et al., J. Comput. Chem. 24, 1999 (2003).
B. R. Brooks, C. L. Brooks, A. D. MacKerell, Jr., et al., J. Comput. Chem. 30, 1545 (2009).
B. T. Castle, S. McCubbin, L. S. Prahl, et al., Mol. Biol. Cell. 28, 1238 (2017).https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E16-08-0567
M. Piehl, U. S. Tulu, P. Wadsworth, and L. Cassimeris, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101, 1584 (2004).
S. S. Andersen, A. J. Ashford, R. Tournebize, et al., Nature (London, U.K.) 389, 640 (1997).
N. M. Rusan, U. S. Tulu, C. Fagerstrom, and P. Wadsworth, J. Cell. Biol. 158, 997 (2002).https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200204109
L. D. Belmont and T. J. Mitchison, Cell 84, 623 (1996).
D. J. Odde and H. M. Buettner, Ann. Biol. Eng. 23, 268 (1995).
S. Leibler and M. Dogterom, Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1347 (1993).
F. Mollaamin, F. Kandemirli, and M. Monajjemi, Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 12, 3780 (2022). https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC123.37803789
M. A. Moulaee, M. Monajjemi, J. Mehrzad, et al., Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 12, 1428 (2022). https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC122.14281436
M. Monajjemi, F. Kandemirli, H. Sakhaeinia, and F. Mollaamin, Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 12, 2646 (2022). https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC122.26462659
M. A. Moulaee, M. Monajjemi, J. Mehrzad, et al., Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 11, 9501 (2021). https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC112.95019512
P. Niethmmer, P. Bastiaens, and E. Karsenti, Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 303, 1862 (2004).
P. N. Zakharov, V. Gudimchuk, A. Voevodin, et al., Biophys. J. 109, 2574 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2015.10.048
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naghsh, F., Monajjemi, M. Thermodynamic Study of Assembling ↔ Disassembling of Microtubules via the Monte Carlo Simulation. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 96, 1474–1483 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024422070111
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024422070111