Abstract
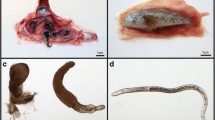
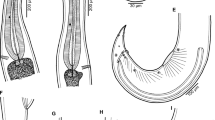
For the first time, the spreading of a fearsome non-native parasite nematode Anguillicoloïdes crassus is studied in European Eel Anguilla anguilla in 4 different coastal ecosystems throughout 12 years. We found that the parasite become more abundant with time in each study site; only 4.8% of eels inhabited brackish water (Mellah Lagoon) are infected while—over the third of fish are infected in the other waterbodies parasite nematode is presented in fish of all ages as well as of both sex; however infected specimens are less common among juveniles and males Based on the evaluation of the swimbladder degenerative index, we found that swimbladder is damaged in more than a half of fish captured in freshwater, however the opposite situation is observed in the brackish water.There is a significant difference in age, length, weight and condition between infected and uninfected fish.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Belpaire, C., Pujolar, J.M., Geeraerts, C. and Maes, G.E., Contaminants in eels and their role in the collapse of the eel stocks, in Biology and Ecology of Anguillid Eels, Arai, T., Ed., Florida: Boca Raton, 2016.
Boon, J.H., Cannaerts, V.M.H., Augustijn, H., et al., The effect of different infection levels with infective larvae of Anguillicola crassus on haematological parameters of European eel (Anguilla anguilla), Aquaculture, 1990, vol. 87, pp. 243−253. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(90)
Bornarel, V., Lambert, P, Briand, C., et al., Modelling the recruitment of European eel (Anguilla anguilla) throughout its European range, ICES J. Mar. Sci., 2017, vol. 75, pp. 541−552. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fsx180.90062-R
Boudjadi, Z., Tahri, M., Djebari, N., et al., Etude de l’infestation des anguilles (Anguilla anguilla) par le nématode (Anguillicola crassus) dans l’estuaire du Mafrag (Algérie), Mésogée, 2009, vol. 65, pp. 5966.
Bush, A.O., Lafferty, K.D., Lotz, J.M. and Shostak, A.W., Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited, J. Parasitol., 1997, vol. 83, pp. 575−583.
Byer, J.D., Lebeuf, M., Trottier, S., et al., Trends of persistent organic pollutants in American eel (Anguilla rostrata) from eastern Lake Ontario, Canada, and their potential effects on recruitment, Sci. Total Environ., 2015, vol. 529, pp. 231−242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.05.054
Castonguay, M., Hodson, P.V., Moriarty, C., et al., Is there a role of ocean environment in American and European eel decline? Fish Oceanogr., 1994a, vol. 3, pp. 197−203.
Castonguay, M., Hodson, P.V., Couillard, C.M., et al., Why is recruitment of the American eel, Anguilla rostrata, declining in the St. Lawrence River and Gulf?, Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci., 1994b, vol. 51, pp. 479−488.
Dekker, W., Status of the European eel stock and fisheries, in Eel Biology, Aida, K., Eds., Tokyo: Springer-Verlag, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-65907-5_17
Dekker, W. and Casselman, J.M., The Québec Declaration of Concern about eel declines−11 years later: Are eels climbing back up the slippery slope?, Fisheries, 2014, vol. 39, pp. 613−614. https://doi.org/10.1080/03632415.2014.979342
Dekker, W., Casselman, J.M., Cairns, D.K., et al., Québec Declaration of Concern: Worldwide decline of eel resources necessitates immediate action, Fisheries, 2003, vol. 28, no. 12, pp. 28−30. https://edepot.wur.nl/40989
Dhaouadi, R., Sghaier, A., Aloui, N., et al., Etude de l’infestation de l’anguille européenne, Anguilla anguilla, par le nématode Anguillicoloides crassus dans la lagune de Ghar El Melh (Nord de la Tunisie), Mar. Life, 2014, vol. 18, pp. 17−24.
Diekmann, M., Simon, J. and Salva, J., On the actual recruitment of European eel (Anguilla anguilla) in the River Ems, Germany, Fish. Manag. Ecol., 2019, vol. 26, pp. 20−30. https://doi.org/10.1111/fme.12314
Drouineau, H., Durif, C., Castonguay, M., et al., Freshwater eels: A symbol of the effects of global change, Fish Fish., 2018, vol. 19, pp. 903−930. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12300
EELREP, Estimation of the reproduction capacity of European eel, Final report, EU contract Q5RS-2001–01836, Leiden : Leiden Univ., 2005. http://www.fishbiology.net/eelrepsum.html
Fazio, G., Moné, H., Da Silva, C., et al., Changes in gene expression in European eels (Anguilla anguilla) induced by infection with swim bladder nematodes (Anguillicola crassus), J. Parasitol., 2009, vol. 95, pp. 808−816. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-1705.1
Feunteun, E., Management and restoration of European eel population (Anguilla anguilla): An impossible bargain, Ecol. Eng., 2002, vol. 18, pp. 575−591. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8574(02)00021-6
Fèvre, E.M., Bronsvoort, B.M.D.C., Hamilton, K.A. and Cleaveland, S., Animal movements and the spread of infectious diseases, Trends Microbiol., 2006, vol. 14, pp. 125−131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2006.01.004
Fries, L.T., Williams, D.J. and Johnson, S.K., Occurrence of Anguillicola crassus, an exotic parasitic swim bladder nematode of eels, in the Southeastern United States, Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc., 1996, vol. 125, pp. 794−797. https://doi.org/10.1577/1548-8659(1996)125<0794:NOOCAE>2.3.CO;2
Gargouri Ben Abdallah, L. and Maamouri, F., Spatio-temporal dynamics of the nematode Anguillicola crassus in Northeast Tunisian lagoons, C. R. Biol., 2006, vol. 329, pp. 785−789. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao050181
Giari, L., Castaldelli, G., Gavioli, A., et al., Long-term ecological analysis of Anguillicola crassus occurrence and impact on the European eel population in a Mediterranean lagoon (North Italy), Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 2021, vol. 249, Article 107117. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECSS.2020.107117
ICES, Report of the 2011 session of the Joint EIFAAC/ICES Working Group on Eels, EIFAAC Occasional Paper, No. 48, ICES CM 2011/ACOM: 18, Rome: FAO, 2011. https://doi.org/10.17895/ices.pub.8810
Jakob E., Walter, T. and Hanel, R., A checklist of the protozoan and metazoan parasites of European eel (Anguilla anguilla): checklist of Anguilla anguilla parasites, J. Appl. Ichthyol., 2009, vol. 32, pp. 757−804. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2009.01345.x
Johnson, A., Hatfield, C. and Milne, B., Simulated diffusion dynamics in river networks, Ecol. Model., 1995, vol. 83, pp. 311−325. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3800(94)00107-9
Kennedy, C.R., The distribution and abundance of the nematode Anguillicola australiensis in eels Anguilla reinhardtii in Queensland, Australia, Folia Parasitol., 1994, vol. 41, pp. 279−285.
Kennedy, C.R. and Fitch, D.J., Colonization, larval survival and epidemiology of the nematode Anguillicola crassus, parasitic in the eel, Anguilla anguilla, in Britain, J. Fish Biol., 1990, vol. 36, pp. 117–131. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1990.tb05588.x
Kettle, A.J., Asbjørn Vøllestad, L. and Wibig, J., Where once the eel and the elephant were together: Decline of the European eel because of changing hydrology in southwest Europe and northwest Africa?, Fish Fish., 2011, vol. 12, pp. 380−411. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-2979.2010.00400.x
Kirk, R.S., The impact of Anguillicola crassus on European eels, Fish Manag. Ecol., 2003, vol. 10, pp. 385−394. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2400.2003.00355.x
Kirk, R.S., Kennedy, C.R. and Lewis, J.W., Effect of salinity on hatching, survival and infectivity of Anguillicola crassus (Nematoda: Dracunculoidea) larvae, Dis. Aquat. Org., 2000, vol. 40, pp. 211−218. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao040211
Knopf, K., The swimbladder nematode Anguillicola crassus in the European eel Anguilla anguilla and the Japanese eel Anguilla japonica: differences in susceptibility and immunity between a recently colonized host and the original host, J. Helminthol., 2006, vol. 80, pp. 129−136. https://doi.org/10.1079/JOH2006353
Kristmundsson, Á. and Helgason, S., Parasite communities of eels Anguilla anguilla in freshwater and marine habitats in Iceland in comparison with other parasite communities of eels in Europe, Folia Parasitol., 2007, vol. 54, pp. 141–153. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2007.019
Kutz, S.J., Hoberg, E.P., Polley, L. and Jenkins, E.J., Global warming is changing the dynamics of Arctic host-parasite systems, Proc. R. Soc. B, 2005, vol. 272, pp. 2571−2576. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2005.3285
Larsen, M.H. and Mouritsen, K.N., Temperature-parasitism synergy alters intertidal soft-bottom community structure, J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol., 2014, vol. 460, pp. 109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2014.06.011
Lefebvre, F., Contournet, P., Priour, F., et al., Spatial and temporal variation in Anguillicola crassus counts: Results of a 4 year survey of eels in Mediterranean lagoons, Dis. Aquat. Org., 2002a, vol. 50, pp. 181–188. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao050181
Lefebvre, F., Contournet, P. and Crivelli, A.J., The health state of the eel swimbladder as a measure of parasite pressure by Anguillicola crassus, Parasitol., 2002b, vol. 124, pp. 457−463. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182001001378
Lefebvre, F., Sergent, E., Acou, A., et al., Recruitment of glass eels (Anguilla anguilla) on the French Mediterranean coast: A comparative analysis of biometric and pigmentation characteristics during the 1974−75 and 2000−2001 sampling seasons, Bull. Fr. Pêche Piscic., 2003, vol. 368, pp. 85−96.
Lefebvre, F., Fazio, G., and Crivelli, A.J., Anguillicoloides crassus, in Fish Parasites: Pathobiology and Protection, Woo, P.T.K. and Buchmann, K., Eds., Oxford: CABI, 2012a.
Lefebvre, F., Wielgoss, S., Nagasawa, K., and Moravec, F., On the origin of Anguillicoloides crassus, the invasive nematode of anguillid eels, Aquat. Invas., 2012b, vol. 7, pp. 443–453.
Lefebvre, F., Fazio, G., Mounaix, B., and Crivelli, A.J., Is the continental life of the European eel Anguilla anguilla affected by the parasitic invader Anguillicoloides crassus?, Proc. R. Soc. B, 2013, vol. 280, pp. 2012−2916. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2012.2916
Meddour, A. and Meddour-Bouderda, K., Bilan d’une pisciculture extensive et parasites des poissons de la lagune Mellah et du lac Oubeïra (Parc National d’El Kala), Procceding des Journées Internationales sur les Sciences de la Mer J’NESMA99, Atelier B, 657–670, Alger, 1999. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/270051373
Moravec, F., Dracunculoid and Anguillicoloid Nematodes Parasitic in Vertebrates, Prague: Academia, 2006.
Nagasawa, K., Kim, Y.G., and Hirose, H., Anguillicola crassus and A. globiceps (Nematoda: Dracunculoidea) parasitic in the swim bladder of eels (Anguilla japonica and A. anguilla) in East Asia: A review, Folia Parasitol., 1994, vol. 41, pp. 127−137.
Neto, A.F., Passos, D., Costa, J.L., et al., Infection of Anguilla anguilla by the parasite Anguillicoloides crassus in Portuguese brackish water systems, Cah. Biol. Mar., 2014, vol. 55, pp. 213−216. https://doi.org/10.3354/DAO02166
Neumann, W., Schwimmblasen parasit Anguillicola bei Aalen, Fisch. Teichwirt., 1985, vol. 36, pp. 1−322.
Ooi, H.K., Wang, W.S., Chang, H.Y., et al., An epizootic of anguillicolosis in cultured American eels in Taiwan, J. Aquat. Anim. Health., 1996, vol. 8, pp. 163−166. https://doi.org/10.1577/1548-8667(1996)008<0163:AEOAIC>2.3.CO;2
Palstra, A.P., Heppener, D.F.M., van Ginneken, V.J.T., et al., Swimming performance of silver eels is severely impaired by the swim-bladder parasite Anguillicola crassus, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 2007, vol. 352, pp. 244−256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2007.08.003
Panfili, J., and Ximenes, M.C., Evaluation de l’âge et de la croissance de l’anguille européenne (Anguilla anguilla L.) en milieu continental: méthodologies, validation, application en Méditerranée et comparaisons en Europe, Bull. Fr. Pêche Piscic., 1994, vol. 335, pp. 43–66.
Panfili, J., Pontual, H., de Troadec, H. and Wright, P.J., Manuel de sclérochronologie des poisons, Brest: Ifremer-IRD Coédition, 2002. https://doi.org/10.4000/books.irdeditions.20901
Pike, C., Crook, V., and Gollock, M., Anguilla Anguilla, in The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2020, e.T60344A152845178. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T6034-4A152845178.en
Sauvaget, B., Fatin, D., and Briand, C., Contamination par Anguillicola crassus de cinq populations d’anguilles (Anguilla anguilla) du littoral de Bretagne Sud (France), Bull. Fr. Pêche Piscic., 2003, vol. 368, pp. 21−26. https://doi.org/10.1051/kmae:2003033
Sorci, G. and Garnier, S., Parasitism, Encyclopedia Ecol., 2008, vol. 2, pp. 2645−2650. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-008045405-4.00814-4
Tahri, M., Crivelli, A.J., Panfili, J., and Bensouilah, M., Health status of the swimbladder of the European eel Anguilla anguilla in northeastern Algeria’s Lake Oubeïra, Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud., 2016, vol. 4, pp. 364−369. https://www.fisheriesjournal.com/archives/2016/vol4issue1/PartE/4-1-10.pdf
Thomas, K. and Ollevier, F., Hatching, survival, activity and penetration efficiency of second-stage larvae of Anguillicola crassus (Nematoda), Parasitology, 1993, vol. 197, pp. 211−217. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182000067329
Turner, W.C., Kamath, P.L., van Heerden, H., et al., The roles of environmental variation and parasite survival in virulence−transmission relationships, R. Soc. Open. Sci., 2021, vol. 8, Article no. 210088. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.210088
van Banning, P. and Haenen, O.L.M., Effects of the swim bladder nematode Anguillicola crassus in wild and farmed eel, Anguilla anguilla, in Pathology in Marine Science, Perkins, F.O., Cheng, T.C., Eds., San Diego: Academic Press, 1990. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03855.x
Wielgoss, S., Taraschewski, H., Meyer, A., and Wirth, T., Population structure of the parasitic nematode Anguillicola crassus, an invader of declining North Atlantic eel stocks, Mol. Ecol., 2008, vol. 17, pp. 3478−3495.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Dr. Seraina Emilia Bracamonte from Department of Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology (Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales—MNCN, Spain) for her contribution to the creation of the GLM-model.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement on the welfare of humans or animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tahri, M., Bensouilah, M. The European Eel Anguilla anguilla (Anguillidae) Invasion by the Allochthone Nematode Anguillicoloïdes crassus in Southern Mediterranean. J. Ichthyol. 63, 103–111 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945223010150
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945223010150