Abstract
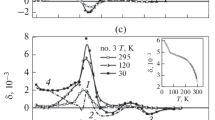
The spectral, temperature, and magnetic field dependences of the magneto-optical transversal Kerr effect (TKE) have been studied along with the optical spectra of InFeAs layers formed by ion implantation with further pulsed laser melting at different laser pulse energies. A strong dependence of the magneto-optical and optical properties of InFeAs layers on the pulse energy has been revealed. The TKE spectra of the specimen formed at a minimum pulse energy (W = 0.1 J/cm2) indicate the presence of ferromagnetic (In, Fe)As nanoclusters with a Curie temperature of ≈180 K in the weakly doped semiconductive matrix and the absence of secondary magnetic phases. The TKE spectra of layers formed at W = 0.15–0.4 J/cm2 are a superposition of the contributions from ferromagnetic (In,Fe)As nanoareas distributed in the volume and near-surface Fe inclusions. The predominance of the iron contribution in the spectra indicates the intensification of Fe diffusion towards the surface with an increase in the laser pulse energy. Anisotropy in the magneto-optical and optical spectra confirms anisotropic chemical phase separation in the layers.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
P. N. Hai, L. D. Anh, S. Mohan, T. Tamegai, M. Kodzuka, T. Ohkubo, K. Hono, and M. Tanaka, “Growth and characterization of n-type electron-induced ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 182403 (2012).
P. N. Hai, L. D. Anh, and M. Tanaka, “Electron effective mass in n-type electron-induced ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As: Evidence of conduction band transport,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 252410 (2012).
S. Sakamoto, L. D. Anh, P. N. Hai, G. Shibata, Y. Takeda, M. Kobayashi, Y. Takahashi, T. Koide, M. Tanaka, and A. Fujimori, “Magnetization process of the n-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As:Be studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism,” Phys. Rev. B 93, 035203 (2016).
N. T. Tu, P. N. Hai, L. D. Anh, and M. Tanaka, “High-temperature ferromagnetism in heavily Fe-doped ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 192401 (2016).
N. T. Tu, P. N. Hai, L. D. Anh, and M. Tanaka, “Heavily Fe-doped ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)Sb with high Curie temperature and large magnetic anisotropy,” Appl. Phys. Exp. 12, 103004 (2019).
P. N. Hai, M. Yoshida, A. Nagamine, and M. Tanaka, “Inhomogeneity-induced high temperature ferromagnetism in n-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As grown on vicinal GaAs substrates,” Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 59, 063002 (2020).
Y. Yuan, R. Hübner, M. Birowska, Ch. Xu, M. Wang, S. Prucnal, R. Jakiela, K. Potzger, R. Böttger, S. Facsko, J. A. Majewski, M. Helm, M. Sawicki, Sh. Zhou, and T. Dietl, “Nematicity of correlated systems driven by anisotropic chemical phase separation,” Phys. Rev. Mater. 2, 114601 (2018).
T. Dietl, K. Sato, T. Fukushima, A. Bonanni, M. Jamet, A. Barski, S. Kuroda, M. Tanaka, P. N. Hai, and H. Katayama-Yoshida, “Spinodal nanodecomposition in semiconductors doped with transition metals,” Rev. Mod. Phys. 87, 1311–1377 (2015).
L. M. C. Pereira, “Experimentally evaluating the origin of dilute magnetism in nanomaterials,” J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 50, 393002 (2017).
K. Ando, Magneto-Optics of Diluted Magnetic Semiconductors: New Materials and Applications, Magneto-Optics, Ed. by S. Sugano and N. Kojima (Springer, Berlin, 2000), Vol. 128, pp. 211–241.
E. D. Palik and R. T. Holm, Indium arsenide, Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids, Ed. by E. D. Palik (Academic, Orlando, 1985), pp. 479–489.
P. B. Johnson and R. W. Christy, “Optical constants of transition metals: Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Pd,” Phys. Rev. B 9, 5056–5070 (1974).
T. J. Kim, J. J. Yoon, S. Y. Hwang, Y. W. Jung, T. H. Ghong, Y. D. Kim, H. J. Kim, and Y.-C. Chang, “InAs critical-point energies at 22 K from spectroscopic ellipsometry,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 171912 (2010).
E. A. Gan’shina, L. L. Golik, Z. E. Kun’kova, G. S. Zykov, A. I. Rukovishnikov, and Yu. V. Markin, “Magnetic inhomogeneity manifestations in the magneto-optical spectra of (In–Mn)As layers,” IEEE Magn. Lett. 11, 2502105 (2020).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to A.I. Rukovishnikov for the measurements of the ellipsometry spectra.
Funding
This study was performed within the state assignment to the Kotel’nikov Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics (Russian Academy of Sciences).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by E. Glushachenkova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gan’shina, E.A., Kun’kova, Z.E., Pripechenkov, I.M. et al. Magneto-Optical Probing of the Magnetic State and Phase Composition of InFeAs Layers. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 123, 1098–1104 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22601287
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X22601287