Abstract
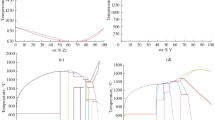
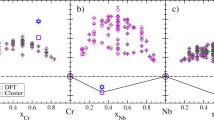
Based on the CALPHAD method, a description of the Cr–Nb–Ti–V–Zr alloy system was formulated and temperature dependences of changes in the phase composition of high-entropy CrxNbTiVZr alloys (for x = 0.5, 0.75, 1, and 1.25) were calculated.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
V. F. Gorban’, N. A. Krapivka, and S. A. Firstov, “High-entropy alloys: Interrelations between electron concentration, phase composition, lattice parameter, and properties,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 118, 970–981 (2017).
V. F. Gorban, N. A. Krapivka, S. A. Firstov, and D. V. Kurilenko, “Role of various parameters in the formation of the physicomechanical properties of high-entropy alloys with bcc lattices,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 119, 477–481 (2018).
N. I. Kourov, V. G. Pushin, A. V. Korolev, Yu. V. Knyazev, M. V. Ivchenko, and Yu. M. Ustyugov, “Peculiar features of physical properties of the rapidly quenched AlCrFeCoNiCu high-entropy alloy,” J. Alloys Compd. 636, 304–309 (2015).
M. V. Ivchenko, V. G. Pushin, A. N. Uksusnikov, N. Wanderka, and N. I. Kourov, “Specific features of cast high-entropy AlCrFeCoNiCu alloys produced by ultrarapid quenching from the melt,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 114, 503–513 (2013).
M. V. Ivchenko, V. G. Pushin, A. N. Uksusnikov, and N. Wanderka, “Microstructure features of high-entropy equiatomic cast AlCrFeCoNiCu alloys,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 114, 514–520 (2013).
O. N. Senkov, G. B. Wilks, J. M. Scott, and D. B. Miracle, “Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys,” Intermetallics 19, 698–706 (2011).
O. N. Senkov, C. Woodward, and D. B. Miracle, “Microstructure of aluminum-containing refractory high-entropy alloys,” JOM 66, 2030–2042 (2014).
C. Li, Y. Xue, M. Hua, T. Cao, L. Ma, and L. Wang, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of AlxSi0.2CrFeCoNiCu1 – x high entropy alloys,” Mater. Des. 90, 601–609 (2016).
E. Eshed, N. Larianovsky, A. Kovalevsky, V. Popov, Jr., I. Gorbachev, V. Popov, and A. Katz-Demyanetz, “Microstructural evolution and phase formation in 2nd-generation refractory-based high entropy alloys,” Materials 11, 175–187 (2018).
F. Zhang, C. Zhang, S. L. Chen, J. Zhu, W. S. Cao, and U. R. Kattner, “An understanding of high entropy alloys from phase diagram calculations, “CALPHAD 45, 1–10 (2014).
H. L. Lukas, S. G. Fries, and B. Sundman, Computational Thermodynamics: The Calphad Method (Cambridge University Press, 2007),
M. Hillert and L.-I. Staffonsson, “The regular solution model for stoichiometric phases and ionic melts,” Acta Chem. Scand. 24, 3618–3626 (1970).
B. Sundman and J. Agren, “A regular solution model for phase with several components and sublattices, suitable for computer applications,” J. Phys. Chem. Solids 42, 297–301 (1981).
A. T. Dinsdale, “SGTE data for pure elements,” CALPHAD 15, 317–425 (1991).
J. Y. Lee, J. H. Kim, S. I. Park, and H. M. Lee, “Phase equilibrium of the Ti–Cr–V ternary system in the non-burning β-Ti alloy region,” J. Alloys Compd. 291, 229–238 (1999).
J. Pavlů, J. Vřešt’ál, and M. Šob, “Thermodynamic modeling of Laves phases in the Cr–Hf and Cr–Ti systems: Reassessment using first-principles results,” CALPHAD 34, 215–221 (2010).
W. D. Zhuang, J. Y. Shen, Y. Q. Liu, L. Ling, S. L. Shang, Y. Du, and J. C. Schuster, “Thermodynamic optimization of the Cr–Ti system,” Z. Metallkd. 91, 121–127 (2000).
D. M. Cupid, M. J. Kriegel, O. Fabrichnaya, F. Ebrahimi, and H. J. Seifert, “Thermodynamic assessment of the Cr–Ti and first assessment of the Al–Cr–Ti systems,” Intermetallics 19, 1222–1235 (2011).
N. Saunders, “System Cr–Ti,” In Thermochemical Database for Light Metal Alloys (Volume 2), Ed. by A. Ansara, T. Dinsdale, and M. H. Rand (Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg, 1998).
G. Ghosh, “Thermodynamic and kinetic modeling of the Cr–Ti–V system,” J. Phase Equilib. 23, 310–328 (2002).
B.-J. Lee and D. N. Lee, “A thermodynamic evaluation of the Fe–Cr–V–C system,” J. Phase Equilib. 13, 349–364 (1992).
C. Guo, C. Li, X. Zheng, and Zh. Du, “Thermodynamic modeling of the Fe–Ti–V system,” CALPHAD 38, 155–160 (2012).
J. Cui, C. Guo, L. Zou, Ch. Li, and Zh. Du, “Experimental investigation and thermodynamic modeling of the Ti–V–Zr system,” CALPHAD 55 (Part 2), 189–198 (2016).
C. Servant, “Thermodynamic assessments of the phase diagrams of the hafnium–vanadium and vanadium–zirconium systems,” J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 26, 39–49 (2005).
X.-S. Zhao, G.-H. Yuan, M.-Y. Yao, Q. Yue, and J.‑Y. Shen, “First-principles calculations and thermodynamic modeling of the V–Zr system,” CALPHAD 36, 163–168 (2012).
H.-J. Lu, W.-B. Wang, N. Zou, J.-Y. Shen, X.-G. Lu, and Y.-L. He, “Thermodynamic modeling of Cr–Nb and Zr–Cr with extension to the ternary Zr–Nb–Cr system,” CALPHAD 50, 134–143 (2015).
C. Schmetterer, A. Khvan, A. Jacob, B. Hallstedt, and T. Markus, “A new theoretical study of the Cr–Nb system,” J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 35, 434–444 (2014).
Y. Peng, P. Zhou, M. Bu, W. Zhang, and Y. Du, “A thermodynamic evaluation of the C–Cr–Nb system,” CALPHAD 53, 10–19 (2016).
J. Pavlů, J. Vřešt’ál, and M. Šob, “Re-modeling of Laves phases in the Cr–Nb and Cr–Ta systems using first-principles results,” CALPHAD 33, 179–186 (2009).
J. G. Costa Neto, S. G. Fries, and H. L. Lukas, “Thermodynamic optimisation of the Nb–Cr system,” CALPHAD 17, 219–228 (1993).
A. Fernandez-Guillermet, “Thermodynamic analysis of the stable phases in the Zr–Nb system and calculation of the phase diagram,” Z. Metallkd. 82, 478–487 (1991).
J. Pavlů, J. Vřešt’ál, and M. Šob, “Stability of Laves phases in the Cr–Zr system,” CALPHAD 33, 382–387 (2009).
Y. Yang, L. Tan, H. Bei, and J. T. Busby, “Thermodynamic modeling and experimental study of the Fe–Cr–Zr system,” J. Nucl. Mater. 441, 190–202 (2013).
K. C. Hari Kumar, P. Wollants, and L. Delaey, “Thermodynamic calculation of Nb–Ti–V phase diagram,” CALPHAD 18, 71–79 (1994).
N. Saunders, “System Nb–Ti,” in Thermochemical Database for Light Metal Alloys (Volume 2), Ed. by A. Ansara, T. Dinsdale, and M. H. Rand (Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg, 1998).
B.-J. Lee, “Thermodynamic assessment of the Fe–Nb–Ti–C–N system,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32A, 2423–2439 (2001).
Y. Zhang, H. Liu, and Zh. Jin, “Thermodynamic assessment of the Nb–Ti system,” CALPHAD 25, 305–317 (2001).
H. Liang and Y. A. Chang, “Thermodynamic modeling of the Nb–Si–Ti ternary system,” Intermetallics 7, 561–570 (1999).
A. V. Khvan, K. Chang, and B. Hallstedt, “Thermodynamic assessment of the Fe–Nb–V system,” CALPHAD 43, 143–148 (2013).
FUNDING
The work was performed in the framework of the state task according to the theme “Spin,” no. AAAA-A18-118020290104-2 with the support of the program of basic research of the Ural Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (project no. 18-10-2-37).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by S. Gorin
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorbachev, I.I., Popov, V.V., Katz-Demyanetz, A. et al. Prediction of the Phase Composition of High-Entropy Аlloys Based on Cr–Nb–Ti–V–Zr Using the Calphad Method. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 120, 378–386 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X19040069
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X19040069