Abstract
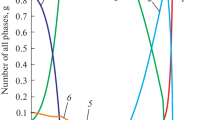
Structural and microstructural changes that arise in the course of the heat treatment of Cr–Ni–Mo austenitic stainless steels with different concentrations of titanium and phosphorus have been studied. It has been found that the alloying with phosphorus decreases the lattice parameter of these steels. The phosphorus contribution to this effect is 0.015 ± 0.002 Å/at %. Aging at a temperature of 670 K for about 20 h leads to the precipitation of dispersed needle-like particles, which are most likely to be iron phosphides. In the temperature range of 700–800 K, in austenitic steels, the atomic separation of the solid solution occurs, the intensity of which decreases upon alloying with titanium or phosphorus at concentrations of 1.0 and 0.1 wt %, respectively. At higher temperatures (about 950 K), the formed precipitates of the Ni3Ti (γ') phase increase in size to 7–10 nm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. J. Maziasz, “Formation and stability of radiationinduced phases in neutron irradiated austenitic and ferritic steels,” J. Nucl. Mater. 169, 95–115 (1989).
T. Okita, W. G. Wolfer, F. A. Garner, and N. Sekimura, “Effects of titanium additions to austenitic ternary alloys on microstructural evolution and void swelling,” Philos. Mag. 85, 2033–2048 (2005).
V. V. Sagaradze, V. M. Nalesnik, S. S. Lapin, and V. M. Aliabev, “Precipitation hardening and radiation damageability of austenitic stainless steels,” J. Nucl. Mater. 202, 137–144 (1993).
C. David, B. K. Panigrahi, S. Balaji, A. K. Balamurugan, K. G. M. Nair, G. Amarendra, C. S. Sundar, and R. Baldev, “A Study of the effect of titanium on the void swelling behavior of D9 steels by ion beam simulation,” J. Nucl. Mater. 383, 132–136 (2008).
H. Kurishita, T. Muroga, H. Watanabe, N. Yoshida, H. Kayano, and M. L. Hamilton, “Effect of FFTF irradiation on tensile properties of P- and Ti-modified model austenitic alloys with small amounts of boron,” J. Nucl. Mater. 212, 519–524 (1994).
I. Shibahara, N. Akasaka, S. Onose, H. Okada, and S. Ukai, “Swelling of advanced austenitic stainless steels developed for the environment of heavy neutron exposure,” J. Nucl. Mater. 212–215, 487–491 (1994).
F. A. Garner and W. G. Wolfer, “The effect of solute additions on void nucleation,” J. Nucl. Mater. 102, 143–150 (1981).
H. Watanabe, A. Aoki, H. Murakami, T. Muroga, and N. Yoshida, “Effects of phosphorus on defect behavior, solute segregation and void swelling in electron irradiated Fe–Cr–Ni alloys,” J. Nucl. Mater. 155–157, 815–822.
T. Muroga, F. A. Garner, and J. M. McCarthy, “The Effect of phosphorous on microstructures of Fe–15Cr–25Ni alloys irradiated with fast neutrons,” J. Nucl. Mater. 168, 109–120 (1989).
H. Watanabe, T. Muroga, and N. Yoshida, “The temperature dependent role of phosphorus and titanium in microstructural evolution of Fe–Cr–Ni alloys irradiated in FFTF,” J. Nucl. Mater. 228, 261–274 (1996).
S. E. Danilov, V. L. Arbuzov, and V. A. Kazantsev, “Radiation-induced separation of solid solution in Fe‒Ni invar,” J. Nucl. Mater. 414, 200–204 (2011).
N. N. Alekseenko, A. D. Amaev, I. V. Gorynin, and V. A. Nikolaev, Radiation Damage of Nuclear Power Plant Pressure Vessel Steels (Am. Nucl. Soc., La Grange Park, IL, 1997; Energoatomizdat, Moscow, 1981).
H. M. Rietveld, “A Profile Refinement Method for Nuclear and Magnetic Structures,” J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2, 65–71 (1969).
J. Rodriges-Carvajal, “Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction,” Physica A 192, 55–69 (1993).
V. L. Arbuzov and S. E. Danilov, “Effect of titanium doping on accumulation and annealing of radiation defects in austenitic steel 16Cr15Ni3Mo(0-1)Ti at low temperature (80 K) electron irradiation,” IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering 110, 012033 (2016).
V. L. Arbuzov, K. V. Shalnov, S. E. Danilov, A. E. Davletshin, N. L. Pecherkina, and V. V. Sagaradze, “Observation of segregation deposits in iron–nickel–titanium alloy using scanning tunneling microscopy,” Tech. Phys. Lett. 25, 134–135 (1999).
E. Gudremon, Special Steels, Ed. by A.S. Zaimovskii, M.L. Bernshtein, and V.S. Mes’kin, Edition 2 (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1966) [in Russian].
E. H. Lee and L. K. Mansur, “A Mechanism of Swelling Suppression in Phosphorous-Modified Fe–Ni–Cr Alloys,” J. Nucl. Mater. 141–143, 695–702 (1986).
N. Akasaka, K. Hattori, S. Onose, and S. Ukai, “Effect of Temperature Change on Void Swelling in P, Ti-Modified 316 Stainless Steel,” J. Nucl. Mater. 271–272, 370–375 (1999).
K. Fukuya, S. Nakahigashi, S. Ozaki, and S. Shima, “Effect of Phosphorus, Silicon and Sulphur on Microstructural Evolution in Austenitic Stainless Steels During Electron Irradiation,” J. Nucl. Mater. 179–181, 1057–1060 (1999).
V. L. Arbuzov, S. E. Danilov, V. A. Kazantsev, and V. V. Sagaradze, “Radiation-Induced Strengthening of Al- and Ti-Modified Fe-Ni Alloys During Electron Irradiation,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 115, 1017–1022 (2011).
A. P. Druzhkov, V. L. Arbuzov, D. A. Perminov, and K. V. Shal’nov, “Effect of Precipitate Particles of Intermetallic Compounds on the Accumulation of Radiation Defects in Austenitic Fe–Ni–Ti Alloys,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 96, 509–513 (2003).
V. L. Arbuzov, B. N. Goshchitskii, S. E. Danilov, A. V. Kar’kin, and D. A. Perminov, “Effect of Neutron and Electron Irradiation on Radiation-Induced Separation of Solid Solutions in the Fe–Ni and Fe–Ni–P Alloys,” Phys. Met. Metallogr. 106, 266–275 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.L. Arbuzov, I.F. Berger, V.I. Bobrovskii, V.I. Voronin, S.E. Danilov, V.A. Kazantsev, N.V. Kataev, V.V. Sagaradze, 2018, published in Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 2018, Vol. 119, No. 4, pp. 387–392.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arbuzov, V.L., Berger, I.F., Bobrovskii, V.I. et al. Thermal Effects That Arise upon Different Heat Treatments in Austenitic Steels Alloyed with Titanium and Phosphorus. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 119, 368–373 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X18040026
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X18040026