Abstract
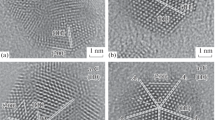
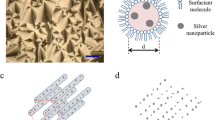
Transmission electron microscopy, selected-area electron diffraction, and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) have been used to determine the morphological and phase features of silver nanoparticles synthesized by a physical method of electric explosion of silver wires. In the nanoparticles obtained, the presence of a hexagonal phase was detected besides the cubic phase and the size dependence of the phase composition of the nanoparticles has been revealed; all particles smaller than 25 nm only had a hexagonal structure, particles with sizes of 25–30 nm contained both the hexagonal and cubic phases, and particles larger than 30 nm had only a cubic structure. Based on an analysis of the conditions of synthesis of silver nanoparticles, an attempt to explain the mechanism of the stabilization of the hexagonal phase depending on the particle size was undertaken.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. I. Bublik, “Electron-diffraction study of silver thin films”, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 95, 521–524 (1954).
M. I. Novgorodova, A. I. Gorshkov, A. V. Mokhov, and P. P. Perstnev, “New structural modifications of silver”, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 243, 1289–1291 (1978).
D. Novgorodova, A. Gorshkov, and A. Mokhov, “Native silver and its new structural modifications”, Int. Geology Review. 23, 485–494 (1981).
P. Taneja, R. Banerjee, P. Ayyub, and G. K. Dey, “Observation of a hexagonal (4H) phase in nanocrystalline silver”, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 64, 033405 (2001)
I. S. Martynov, V. V. Krasilnikov, I. N. Perepelkin, V. A. Ruzhitskii, and Ya. E. Gendy, “Radiation transformation of hexagonal structure of silver in cubic one at irradiation by helium ions”, Vopr. At. Nauki Tekhn., no. 1, 49–56 (2006).
Yu. A. Krutyakov, A. A. Kudrinskiy, A. Yu. Olenin, and G. V. Lisichkin, “Synthesis and properties of silver nanoparticles: Advances and prospects”, Russ. Chem. Rev. 77, 233–257 (2008).
Yu. A. Kotov, “Electric explosion of wires as a method for preparation of nanopowders”, J. Nanopartic. Res. 5, 539–550 (2003)
Phase Diagrams of Binary Metallic Systems. A Handbook, Ed. by N. P. Lyakishev (Mashinostroenie, Moscow, 1996).
E. L. Nagaev, “Small metal particles”, Phys.-Usp. 35, 747–782 (1992).
Z. A. Tian, R. S. Liu, H. R. Liu, C. X. Zheng, Z. Y. Hou, and P. Peng, “Molecular dynamics simulation for cooling rate dependence of solidification microstructures of silver”, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 354, 3705–3712 (2008)
R. McPherson, “Formation of metastable phases in flame and plasma-prepared alumina”, J. Mater. Sci. 8, 851–858 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.M. Murzakaev, 2017, published in Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 2017, Vol. 118, No. 5, pp. 486–492.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murzakaev, A.M. Size dependence of the phase composition of silver nanoparticles formed by the electric explosion of a wire. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 118, 459–465 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X1705009X
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X1705009X