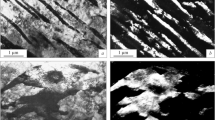
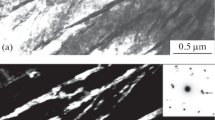
Abstract
Mechanical properties of chromium-nickel-molybdenum steels with the carbon contents of 0.1 to 0.4% after slow continuous cooling in the bainitic range have been determined, and the structure has been investigated. It has been shown that, at a carbon content of about 0.10–0.15% and upon additional alloying with silicon and aluminum after such a heat treatment, in steels, the structure of carbide-free bainite is formed and a substantial enhancement in the impact toughness is observed compared to bainite containing carbide precipitates. The enhancement in the level of toughness is related to the presence in carbide-free bainite of an appreciable amount of retained austenite enriched with carbon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia, Bainite in Steels, 2nd Ed. (The Institute of Materials, London, 2001).
Z. Bojarski and T. Bold, “Structure and properties of carbide-free bainite,” Acta Metall. 22, 1223–1234 (1974).
F. G. Caballero and H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia, “Very strong bainite,” Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater.Sci. 8, 251–257 (2004).
A. Yu. Kaletin, Candidate Sci. (Eng.) Dissertation, Sverdlovsk, 1985.
C. Garcia-Mateo, F. G. Caballero, and H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia, “Mechanical properties of low-temperature bainite,” Mater. Sci. Forum 500, 495–502 (2005).
Yu. M. Kaletin, A. G. Ryzhkov, and A. Yu. Kaletin, “Effect of silicon and aluminum on the properties of structural chromium-nickel steels with a bainitic structure,” Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Chern. Metall., No. 6, 96–99 (1989).
M. N. Georgiev, A. Yu. Kaletin, Yu. N. Simonov, and V. M. Schastlivtsev, “Influence of the stability of retained austenite on the cracking resistance of structural steel,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., No. 1, 113–121 (1990).
B. P. V. Sandvik, “The bainite reaction in Fe-Si-C alloys: The primary stage,” Metall. Trans. A 13, 777–787 (1982).
J. C. Hell, M. Dehmas, S. Allain, and J. M. Prado, “Microstructure-properties relationships in carbide-free bainitic steels,” ISIJ Int. 51, 1724–1732 (2011).
A. Yu. Kaletin, V. M. Schastlivtsev, N. T. Kareva, and M. A. Smirnov, “Embrittlement of structural steel with a bainitic structure upon tempering,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved. 56, 366–371 (1983).
V. M. Schastlivtsev, Yu. V. Kaletina, M. A. Smirnov, and A. Yu. Kaletin, “Structure and properties of structural steels after thermomechanical treatment in the bainitic range of temperatures,” Deform. Razrush. Mater., No. 4, 1–9 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.Yu. Kaletin, A.G. Ryzhkov, Yu.V. Kaletina, 2015, published in Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 2015, Vol. 116, No. 1, pp. 114–120.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaletin, A.Y., Ryzhkov, A.G. & Kaletina, Y.V. Enhancement of impact toughness of structural steels upon formation of carbide-free bainite. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 116, 109–114 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X15010068
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X15010068