Abstract
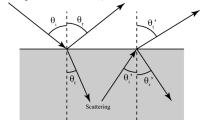
The surface structure is an important factor that affects the polarization properties, which is useful information for object detection. This paper studies the influences of surface structures on polarization properties by the examination of man-made objects and nature objects using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and white light confocal microscope. In the work, polarization imaging was discussed, and a system was set up to obtain polarization images. Comparing the degree of linear polarization (DOLP) images with traditional spectral images, there are obvious differences between man-made objects and nature objects on the micro- and nano-scales. The experiment results indicate that surface structures have significant influences on polarization properties, and such characteristic can be used to identify the differences between objects or materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Miyazaki and K. Ikeuchi, IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis Machine Intelligence 29 (11), 2018 (2007).
Y. Zhao, P. Gong, and Q. Pan, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing 46 (10), 3337 (2008).
D. Fixler and Z. Zalevsky, Proc. SPIE 8221 (2012).
T. I. Karu, G. S. Kalendo, V. S. Letokhov, and V. V. Lobko, Nuovo Cimento D 1 (6), 828 (1982).
S. Tominaga and A. Kimachi, Opt. Eng. 47 (12), 123201 (2008).
Yu. P. Sinichkin, A. V. Spivak, and D. A. Yakovlev, Opt. Spectrosc. 107 (6), 873 (2009).
J. Lin and Y. Lo, Opt. Laser Eng. 47 (9), 948 (2009).
V. C. Vanderbilt, L. Grant, and C. Daughtry, Proc. IEEE 73 (6), 1012 (1985).
B. Zhou, J. Xuan, H. Zhao, G. J. Chepko, M. T. Freedman, and K. Y. Zou, Proc. IEEE Life Sci. Syst. Appl. Workshop, 217–220 (2007).
A. M. El-Saba, M. S. Alam, and A. Surpanani, Proc. SPIE 6240 (2006).
C. Devaraj, M. Gartley, and J. Schott, Proc. SPIE 8873, 88730C (2013).
I. Leonard, A. Alfalou, and C. Brosseau, Opt. Express 21 (24), 29283 (2013).
M. W. Hyde, J. D. Schmidt, and M. J. Havrilla, Opt. Express 17 (24), 22138 (2009).
R. G. Priest and S. R. Meier, Opt. Eng. 41 (5), 988 (2002).
M. G. Gartley, Rochester Institute of Technology (2007).
Z. Chao-Yang, C. Hai-Feng, C. Zhao-Hui, and Z. Wen-Wei, Proc. SPIE 7383, 73830N-1 (2009).
J. E. Solomon, Appl. Opt. 20 (9), 1537 (1981).
P. Clemenceau, S. Breugnot, and L. Collot, Proc. SPIE 3380 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Yu, M. & Wang, Z. Influences of surface structures on polarization properties. Opt. Spectrosc. 119, 728–731 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0030400X15100173
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0030400X15100173