Abstract
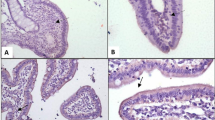
Microbiota of the fish gut contains many beneficial bacteria that can be used as probiotics in aquaculture. In this study, several in vitro assays along with an in vivo safety assessment were performed to decipher the probiotic potential of an autochthonous bacterial strain Pseudomonas mosselii COFCAU_PMP5, isolated from the gut of Labeo rohita. The isolate was antagonistic to 14 pathogenic bacteria, survived a wide range of pH (2–9) and tolerated high bile concentration (up to 10%). The strain COFCAU_PMP5 showed significant in vitro mucosal adherence, auto-aggregation capacity, and cell surface hydrophobicity. As a measure of safety prerequisites, the strain was found, besides being non-pathogenic to L. rohita, to be non-hemolytic and sensitive to several antibiotics. Moreover, the strain could produce extracellular enzymes and showed significant free radical scavenging activity, indicating additional beneficial properties. The probiotic potential of the strain Pseudomonas entomophila COFCAU_PEP4, isolated from an autochthonous source, was established by in vitro and safety assessments.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Agaras, B.C., Scandiani, M., Luque, A., FernaÂndez, L., Farina, F., Carmona, M., Gally, M., Romero, A., Wall, L., and Valverde, C., Quantification of the potential biocontrol and direct plant growth promotion abilities based on multiple biological traits distinguish different groups of Pseudomonas spp. isolates, Biol. Control, 2015, vol. 90, pp. 173–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2015.07.003
Balakrishna, A. and Kumar, N.A., Preliminary studies on siderophore production and probiotic effect of bacteria associated with the guppy, Poecilia reticulata (Peters, 1859), Asian Fish Sci., 2012, vol. 25, pp. 193–205. https://doi.org/10.33997/j.afs.2012.25.2.008
Balcázar, J.L., Vendrell, D., De Blas, I., Ruiz-Zarzuela, I., Muzquiz, J.L., and Girones, O., Characterization of probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from intestinal microbiota of fish, Aquaculture, 2008, vol. 278, pp. 188–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.03.014
Banerjee, G. and Ray, A.K., Bacterial symbiosis in the fish gut and its role in health and metabolism, Symbiosis, 2018, vol. 72, pp. 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-016-0441-8
Banerjee, S. and Ghosh, K., Enumeration of gut associated extracellular enzyme-producing yeasts in some freshwater fishes, J. App. Ichthyol., 2014, vol. 30, pp. 986–993. https://doi.org/10.1111/jai.12457
Brand-Williams, W. Cuvelier, M.E., and Berset, C., Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity, Lebenson. Wiss. Technol., 1995, vol. 28, pp. 25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0023-6438(95)80008-5
De Smet, I., Hoorde, L.V., Woestyne, M.V., Christia-ens, H., and Verstraete, W., Significance of bile salt hydrolytic activities of lactobacilli, J. Appl. Bacteriol., 1995, vol. 79, pp. 292–301. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1995.tb03140.x
Del Re, B., Sgorbati, B., Miglioli, M., and Palenzona, D., Adhesion, autoaggregation and hydrophobicity of 13 strains of Bifidobacterium longum, Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 31, pp. 438–442. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.00845.x
Emam, A.M. and Dunlap, C.A., Genomic and phenotypic characterization of Bacillus velezensis AMB-y1; a potential probiotic to control pathogens in aquaculture. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2020, vol. 113, pp. 2041–2052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01476-5
European Food Safety Authority, Technical specifications for the analysis and reporting of data on antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in the European Union Summary Report, EFSA J., 2012, vol. 10, p. 2587.
FAO/WHO, Report on Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Evaluation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria, October 1−4, Cordoba, Argentina, 2001.
Gram, L.O.N.E., Inhibitory effect against pathogenic and spoilage bacteria of Pseudomonas strains isolated from spoiled and fresh fish, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1993, vol. 59, pp. 2197–2203. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.59.7.2197-2203.1993
Han, Q., Kong, B., Chen, Q., Sun, F., and Zhang, H., In vitro comparison of probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Harbin dry sausages and selected probiotics, J. Funct. Foods, 2017, vol. 32, pp. 391–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.03.020
James, G., Das, B.C., Jose, S. and Kumar, V.J.R., Bacillus as an aquaculture friendly microbe, Aquacult. Int., 2021, vol. 29, pp. 323–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00630-0
Joseph, S.W., Colwell, R.R., and Kaper, J.B., Vibrio parahaemolyticus and related hallophilic vibrios, Crit. Rev. Microbiol., 1982, vol. 10, pp. 73–124. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408418209113506
Kavitha, M., Raja, M., and Perumal, P., Evaluation of probiotic potential of Bacillus spp. isolated from the digestive tract of freshwater fish Labeo calbasu (Hamilton, 1822), Aquacult. Rep., 2018, vol. 11, pp. 59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2018.07.001
Khan, M.I.R., Choudhury, T.G., Kamilya, D., Monsang, S.J., and Parhi, J., Characterization of Bacillus spp. isolated from intestine of Labeo rohita—towards identifying novel probiotics for aquaculture, Aquacult. Res., 2021, vol. 52, pp. 822–830. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14937
Lee, S., Lee, J., Jin, Y.I., Jeong, J.C., Chang, Y.H., Lee,Y., Jeong, Y., and Kim, M., Probiotic characteristics of Bacillus strains isolated from Korean traditional soy sauce, LWT− Food Sci. Technol., 2017, vol. 79, pp. 518–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.08.040
Lemos, M.L., Toranzo, A.E., and Barja, J.L., Antibiotic activity of epiphytic bacteria isolated from intertidal seaweeds, Microb. Ecol., 1985, vol. 11, pp. 149–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02010487
Midhun, S.J., Neethu, S., Vysakh, A., Sunil, M.A., Radhakrishnan, E.K., and Jyothis, M., Antibacterial activity of autochthonous bacteria isolated from Anabas testudineus (Bloch, 1792) and it’s in vitro probiotic characterization, Microb. Pathog., 2017, vol. 113, pp. 312–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.10.058
Nakamura, A., Takahashi, K.G., and Mori, K., Vibriostatic bacteria isolated from rearing seawater of oyster brood stock: potentiality as biocontrol agents for vibriosis in oyster larvae, Fish Pathol., 1999, vol. 34, pp. 139–144. https://doi.org/10.3147/jsfp.34.139
Nikoskelainen, S., Salminen, S., Bylund, G., and Ouwehand, A.C., Characterization of the properties of human-and dairy-derived probiotics for prevention of infectious diseases in fish, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 67, pp. 2430–2435. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.6.2430-2435.2001
Novik, G., Savich, V., and Kiseleva, E., An insight into beneficial Pseudomonas bacteria, Microbiology in Agriculture and Human Health, 2015, vol. 1, pp. 73–105. https://doi.org/10.5772/60502
Padmavathi, T., Bhargavi, R., Priyanka, P.R., Nira-njan, N.R., and Pavitra, P.V., Screening of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria and production of amylase and its partial purification, J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol., 2018, vol. 16, pp. 357–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2018.03.005
Ringo, E., Strom, E., and Tabachek, J.A., Intestinal micro flora of salmonids: a review, Aquacult. Res., 1995, vol. 26, pp. 773–789. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.1995.tb00870.x
Ruch, R.J., Cheng, S.J., and Klaunig, J.E., Prevention of cytotoxicity and inhibition of intracellular communication by antioxidant catechins isolated from Chinese green tea, Carcinogenesis, 1989, vol. 10, pp. 1003–1008. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/10.6.1003
Spelhaug, S.R. and Harlander, S., Inhibition of food-borne bacterial pathogens by bacteriocins from Lactococcus lactis, Pediococcus pentosaceus, J. Food. Prot., 1989, vol. 52, pp. 856—862. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-52.12.856
Stephens, W.Z., Burns, A.R., Stagaman, K., Wong, S., Rawls, J.F., Guillemin, K., and Bohannan, B.J., The composition of the zebrafish intestinal microbial community varies across development, The ISME J., 2016, vol. 10, pp. 644–654. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.140
Tuomola, E., Crittenden, R., Playne, M., Isolauri, E., and Salminen, S., Quality assurance criteria for probiotic bacteria, Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 2001, vol. 73, pp. 393s–398s. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/73.2.393s
Van Doan, H., Hoseinifar, S.H., Ringø, E., Ángeles Esteban, M., Dadar, M., Dawood, M.A., and Faggio, C., Host-associated probiotics: a key factor in sustainable aquaculture, Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquacult., 2020, vol. 28, pp. 16–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2019.1643288
Verschuere, L., Rombaut, G., Sorgeloos, P., and Verstraete, W., Probiotic bacteria as biological control agents in aquaculture, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2000, vol. 64, pp. 655–671. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.64.4.655-671.2000
Vine, N.G., Leukes, W.D., and Kaiser, H., Probiotics in marine larviculture, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2006, vol. 30, pp. 404–427. https://doi.org/10.13031/aim.202100522
Wanka, K.M., Damerau, T., Costas, B., Krueger, A., Schulz, C., and Wuertz, S., Isolation and characterization of native probiotics for fish farming, BMC Microbiol., 2018, vol. 18, pp. 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-018-1260-2
Weisburg, W.G., Barns, S.M., Pelletier, D.A., and Lane, D.J., 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study, J. Bacteriol., 1991, vol. 173, pp. 697−703. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.173.2.697-703.1991
Xing, J., Wang, G., Zhang, Q., Liu, X., Gu, Z., Zhang, H., Chen, Y.Q., and Chen, W., Determining antioxidant activities of lactobacilli cell-free supernatants by cellular antioxidant assay: a comparison with traditional methods, PLoS One, 2015, vol.10, p. e0119058. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119058
Yamashita, M.M., Ferrarezi, J.V., Do Vale Pereira, G., Júnior, G.B., Da Silva, B.C., Pereira, S.A., Martins, M.L., and Mouriño, J.L.P., Autochthonous vs allochthonous probiotic strains to Rhamdia quelen, Microb. Pathog., 2020, vol. 139, p. 103897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103897
Funding
The study was financially supported by a research grant from Department of Biotechnology, New Delhi, India [BT/PR25008/NER/95/953/2017].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
These authors contributed equally.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
All experimental procedures involving fish were performed in accordance with the guidelines suggested by the ethical committee of the institute.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devi, A.A., Khan, M.I., Choudhury, T.G. et al. In Vitro Assessment of Probiotic Potential of an Autochthonous Bacterial Isolate, Pseudomonas mosselii COFCAU_PMP5. Microbiology 91, 207–214 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261722020047
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261722020047