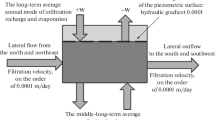
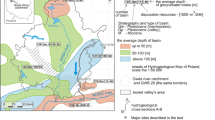
Abstract
An additional very important and, possibly, unique feature of the Caspian sedimentary basin—the retention of sedimentary water in the Pleistocene aquifer system of the North Caspian and Near-Caspian regions—is discussed. It is shown that increase of the groundwater mineralization was caused by its metamorphization during diagenesis. Under conditions of the integrity of sedimentary water during geological history, hydromicaceous clays serve as the main source providing a significant increase of mineralization in the interstitial water of marine sediments and groundwater. The comprehensive examination of sedimentary processes in the Neopleistocene Caspian Basin and groundwater formation in the Pleistocene aquifer system of the northern Near-Caspian region made it possible to determine (and, frequently, to quantify) a system of specific natural factors and conditions (at the quantitative level in many cases). They can be used for the assessment of retention or displacement of sedimentary water from the sedimentary basin with a high degree of confidence. This is of great importance for the study of present-day sedimentary basins and geological reconstructions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkowitz, B., Dror, I., and Yaron, B., Contaminant Geochemistry. Interaction and Transport in the Subsurface Environment, Berlin: Heidelberg, 2008.
Brezgunov, V.S. and Ferronskii, V.I., Macro- and Microelements in the Interstitial Water of Deep-Water Areas of the Southern and Middle Caspian Sea, Water. Resour., 2010, vol. 37, no. 6, pp. 825–834.
Brusilovskii, S.A. and Lapteva, L.A., Chlorium content in silt solutions: Geochemical indicator of the submarine discharge of groundwaters in the Caspian Sea, in Kompleksnye issledovaniya Kaspiiskogo morya (Complex Studies of the Caspian Sea), Moscow: MGU, 1976, issue 5, pp. 168–188.
Brusilovskii, S.A. and Lapteva, L.A., Osnovnye zakonomernosti raspredeleniya khlorid-ionov v ilovykh vodakh Kaspiiskogo morya. Khimiko-okeanologicheskie issledovaniya (Main Regularities in the Distribution of Chloride Ions in Mud Waters of the Caspian Sea: Chemical Oceanographic Studies), Moscow: Nauka, 1977, pp. 20–35.
Butuzova, G.Yu., Gidrotermal’noe rudoobrazovanie v riftovoi zone Krasnogo morya (Hydrothermal Ore Formation in the Rift Zone of the Red Sea), Moscow: GEOS, 1998.
Chekhovskikh, M.M. and Pit’eva, K.E., Study of regularities in variation of the chemical composition of solutions squeezed out from monomineral clays at different pressures, in Svyazannaya voda v dispersnykh sistemakh (Bound Water in Dispersed Systems), Moscow: MGU, 1972, issue 2, pp. 180–194.
Dagan, G., Flow and Transport in Porous Formation, New York: Springer, 1989.
Demin, V.V., Role of humic acids in the irreversible sorption and biochemistry of heavy metals in soils, Izv. Timiryaz. Sels.-Khoz. Akad., 1994, no. 2, pp. 19–86.
Dyunin, V.I., Gidrogeodinamika glubokikh gorizontov neftegazonosnykh basseinov (Hydrodynamics of Deep Horizons of Petroliferous Basins), Moscow: Nauchn. Mir, 2000.
Dzhamalov, R.G., Zektser, I.S., and Meskheteli, A.V., Podzemnyi stok v morya i mirovoi okean (Underground Discharge into the Sea and World Ocean), Moscow: Nauka, 1977.
Engel’gard, V., Porovoe prostranstvo osadochnykh porod (Pore Space in Sedimentary Rocks), Moscow: Nedra, 1964.
Fedorov, F.M. and Lefevre, G., Sorption mechanisms and models. Their influence on transport calculation, in Uranium in the Environment. Mining Impact and Consequences, Merkel, B.J. and Hasche-Berger, A, Eds., 2006.
Fedorov, P.V., Pleistotsen Ponto-Kaspiya (Pleistocene of the Ponto-Caspian Region), Moscow: Nauka, 1978.
Gilham, R.W., Sudicky, E.A., Cherry, J.A., and Frind, E.O., An advection diffusion concept for solute transport in heterogeneous unconsolidated geologic deposits, Water Resour. Res., 1984, vol. 20, pp. 369–378.
Golovanova, O.V., Formation of Pleistocene groundwaters in the modern Caspian region in connection with exploitation of the Astrakhan gas complex, Extended Abstract of PhD (Geol.–Miner.) Dissertation, Moscow: Moscow State Univ., 2004.
Golovanova, O.V., Specifics of the differentiation of sedimentary material during the accumulation of Pleistocene–Holocene sediments in the northern Caspian and near-Caspian regions, in Fundamental’nye problemy kvartera: itogi izucheniya i osnovnye napravleniya dal’neishikh issledovanii (Fundamental Problems of the Quaternary: Results of the Study and Main Lines of Further Research), Moscow: GEOS, 2007, pp. 79–82.
Golovanova O.V. Groundwaters of the Pleistocene Aquifer System in the North Caspian and Near-Caspian Regions: Communication 1. Character of Water Exchange and Factors of Sedimentary Water Integrity, Lithol. Miner. Resour., 2015, no. 3, pp. 231–247.
Grichuk, D.V., Experimental study of the metamorphization of mud waters in marine sediments during sulfate reduction, in Zakonomernosti formirovaniya khimicheskogo sostava prirodnykh vod (Formation Regularities of the Chemical Composition of Natural Waters), Moscow: MGU, 1981, pp. 83–98.
Gurskii, Yu.N., Geokhimiya litogidrosfery vnutrennikh morei. Soobshchenie 1. Metody izucheniya i protsessy formirovaniya khimicheskogo sostava ilovykh vod v otlozheniyakh Chernogo, Azovskogo, Kaspiiskogo, Belogo, Baltiiskogo morei (Geochemistry of the Lithohydrosphere of Internal Seas: Communication 1. Methods of Study and Formation Processes of the Chemical Composition of Mud Waters in Sediments of the Black, Azov, Caspian, White, and Baltic Seas), Moscow: GEOS, 2003.
Gurskii, Yu.N., Geokhimiya litogidrosfery vnutrennikh morei. Soobshchenie 2. Ilovye vody Krasnogo i Sredizemnogo morei. Zony estuariev. Zakonomernosti formirovaniya i klassifikatsiya vod litogidrosfery (Geochemistry of the Lithohydrosphere of Internal Seas: Communication 2. Mud Waters in the Red and Mediterranean Seas. Estuarine Zones. Formation Regularities and Classification of Waters in the Lithohydrosphere), Moscow: GEOS, 2007.
Horne, R.A., Marine Chemistry, New York: Wiley-Intersciences, 1969. Translated under the title Morskaya khimiya, Moscow: Mir, 1972.
Ivanov, V.A., Prusov, A.V., Ryabtsev, Yu.N., and Shapiro, N.B., Fizicheskie mekhanizmy smesheniya morskikh vod s vodami submarinoi razgruzki (Physical Mechanisms of the Mixing of Seawater with the Submarine Discharge Water), Sevastopol: MGI NAN Ukrainy, 2009.
Kholodov, V.N., Postsedimentatsionnye preobrazovaniya v elizionnykh basseinakh (Postsedimentary Transformations in Elisional Basins), Moscow: Nauka, 1983.
Kholodov, V.N., Sedimentary Basins: Regularities in Their Formation and Classification Principles. Communication 2. Sedimentary Rock Basins, Lithol. Miner. Resour., 2010, no. 3, pp. 238–274.
Khrustalev, Yu.P., Zakonomernosti Sovremennogo osadkonakopleniya v Severnom Kaspii (Regularities of Recent Sedimentation in the northern Caspian region), Rostov-on-Don: Rostov. Univ., 1978.
Kozlov, V.G. and Levshenko, T.V., Microelements in pore waters of Upper Cenozoic sediments in the southern Caspian region, Byull. Mosk. O-va Isp. Prirody. Otd. Geol, 1987, vol. 62, no. 4, pp. 130–134.
Krainov, S.R., Ryzhenko, B.N., and Shvets, V.M., Geokhimiya podzemnykh vod (Geochemistry of Groundwaters), Moscow: Nauka, 2004.
Lebedev, L.I., Maev, E.G., Bordovskii, O.K., and Kulakova, L.S., Osadki Kaspiiskogo morya (Sediments of the Caspian Sea), Moscow: Nauka, 1973.
Lekhov, A.V., Fiziko-khimicheskaya gidrodinamika (Physicochemical Hydrodynamics), Moscow: MGU, 2010.
Leonova, G.A., Geochemical role of plankton of continental water systems in the concentration and redistribution of microelements, Extended Abstract of DSc (Geol.–Miner.) Dissertation, Novosibirsk: Inst. Geol. Miner., 2007.
Leont’ev, O.K., Maev, E.G., and Rychagov, G.I., Geomorfologiya beregov i dna Kaspiiskogo morya (Geomorphology of Coasts and Bottom of the Caspian Sea), Moscow: MGU, 1977.
Levshenko, T.V., Role of organic matter in metamorphization of the chemical composition of pore waters in recent sedimentation basins, Geol. Nefti Gaza, 1981, no. 4, pp. 38–42.
Lisitsin, A.P., Lavinnaya sedimentatsiya i pereryvy v osadkonakoplenii v moryakh i okeanakh (Avalanche Sedimentation and Hiatuses in Seas and Oceans), Moscow: Nauka, 1988.
Lubchenko, I.Yu., Kholodov, V.N., Khrustalev, Yu.P., et al., Kaspiiskoe more: Problemy sedimentogeneza (The Caspian Sea: Problems of Sedimentogenesis), Moscow: Nauka, 1989.
Luhrmann, L., Noseck, U., and Tix, C., Model on contaminant transport in porous media in the presence of colloids applied to actinide migration in column experiments, Water Res. Res., 1998, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 421–426.
Lukner, L. and Shestakov, V.M., Modelirovanie geofil’tratsii (Modeling of Geofiltration), Moscow: Nedra, 1976.
Meier, H., Zimmerhackl, E., and Zietler, G., Modeling of colloid-associated radionuclide transport in porous groundwater aquifer at the Gorleben site, Germany, Geochem. J., 2003, vol. 37, pp. 325–350.
Moiseev, Yu.G., Perov, A.A., Sorokin, N.A., et al., Some experimental results related to the municipal service hydrological-optical complex, in Morskoe i ekologicheskoe priborostroenie (Marine and Ecological Instrumentation), Sevastopol: MGI NAN Ukrainy, 1995, p. 95.
Pit’eva, K.E., Gidrogeokhimiya (Hydrogeochemistry), Moscow: MGU, 1988.
Pit’eva, K.E. and Golovanova, O.V., Prediction of the influence of large industrial complexes on the quality of underground and river waters during the Caspian Sea level rise, in Materialy mezhdunarodnogo simpoziuma “Podzemnyi stok v pribrezhnoi zone” (Materials of the Int. Symp. “Underground Discharge in the Coastal Zone”), Moscow, 1996.
Pit’eva, K.E., Golovanova, O.V., Melamed, I.G., and Chekhovskikh, M.M., Hydrogeochemical conditions of the Pleistocene aquifer system in the lower Volga region, Vestn. Mosk. Geol. Univ., Ser. Geol., 2005a, no. 2, pp. 54–59.
Pit’eva, K.E., Golovanova, O.V., Melamed, I.G., and Chekhovskikh, M.M., Formation of the chemical composition of Pleistocene groundwaters in the lower Volga region, Vestn. Mosk. Geol. Univ., Ser. Geol., 2005b, no. 3, pp. 62–68.
Pushkina, Z.V., Groundwaters in Recent, Quaternary, and Pliocene sediments of the southern Caspian region, Litol. Polezn. Iskop., 1963, no. 3, pp. 3–18.
Reaction and Movement of Organic Chemical in Soils, Soil Sci. Am. Spec. Publ., 1989, no. 22.
Rumynin, V.G., Geomigratsionnye modeli v gidrogeologii (Geomigration Models in Hydrogeology), St. Petersburg: Nauka, 1158.
Rumynin, V.G. and Sindalovskii, L.N., Study of the influence of injection of sea waters upon the quality of groundwaters in the Andarax delta region (Almeria province, Spain), Geoekologiya, 2006, no. 6, pp. 496–508.
Sayles, F.L., The composition and diagenesis of interstitial solution, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1979, vol. 43, pp. 527–545.
Sergeeva, E.S., Frolov, V.T., Shvanov, V.N., et al., Sistematika i klassifikatsiya osadochnykh porod i ikh analogov (Systematics and Classification of Sedimentary Rocks and Their Analogs), St. Petersburg: Nedra, 1998.
Sharer, M., Park, J.-H., Voice, Th.C., and Boyd, S.A., Time dependence of chlorobenzene sorption/desorption by soils, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 2003, vol. 67, pp. 1740–1745.
Shchetinin, Yu.T., Kondrat’ev, S.I., Dolotov, V.V., et al., Submarine sources of fresh water on the southern coast of Crimea, in Issledovaniya shel’fovoi zony Azovo-Chernomorskogo basseina (Study of the Shelf Zone of the Azov–Black Sea Basin), Sevastopol: MGI, 1995, pp. 116–124.
Shestakov, V.M., Gidrogeodinamika (Hydrogeodynamics), Moscow: MGU, 1995.
Shishkina, O.V., Geokhimiya morskikh i okeanicheskikh ilovykh vod (Geochemistry of Marine and Oceanic Mud Waters), Moscow: Nauka, 1972.
Steefel, C.I., Caroll, S., Zhao, P., and Roberts, S., Cesium migration in Handford sediment: a multisite cation exchange model based on laboratory transport experiments, J. Contam. Hydrol., 2003, vol. 67, pp. 219–246.
Strakhov, N.M., Diagenesis of sediments and its significance for sedimentary ore formation, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Geol., 1953, no. 5, pp. 12–49.
Strakhov, N.M., Sedimentation in the Caspian Sea, in Obrazovanie osadkov v sovremennykh vodoemakh (Formation of Sediments in Recent Basins), Moscow: AN SSSR, 1954, pp. 137–179.
Strakhov, N.M., Cognition of diagenesis, in Voprosy mineralogii osadochnykh obrazovanii (Problems in the Mineralogy of Sedimentary Formations), Lvov: L’vov. Univ., 1956, issue 3/4, pp. 137–179.
Strakhov, N.M., Osadkonakoplenie v sovremennykh vodoemakh: Izbr. tr. (Sedimentation in Recent Basins: Collected Works), Knipper, A.L, Ed., Moscow: Nauka, 1993.
Tageeva, N.V. and Tikhomirova, M.M., Geokhimiya porovykh vod pri diageneze morskikh osadkov (Hydrochemistry of Interstitial Waters in the Diagenesis of Marine Sediments), Moscow: AN SSSR, 1962.
Tinsley, I.J., Chemical Concepts in Pollutant Behavior,, New Jersey:. Willey and Sons,, 2004.
Tompson, A.F.B., Numerical simulation of chemical migration in physically and chemically heterogeneous porous media, Water Resour. Res., 1993, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 3709–3726.
Tompson, A.F.B. and Jackson, K.J., Reactive transport in heterogeneous systems: An overview, Rev. Mineral. Geochem., 1996, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 269–310.
Van de Weerd, H., Leijnse, A., and van Riemsdijk, W.H., Transport of reactive colloids and contaminants in groundwater: effect of nonlinear kinetic interactions, J. Contam. Hydrol., 1998, vol. 32, pp. 313–331.
Varshal, G.M., Velyukhanova, T.K., Chkhetiya, D.N, et al., Sorption on Humic Acids as a Basis for the Mechanism of Primary Accumulation of Gold and Platinum Group Elements in Black Shales, Lithol. Miner. Resour., 2000, no. 6, pp. 538–545.
Vershinin, A.V. and Rozanov, A.G., Khimicheskii obmen na granitse voda-dno v okeanakh i moryakh (Chemical Exchange at the Water–Bottom Interface in Oceans and Seas), Moscow: GEOS, 2002.
Walter, A.L., Frind, E.O., Blowes, D.W., et al., Modeling of multicomponent reactive transport in groundwater. 1. Model development and evaluation, Water Resour. Res., 1994a, vol. 30, no. 11, pp. 3137–3148.
Walter, A.L., Frind, E.O., Blowes, D.W., et al., Modeling of multicomponent reactive transport in groundwater. 2. Metal mobility in aquifers impacted by acidic mine tailings discharge, Water Resour. Res., 1994b, vol. 30, no. 11, pp. 3149–3158.
Wittman, R.S., Buck, E.C., and Hanson, B.D., Data analysis of plutonium sorption on colloids in a minimal kinetics model, Techn. Rep. Pacific Northwest National Lab., 2005, PNNL-15285.
Yanina, T.A., Paleogeography of the Ponto-Caspian basins in the Pleistocene based on the results of malacofaunistic analysis, Extended Abstract of DSc (Geogr.) Dissertation, Moscow: Moscow State Univ., 2009.
Zatenatskaya, N.P., Porovye vody osadochnykh porod (Interstitial Waters in Sedimentary Rocks), Moscow: Nauka, 1974.
Zektser, I.S., Dzhamalov, R.G., and Meskheteli, A.V., Podzemnyi vodoobmen sushi i morya (Underground Water Exchange between Land and Sea), Leningrad: Gidrometeoizdat, 1984.
Zverev, V.P., Podzemnye vody zemnoi kory i geologicheskie protsessy (Groundwaters in the Earth’s Crust and Geological Processes), Moscow: Nauchn. Mir, 2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.V. Golovanova, 2015, published in Litologiya i Poleznye Iskopaemye, 2015, No. 4, pp. 362–382.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golovanova, O.V. Groundwater of the Pleistocene aquifer system in the North Caspian and Near-Caspian regions: Communication 2. Significance of sedimentary water integrity for the development of sedimentary basins and paleogeological reconstructions. Lithol Miner Resour 50, 322–340 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0024490215040021
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0024490215040021