Abstract
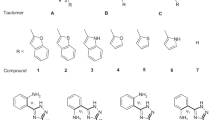
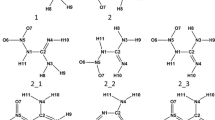
Some drugs have two tautomeric structures in the liquid state and the tautomeric equilibrium is formed between these structures. The reaction rate and equilibrium constant of this reaction varies in different solvents. Thus, the determination of the appropriate solvent to separate tautomers is important. In this research, we used the DFT level of B3LYP and the 6-311++G** basis set to obtain the proper solvent for Nexium, Skelaxin, Aldara and Efavirenz drugs. All calculations were made above the melting point of the mentioned drugs, because these drugs are solid at room temperature. The solvent effect is included in the calculation utilizing the polarizable continuum model PCM. The transition state of the tautomeric reaction is determined using the quadratic synchronous transit (QST2) method. The geometry, energy, and dipole moment of transition states are analyzed in different solvent. The root mean square deviation (RMSD) analysis is performed to determine the degree of a structure deviation of tautomer 1 and tautomer 2 from the transition state in different solvents. It is found that the RMSD value for tatumer1 is higher than that for tautomer 2 in all studied drugs. The proper solvent for the separation of tautomers is determined from the analysis of thermodynamics and kinetics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. R. Katritzky, C. D. Hall, B. E.-D. M. El-Gendy, and B. Draghici. J. Comput.–Aided Mol. Des., 2010, 24,475.
Y. C. Martin. J. Comput.–Aided Mol. Des., 2009, 23,693.
K. McKeage, S. K. Blick, J. D. Croxtall, K. A. Lyseng-Williamson KA, and G. M. Keating. Drugs, 2008, 68, 1571.
P. Miner, P. O. Katz, Y. Chen, and M. Sostek. Am. J. Gastroenterol., 2003, 98, 2616.
P. O. Katz, J. M. Scheiman, and A. N. Barkun. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther., 2006, 23,9.
L. J. Scott, C. J. Dunn, G. Mallarkey, and M. Sharpe. Drugs, 2002, 62, 1503.
J. L. Poklis, J. D. Ropero-Miller, D. Garside, and R. E. Winecker. J. Forensic Sci., 2003, 48,432.
R. B. Bruce, L. Turnbull. J. Newman, and J. Pitts. J. Med. Chem., 1966, 99,286.
R. W. Dent and D. K. Ervin. Curr. Ther. Res., 1975, 18,433.
K. Fathie. Curt. Ther. Res., 1964, 11,677.
A. J. Wagstaff and C. M. Perry. Drugs, 2007, 67, 2187.
S. Salasche and S. Shumack. Clin. Exp. Dermatol., 2003, 28,1.
S. Tyring, M. Conant, M. Marini, W. Van Der Meijden, and K. Washenik. Int. J. Dermatol., 2002, 41,810.
L. Edwards. J Am Acad Dermatol., 43, 2000,12.
R. Gaida, I. Truter, and C. Grobler. S. Afr. J. Psychiatr., 2015, 21,94.
G. I. T. Cavalcante, S. M. M. Vasconcelos, D. S. Macêdo, F. C. F. Sousa, D. J. Woods, and M. M. F. Fonteles. Int. J. Neurosci., 2010, 120,739.
A. D. Becke. J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 5648.
R. G. Parr and W. Yang. Density-functional theory of atoms, molecules. New York: Oxford University Press, 1989.
S. Miertus, E. Scrocco, and J. Tomasi. Chem. Phys., 1981, 55,117.
M. J. Frisch, et al. Gaussian 03, Revision C.02, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT, 2004.
H. Eyring. J. Chem. Phys., 1935, 3,107.
D. S. Wishart, C. Knox, A. C. Guo, D. Cheng, S. Shrivastava, D. Tzur, B. Gautam, and M. Hassanali. Nucleic Acids Res., 2008, 36(Suppl 1), D901–D906.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © 2018 M. Sargolzaei, M. Afshar, H. Nikoofard.
The text was submitted by the authors in English. Zhurnal Strukturnoi Khimii, Vol. 59, No. 2, pp. 309–317, March–April, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sargolzaei, M., Afshar, M. & Nikoofard, H. Solvent Effect on The Equilibrium and Rate Constant of the Tautomeric Reaction in Nexium, Skelaxin, Aldara and Efavirenz Drugs: A Dft Study. J Struct Chem 59, 297–305 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476618020063
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476618020063