Abstract
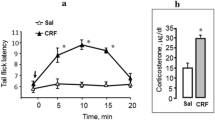
We investigated the effects of the synthetic gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonistic analogue surfagon on the spinal and supraspinal mechnisms of pain formation in intact and gonadectomized male Wistar rats. Alternating current painful stimulation was applied to the tail base, and pain thresholds, as well as emotional/affective responses, were recorded (in mA). Surfagon, when administred intraperitoneally 12 min before the experiments at doses 0.004–150 µg/kg, exerted an algic effect and enhanced pain-induced emotional/affective behavior in the electrocutaneous tail stimulation test. In gonadectomized rats, pain thresholds were elevated on day 12 after castration. Surfagon administration to castrated rats retained the direction of the effects observed in intact animals, indicating their steroid-independent nature. The obtained data demonstrate the presence of both spinal and supraspinal mechanisms of surfagon algic activity in rats during electrocutaneous pain stimulation.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Masalova OO, Kazakova SB, Savateeva-Lyubimova TN, Sivak KV, Sapronov NS, Shabanov PD (2019) Effect of Surfagon on Open Field and Elevated Plus Maze Behavior of Gonadectomized and Non-Gonadectomized Male Rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 168(1): 52–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-019-04644-4
Severianova LA, Bobyntsev II (1995) Neurotropic effects of an luliberin analog administered intraventricularly to rats with varying sensitivity to ethanol. Bull Exp Biol Med 119(2): 120–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02445854
Bobyntsev II, Sever'yanova LA, Kryukov AA (2006) Effect of gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogue on thermal nociception in mice. Bull Exp Biol Med 141(2): 193–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-006-0125-0
Della Corte L, Barra F, Mercorio A, Evangelisti G, Rapisarda AMC, Ferrero S, Bifulco G, Giampaolino P (2020) Tolerability considerations for gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues for endometriosis. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 16(9):759–768. https://doi.org/10.1080/17425255.2020.1789591
Rossi L, Pagani O (2018) The role of gonadotropin-releasing-hormone analogues in the treatment of breast cancer. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 27(4):466–475. https://doi.org/10.1089/jwh.2017.6355
Ortmann O, Weiss JM, Diedrich K (2002) Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and GnRH agonists: mechanisms of action. Reprod Biomed Online 5(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1472-6483(11)60210-1
Bereket A (2017) A critical appraisal of the effect of gonadotropin-releasing hormon analog treatment on adult height of girls with central precocious puberty. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 9(2):33–48. https://doi.org/10.4274/jcrpe.2017.S004
Konda Y, Gantz I, DelValle J, Shimoto Y, Miwa H, Yamada T (1994) Interaction of dual intracellular signaling pathways activated by the melanocortin-3 receptor. J Biol Chem 269(18): 13162–13166.
Buggy JJ (1998) Binding of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone to its G-protein-coupled receptor on B-lymphocytes activates the Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem J 331(Pt 1): 211–226. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3310211
Voronina TA, Guzevatykh LS (2012) Methodological recommendations for the study of analgesic activity of drugs. 197–218. In: Mironov AN (ed) Guidelines for conducting preclinical studies of medicines, Vol 1. Grif and K, M. 197–218. (In Russ).
Severyanova LA, Lazarenko VA, Plotnikov DV, Dolgintsev ME, Kriukov AA (2019) L-Lysine as the molecule influencing selective brain activity in pain-induced behavior of rats. Int J Mol Sci 20(8): 1899. doi:10.3390/ijms20081899https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081899
Zieglgänsberger W (2019) Substance P and pain chronicity. Cell Tissue Res 375(1):227–241. https://doi.org/10.1152/10.1007/s00441-018-2922-y
Treede RD, Margel W (1995) Modern concepts of pain and hyperalgesia beyond the polymodal C-nociceptor. Physiology 10(5): 216–228. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiologyonline.1995.10.5.216
Harris JA, Faust B, Gondin AB, Dämgen MA, Suomivuori CM, Veldhuis NA, Cheng Y, Dror RO, Thal DM, Manglik A (2021) Selective G protein signaling driven by substance P-neurokinin receptor dynamics. Nat Chem Biol 18:109-115. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-021-00890-8
Koroleva SV, Nikolaeva AA, Ashmarin IP (2012) Types of bioinformatic programs in the continuum of regulatory peptides and non-peptide mediators. Traits of interaction of dopamine and serotonin systems. Neurochem J 6(2): 132–143.
Severyanova LA, Bobyntsev II, Plotnikov DV, Lyashev YD (2001) Nitric oxide synthesis in the brain mediates neuro-peptide effects on pain sensitivity and pain-induced aggression. Analgesia 5(3/4): 223–237.
Jennes L, Conn PM (1994) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone and its receptors in rat brain. Front Neuroendocrinol 15(1): 51–77. https://doi.org/10.1006/frne.1994.1003
Jennes L, Eyigor O, Janovick JA, Conn PM (1997) Brain gonadotropin releasing hormone receptors: localization and regulation. Recent Prog Horm Res 52: 475–491.
Leblanc P, Crumeyrolle M, Latouche J, Jordan D, Fillion G, L’Heritier A, Kordon C, Dussaillant M, Rostène W, Haour F (1988) Characterization and distribution of receptors for gonadotropin-releasing hormone in the rat hippocampus. Neuroendocrinology 48(5): 482–488. https://doi.org/10.1159/000125053
Nayebi AR, Ahmadiani A (1999) Involvement of the spinal serotonergic system in analgesia produced by castration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 64(3):467–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0091-3057(99)00113-6
Funding
This work was supported by the Kursk State Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and experimental design (I.I.B.); data collection and processing, statistical analysis (A.O.V., M.E.D., A.A.K.); writing a manuscript (I.I.B., M.E.D.).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest associated with the publication of this article.
Additional information
Translated by A. Polyanovsky
Russian Text © The Author(s), 2022, published in Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I.M. Sechenova, 2022, Vol. 108, No. 1, pp. 121–128https://doi.org/10.31857/S0869813922010034.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bobyntsev, I.I., Vorvul, A.O., Dolgintsev, M.E. et al. Effects of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Analogue Surfagon on Pain Sensitivity in Rats. J Evol Biochem Phys 58, 167–173 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S002209302201015X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S002209302201015X