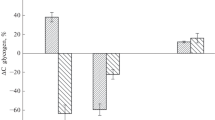
Abstract
We studied the glycogen content in erythrocytes of two Black Sea cartilaginous fishes (Raja clavata, Dasyatis pastinaca) and four teleost species (Trachurus mediterraneus ponticus, Spicara flexuosa, Diplodus annularis, Scorpaena porcus). Glycogen accumulation in erythrocytes of teleost fish was about twice as high as in the ray fishes. Due to the unique ability of thornback ray R. clavata erythrocytes to well preserve their cell integrity in vitro in the cold (4°C), the dynamics of glycogen expenditure in erythrocytes was tracked over 11 days of storage until cell disintegration. Erythrocytes spent glycogen economically: during the entire storage period, only 52% of glycogen were spent. In the black scorpionfish S. porcus, erythrocytes were far less tolerant to being stored in the cold. The stability period of S. porcus erythrocytes suspended in physiological saline did not exceed two days. During this period, no significant changes in the glycogen concentration were observed.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Phillips, M.C.L., Moyes, C.D., and Tufts, B.L., The effects of cell ageing on metabolism in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) red blood cells, J. Exp. Biol., 2000, vol. 203, pp. 1039–1045. PMID: 10683163
Lipunova, E.A. and Skorkina, M.Ju., Fiziologiya krovi (Physiology of Blood), Belgorod, 2007.
Polakof, S., Panserat, S., Soengas, J.L., and Moon, T.W., Glucose metabolism in fish: a review, J. Comp. Physiol. B, 2012, vol. 182, pp. 1015–1045. doi: 10.1007/s00360-012-0658-7
Driedzic, W.R., Clow, K.A., and Short, C.E., Glucose uptake and metabolism by red blood cells from fish with different extracellular glucose levels, J. Exp. Biol., 2013, vol. 216, pp. 437–446. doi: 10.1242/jeb.079178
Walsh, P.J., Wood, C.M., Thomas, S., and Perry, S.F., Characterization of red blood cell metabolism in rainbow trout, J. Exp. Biol., 1990, vol. 154, pp. 475–489. PMID: 2126029
Morozova, A.L., A study of the content of carbohydrates and phosphorous compounds in tissues of the horse mackerel and black scorpionfish at different functional states, Candidate Sci. Diss., Leningrad, 1971.
Morozova, A.L., Astakhova, L.P., and Silkina, E.N., Carbohydrate metabolism in fish swimming, Elementy fiziologii i biokhimii obshchego i aktivnogo obmena u ryb (Elements of Physiology and Biochemistry of Basal and Active Metabolism in Fish), Kiev, 1978, pp. 122–143.
Ferguson, R.A., Tufts, B.L., and Boutilier, R.G., Energy metabolism in trout red cells: consequences of adrenergic stimulation in vivo and in vitro, J. Exp. Biol., 1989, vol. 143, pp. 133–147. PMID: 2732658
Silkin, Yu.A., Korotkov, S.M., and Silkina, E.N., A study of the bioenergetic characteristics of the red blood cells of Black Sea fish: the common stingray (Dasyatis pastinaca L.) and black scorpionfish (Scorpaena porcus L.), Biophysics, 2017, vol. 62(3), pp. 434–439. doi: 10.1134/S0006350917030204
Soengas, J.L. and Moon, T.W., Uptake and metabolism of glucose, alanine and lactate by red blood cells of the American eel Anguilla rastrata, J. Exp. Biol., 1995, vol. 198, pp. 877–888. PMID: 9318662
Nikinmaa, M. and Tiinonen, K., Substrate transport and utilization in fish erythrocytes, Acta Physiol. Scand., 1994, vol. 152, pp. 183–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1994. tb09798.x
Mouses, S.W., Bashan, N., and Gutman, A., Glycogen metabolism in the normal red blood cells, Blood, 1972, vol. 40(6), pp. 836–843. PMID: 5083874
Mouses, S.W., Bashan, N., Gutman, A., and Ockerman, P.A., Glycogen metabolism in glycogen-rich erythrocytes, Blood, 1974, vol. 44(2), pp. 275–284. PMID: 4212036
Sidbury, J.B.Jr., Cornblath, M., Fisher, J., and House, E., Glycogen in erythrocytes of patients with glycogen storage disease, Pediatrics, 1961, vol. 27, pp. 103–111.
Miwa, I. and Suzuki, S., An improved quantitative assay of glycogen in erythrocytes, Ann. Clin. Biochem., 2002, vol. 39, pp. 612–613. doi: 10.1177/000456320203900613
Dridzic, W.R., Clow, K.A., and Short, C.E., Extracellular glucose can fuel metabolism in red blood cells from high glycemic Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) but not low glycemic short-horned sculpin (Myoxocephalus scorpius), J. Exp. Biol., 2014, vol. 217, pp. 3797–3804. doi: 10.1242/jeb.110221
Lambert, F.N., Treberg, J.R., Anderson, W.G., Brandt, C., and Evans, A.N., The physiological stress response of the Atlantic stingray (Hypanus sabinus) to aerial exposure, Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Pt. A, Molecular and Integrative Physiology, 2018, vol. 219–220, pp. 38–43. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.02.009
Cain, D.K., Harms, C.A., and Segars, A., Plasma biochemistry reference values of wild-caught southern stingrays (Dasyatis americana), J. Zoo. Wildl. Med., 2004, vol. 35(4), pp. 471–476. doi: 10.1638/03-107
Bouyoucos, I.A, Talwar, B.S., Brooks, E.J., Brownscombe, J.W., Cooke, S.J., Suski, S., and Mandelman, J.W., Exercise intensity while hooked is associated with physiological status of longline-captured sharks, Conserv. Physiol., 2018, vol. 20.6(1), pp. 1–13. doi: 10.1093/conphys/coy074
Polakof, S., Mommsen, T.P., and Soengas, J.L., Glucosensing and glucose homeostasis from fish to mammals, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 2011, vol. 160B, pp. 123–149. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2011.07.006
Pesquero, J., Roig, T., Bermudez, J., and Sanchez, J., Energy metabolism by trout red blood cells: substrate utilization, J. Exp. Biol., 1994, vol. 193, pp. 183–190. PMID: 9317599
Plisetskaya, E.M., Hormonal regulation of carbohydrate metabolism in lower vertebrates (cyclostomes and fish), Doctorate Sci. Diss., Leningrad, 1972.
Soldatov, A.A., Parfenova, I.A., and Novitskaya, V.N., Monovalent cation and ATP content in erythrocytes of marine fish exposed to experimental hypoxia, Ukr. Biokhim. Zh., 2010, vol. 82, pp. 36–41.
Soldatov, A.A., Golovina, I.V., Kolesnikova, E.E., Sysoeva, I.V., Sysoev, A.A., Kukhareva, T.A., and Kladchenko, E.S., Activity of energy metabolism enzymes and ATP content in the brain and gills of the Black Sea scorpionfish Scorpaena porcus Linnaeus under short-term hypoxia, J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol., 2020, vol. 56(3), pp. 213–223. doi: 10.1134/S0022093020030059
Serebrenikova, T.P. and Nesterov, V.P., Activation of glycogen phosphorylases by glycogen phosphorylase kinases: dependence on ATP concentration and species specificity of the enzymes, J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol., 2002, vol. 38(2), pp. 242–244.
Shmelev, V.K. and Serebrenikova, T.P., Effect of temperature on the kinetics of the phosphorylase reaction and phosphorylase activation induced by phosphorylase kinase in the skate Dasyatis pastinaca, Ukr. Biokhim. Zh., 1987, vol. 59(1), pp. 34–38.
Soldatov, A.A., Peculiarities of organization and functioning of the red blood system in fish, J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol., 2005, vol. 41(3), pp. 272–281. doi: 10.1007/s10893-005-0060-0
Funding
This work was implemented within the State assigniment no. АААА-А19-119012490045-0 “A study of fundamental physical, physiologo-biochemical, reproductive, population and behavioral characteristics of marine hydrobionts”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yu.A. Silkin and E.N. Silkina were responsible for designing the experiments, data collection, writing and editing the manuscript. M.Yu. Silkin provided technical support during experiments, participated in data processing and discussing, as well as in graphic representation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
Experimental protocols met all applicable international, national and institutional principles of handling and using experimental animals for scientific purposes.
This study did not involve human subjects as research objects.
СONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by A. Polyanovsky
The original online version of this article was revised: the issue date is not January 2020, but January 2021
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silkin, Y.A., Silkina, E.N. & Silkin, M.Y. Glycogen as an Energy Storage Substrate in Fish Nucleated Erythrocytes. J Evol Biochem Phys 57, 66–74 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093021010063
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093021010063