Abstract
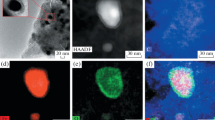
Iron nanopowders ranging in particle size from 20 to 100 nm have been synthesized by reducing a 1-mm-thick iron(III) hydroxide layer in flowing hydrogen at 400°C and then passivated for 6–60 min in flowing argon containing 3% air. Our results demonstrate that the passivated iron nanopowders do not oxidize in air for six months. The iron nanoparticles have been characterized by X-ray diffraction (crystallite size evaluation), Auger electron spectroscopy, and polymolecular adsorption. The passivated iron nanoparticles have been shown to consist of a metallic core and oxide shell 2–4 nm in thickness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vodyanitskii, Yu.N., Ladonin, D.V., and Savichev, A.T., Zagryaznenie pochv tyazhelymi metallami (Soil Contamination with Heavy Metals), Moscow: Pochvennyi Inst. im. V.V. Dokuchaeva RASKhN, 2012.
Ponder, S.M., Darab, J.G., and Mallouk, T.E., Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) aqueous solutions using supported, nanoscale zero-valent iron, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2000, vol. 34, pp. 2564–2569.
Hassan, M.H.A., Small things and big changes in the developing world, Science, 2005, vol. 309, no. 5731, pp. 65–66.
Nurmi, J.T., Tratnyek, P.G., Sarathy, G., Baer, D.R., Amonette, J.E., Pecher, K., Wang, C., Linehan, J.C., Matson, M.W., Penn, R.L., and Driessen, M.D., Characterization and properties of metallic iron nanoparticles: spectroscopy, electrochemistry, and kinetics, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2005, vol. 39, pp. 1221–1230.
Varanasi, P., Fullana, A., and Sidhu, S., Remediation of PCB contaminated soils using iron nano-particles, Chemosphere, 2007, vol. 66, pp. 1031–1038.
Nutt, M.O., Hughes, J.B., and Wong, M.S., Designing Pd-on-Au bimetallic nanoparticle catalysts for trichloroethene hydrodechlorination, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2005, vol. 39, pp. 1346–1353.
Sun Yuan-Pang, Li Xiao-qin, Cao Jiasheng, Zhang Wei-xian, and Wang, H.P., Characterization of zerovalent iron nanoparticles, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2006, vol. 120, nos. 1–3, pp. 47–56.
Liu, Y.Q., Majetich, S.A., Tilton, R.D., Sholl, D.S., and Lowry, G.W., TCE dechlorination rates, pathways, and efficiency of nanoscale iron particles with different properties, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2005, vol. 39, pp. 1338–1345.
Cao, J., Elliott, D., and Zhang, W., Perchlorate reduction by nanoscale iron particles, J. Nanopart. Res., 2005, vol. 7, pp. 499–506.
Quinn, J., Geiger, C., Clausen, C., Brooks, K., Coon, C., and O’Hara, S., Field demonstration of DNAPL dehalogenation using emulsified zero-valent iron, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2005, vol. 39, pp. 1309–1318.
Kharisov, B.I., Rasika, D.H.V., Khrissova, O.V., et al., Iron-containing nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, and environmental applications, RSC Adv., 2012, vol. 2, no. 25, pp. 9325–9358.
Li, L., Fan, M., Brown, R.C., and Van Leeuwen, L., Synthesis, properties, and environmental applications of nanoscale iron based materials: a review, Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2006, vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 405–431.
Noubactep, C., Meinrath, G., Dietrich, P., Sauter, M., and Merkel, B.J., Testing the suitability of zerovalent iron materials for reactive walls, Environ. Chem., 2005, vol. 2, pp. 71–76.
Zelenskii, V.A., Alymov, M.I., Ankudinov, A.B., and Tregubova, I.V., Low-temperature hydrogen reduction of copper powders, Perspekt. Mater., 2009, vol. 6, pp. 83–87.
Yuvakkumar, R., Elango, V., Rajendran, V., and Kannan, N., Preparation and characterization of zerovalent iron nanoparticles, Digest J. Nanomater. Biostruct., 2011, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 1771–1776.
Alymov, M.I. and Leontieva, O.N., Synthesis of nanoscale Ni and Fe powders and properties of their compacts, Nanostruct. Mater., 1995, vol. 6, pp. 393–395.
Rai, A., Park, K., Zhou, L., and Zachariah, M.R., Understanding the mechanism of aluminum nanoparticle oxidation, Combust. Theory Modelling, 2006, vol. 10, pp. 843–859.
Bouillard, J., Vignes, A., Dufaud, O., Perrin, L., and Thomas, D., Ignition and explosion risks of nanopowders, J. Hazardous Mater., 2010, vol. 181, pp. 873–880.
Wang Yanxin, Liang Zhen, Yuan Ximing, and Xu Yongsheng, Preparation of cellular iron using wastes and its application in dyeing wastewater treatment, J. Porous Mater., 2005, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 225–232.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.I. Alymov, N.M. Rubtsov, B.S. Seplyarskii, V.A. Zelenskii, A.B. Ankudinov, 2017, published in Neorganicheskie Materialy, 2017, Vol. 53, No. 9, pp. 929–933.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alymov, M.I., Rubtsov, N.M., Seplyarskii, B.S. et al. Preparation and characterization of iron nanoparticles protected by an oxide film. Inorg Mater 53, 911–915 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168517090011
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168517090011