Abstract
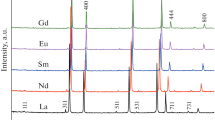
In this paper, we analyze the relationship between the microstructure of new polycrystalline electron–proton conductors, Ln6–x Zr x MoO12 + δ (Ln = La, Nd, Sm; x = 0.2, 0.6), and the reduction and hydration processes in these materials in humid atmospheres (air and argon). The La5.8Zr0.2MoO12.1 solid solution with a rhombohedral structure possesses not only the highest electrical conductivity among the materials studied here but also high stability in various dry and humid, oxidizing (air) and reducing atmospheres. La5.8Zr0.2MoO12.1 ceramic grains have a twin microstructure, and the conductivity of this material along the grain boundaries, consisting of ordered domains, differs little from its bulk conductivity. It seems likely that we observe a “domain wall” effect, typical of La0.95Sr0.05Ga0.9Mg0.1O3–δ (LSGM) oxygen ion conductors [1]. In studies of Ln6–x Zr x MoO12 + δ (Ln = Nd, Sm; x = 0.2, 0.6) ceramics in humid atmospheres, we detected a grain-boundary contribution, which limited the total conductivity, like in perovskite BaZr0.8Y0.2O3–δ. We believe that such conditions lead to a reduction process in these materials and that Mo6+ is reduced before Nd3+ and Sm3+. The process first occurs on grain boundaries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurumada, M., Iguchi, E., and Savytskii, D.I., Correlation between high ionic conductivity and twin structure of La0.95Sr0.05Ga0.9Mg0.1O3–δ, J. Appl. Phys., 2006, vol. 100, paper 014 107.
Kreuer, K.-D., Proton-conducting oxides, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 2003, vol. 33, pp. 333–359.
Guan, J., Dorris, S.E., Balachandran, U., and Uu, M., The effects of dopants and A: B site nonstoichiometry on properties of perovskite-type proton conductors, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1998, vol. 145, pp. 1780–1786.
Kreuer, K.-D., Aspects of the formation and mobility of protonic charge carriers and the stability of perovskite-type oxides, Solid State Ionics, 1999, vol. 125, pp. 285–302.
Kreuer, K.-D., Adams, S., Munch, W., Fuchs, A., Klock, U., and Maier, J., Proton conducting alkaline earth zirconates and titanates for high drain electrochemical applications, Solid State Ionics, 2001, vol. 145, pp. 295–306.
Babilo, P., Udo, T., and Haile, S.M., Processing of yttrium doped barium zirconate for high proton conductivity, J. Mater. Res., 2007, vol. 22, pp. 1322–1330.
Ryu, K.H. and Haile, S.M., Chemical stability and proton conductivity of doped BaCeO3–BaZrO3 solid solutions, Solid State Ionics, 1999, vol. 125, pp. 355–367.
Sun, Z.Q., Fabbri, E., Bi, I., and Traversa, E., Lowering grain boundary resistance of BaZr0.8Y0.2O3–δ with LiNO3 sintering aid improves proton conductivity for fuel cell operation, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011, vol. 13, pp. 7692–7700.
Sun, W.P., Liu, M.F., and Liu, W., Chemically stable yttrium and tin co-doped barium zirconate electrolyte for next generation high performance proton-conducting solid oxide fuel cells, Adv. Energy Mater., 2013, vol. 3, pp. 1041–1050.
Fabbri, E., Bi, I., Tanaka, H., Pergolesi, D., and Traversa, E., Chemically stable Pr and Y co-doped barium zirconate electrolytes with high proton conductivity for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2011, vol. 21, pp. 158–166.
Omata, T. and Otsuka-Yao-Matsuo, S., Electrical properties of proton-conducting Ca2+ doped La2Zr2O7 with a pyrochlore-type structure, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2001, vol. 148, pp. E252–E261.
Labrincha, J.A., Frade, J.R., and Marques, F.M.B., Proton conduction in La2Zr2O7-based pyrochlore materials, Solid State Ionics, 1997, vol. 99, pp. 33–40.
Besikiotis, V., Knee, C.S., Ahmed, I., Haugsrud, R., and Norby, T., Crystal structure, hydration and ionic conductivity of the inherently oxygen-deficient La2Ce2O7, Solid State Ionics, 2012, vol. 228, pp. 1–7.
Shimura, T., Fujimoto, S., and Iwahara, H., Proton conduction in non-perovskite-type oxides at elevated temperatures, Solid State Ionics, 2001, vol. 143, pp. 117–123.
Magrasó, A. and Haugsrud, R., Effect of the La/W ratio and doping on the structure, defect structure, stability and functional properties of proton-conducting lanthanum tungstate La2 8–x W4 + x O54 + δ. A review, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, vol. 2, pp. 12 630–12 641.
Partin, G.S., Korona, D.V., Neiman, A.Ya., and Belova, K.G., Conductivity and hydration of fluoritetype La6–x WO12–1.5x phases (x = 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1), Rus. J. Electrochem., 2015, vol. 51, pp. 381–390.
Savvin, S.N., Shlyakhtina, A.V., Kolbanev, I.V., Knotko, A.V., Belov, D.A., Shcherbakova, L.G., and Nuñez, P., Zr-doped samarium molybdates–potential mixed electron–proton conductors, Solid State Ionics, 2014, vol. 262, pp. 713–718.
Savvin, S.N., Shlyakhtina, A.V., Borunova, A.B., Shcherbakova, L.G., Ruiz-Morales, J.C., and Núñez, P., Crystal structure and proton conductivity of some Zr-doped rare-earth molybdates, Solid State Ionics, 2015, vol. 271, pp. 91–97.
Cros, B. and Czeskleba-Kerner, H., Synthèse et caractérisation des composés stables à 1400°C dans le système La2O3–MoO2–MoO3, Rev. Chim. Miner., 1978, vol. 15, pp. 521–528.
Fournier, J-P., Fournier, J., and Kohlmuller, R., Etude des systemes La2O3–MoO3, Y2O3–MoO3, et des phases Ln6MoO12, Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr., 1970, pp. 4277–4283.
Amsif, M., Magrasó, A., Marrero-Lopez, D., Ruiz-Morales, J.C., Canales-Vazquez, J., and Núñez, P., Mo-substituted lanthanum tungstate La28 − y W4 + y O54 + δ: a competitive mixed electron–proton conductor for gas separation membrane applications, Chem. Mater., 2012, vol. 24, pp. 3868–3877.
Politova, E.D., Torba, J.N., Fortalnova, E.A., Kaleva, G.M., Safronenk, M.G., and Venkovskii, N.U., Phase transitions and transport properties of the bismuth vanadate-based (Bi,La)4(V,Zr)2O11–z ceramics, Acta Phys. Pol. A, 2010, vol. 117, pp. 15–18.
Politova, E.D., Fortalnova, E.A., Kaleva, G.M., Mosunov, A.V., Safronenko, M.G., Venkovskii, N.U., Shvartsman, V.V., and Kleemann, W., Ferroelectric phase transitions and electroconducting properties of ceramic BIMEVOX solid solutions (Me = La, Zr), Ferroelectrics, 2009, vol. 391, pp. 3–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Shlyakhtina, S.N. Savvin, A.V. Knotko, L.G. Shcherbakova, P. Núñez, 2016, published in Neorganicheskie Materialy, 2016, Vol. 52, No. 10, pp. 1126–1133.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shlyakhtina, A.V., Savvin, S.N., Knotko, A.V. et al. Electrical conductivity of Ln6–x Zr x MoO12 + δ (Ln = La, Nd, Sm; x = 0.2, 0.6) ceramics during thermal cycling. Inorg Mater 52, 1055–1062 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168516100149
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168516100149