Abstract
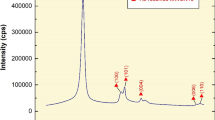
We have studied the stability of ultradispersed diamond and carbon nanotube suspensions in water and aqueous solutions of various salt electrolytes. The results demonstrate that, in the course of coagulation and sedimentation, the particles in suspension become separated into size fractions and form agglomerates several orders of magnitude greater in size than the parent particles, and that the dependence of the suspension concentration on storage time has a linear portion. The sedimentation process in the electrolyte solution-based suspensions proceeds until an almost zero concentration of fine particles is reached. We have determined the settling time of the particles in the suspensions, which determines their stability, and evaluated the porosity of particle conglomerates. The feasibility of suspension redispersion after sedimentation has been examined. Resonication of the suspensions has been shown to restore the particle concentration and size.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kubrak, P.B., Drozdovich, V.B., Zharskii, I.M., and Chaevskii, V.V., Electrochemical deposition and properties of nickel-based composite coatings containing carbon nanomaterials, Gal’vanotekh. Obrab. Poverkhn., 2012, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 43–49.
Burkat, G.K. and Dolmatov, V.Yu., Application of ultrafine-dispersed diamonds in electroplating, Phys. Solid State, 2004, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 703–710.
Krüger, H.G., Knote, A., Schindler, U., et al., Composite ceramic-metal coatings by means of combined electrophoretic deposition and galvanic methods, J. Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 839–844.
Litovka, Yu.V., D’yakov, I.A., Kuznetsova, O.A., et al., Nanomodified electrochemical chromium coatings, Gal’vanotekh. Obrab. Poverkhn., 2011, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 29–33.
Borodin, I.P., Shatov, Yu.S., Shiryaev, V.Yu., and Shcherenkova, I.S., Structure and properties of chromium coatings containing reinforcing diamond nanoparticles, Nanoindustriya, 2011, no. 2, pp. 40–43.
Kozenkov, O.D., Yur’ev, V.A., and Ptashkina, T.V., Aqueous suspensions of carbon nanomaterials for electrolytes, Vestn. Voronezhsk. Gos. Tekh. Univ., 2011, vol. 7, no. 10, pp. 21–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.D. Kozenkov, T.V. Ptashkina, A.T. Kosilov, 2015, published in Neorganicheskie Materialy, 2015, Vol. 51, No. 3, pp. 277–283.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozenkov, O.D., Ptashkina, T.V. & Kosilov, A.T. Stability of ultradispersed diamond and carbon nanotube suspensions in water and aqueous electrolytes for the fabrication of composite electrochemical coatings. Inorg Mater 51, 230–235 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168515030073
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168515030073