Abstract
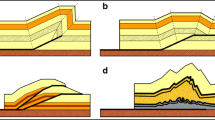
In the Zagros fold-thrust belt, the Fars region is affected by the basement left-lateral strike-slip faults such as the Nezamabad, Razak, and Hendurabi faults which these faults have affected on the folding system of this area and the effect of these faults activity is one of the factors in the folding diversity. Also, the Fars region anticlines are very important in the Zagros fold-thrust belt, due to their huge gas reserves in the Permian‒Triassic carbonate sediments. The Hendurabi faults have major effects on folding style base on changes of the folding geometry. For more analysis, when the effective stress and deformation value is different, the type of fold has been changed in different parts of fold. This case may be created by cropping out of the salt domes, activities of main active faults and other structural elements. The studied area is a special structural feature in the Zagros fold-thrust belt that is shown the effects of the strike slip faults on the folding geometry. In the study area, close fold type in all parts has shown the study anticline affected by the special may be from deformation of the Razak and Hendurabi sinistral strike-slip faults.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. A. Aghanabati, Geology of Iran (Geol. Surv. Iran, 2004).
M.A. Ala, “Salt diapirism in Southern Iran,” AAPG Bull. 58, 1758–1770 (1974).
M. Alavi, “Regional stratigraphy of the Zagros fold-thrust belt of Iran and its proforeland evolution,” Am. J. Sci. 304, 1–20 (2004).
M. Alavi, “Structures of the Zagros fold- and-thrust belt in Iran,” Am. J. Sci. 307, 1064–1095 (2007).
M. Alavi, “Tectonics of the Zagros orogenic belt of Iran: New data and interpretations,” Tectonophysics 2292, 211–238 (1994).
M. Arian, “Physiographic-tectonic zoning of Iran sedimentary basins,” Open J. Geol. 3 (3), 169‒177 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2013.33020
Z. Aram and M. Arian, “Active tectonics of the Gharasu River basin in Zagros, Iran, investigated by calculation of geomorphic indices and group decision using analytic hierarchy process (AHP) software,” Episodes 392, 39‒44 (2016).
M. Arian and Z. Aram, “Relative tectonic activity classification in the Kermanshah Area, Western Iran,” Solid Earth 5, 1277–1291 (2014).
M. Arian, “Clustering of diapiric provinces in the Central Iran basin,” Carbonates and Evaporites 27, 9–18 (2012).
M. Arian, “Seismotectonic-geologic hazards zoning of Iran,” Earth Sci. Res. J. 19, 7‒13 (2015).
M. Arian, H. Alizadeh, and H. Noroozpour, “Satellite geometry of faults and fractures and its relationship with porphyry deposits in northern parts of Dahaj‒Sardoiyeh belt, south of Iran,” Indian J. Sci. Technol. 42 (10), 1303‒1306 (2011).
M. Arian, N. Bagha, R. Khavari, and H. Noroozpour, “Seismic sources and Neotectonics of Tehran Area (North Iran),” Indian J. Sci. Technol. 5, 2379‒2383 (2012).
A. Bahroudi and H. Koyi, “Effect of ductile and frictional décollements on style of extension,” J. Struct. Geol. 25, 2003, 1401–1423 (2003).
F. Barzegar, “Basement fault mapping of Zagros fold belt (SW Iran) based on space-born remote sense data,” in Proceedings of the 10th Thematic Conference “Geologic Remote Sensing: Exploration, Environment and Engineering” (San Antonio, Texas, USA, 1994, Vol. 10), pp. 455‒466.
F. Barzegar, “Introducing Firuzabad and Nezamabad faults,” in Proceedings of the 10th Geosci. Conf. Geol. Surv. Iran (Tehran, February 15–16, 1992), pp. 125–129.
Z. R. Beydoun, M. W. Hughes Clark, and R. Stoneley, “Petroleum in the Zagros basin; a Late Tertiary foreland basin overprinted onto the outer edge of a vast hydrocarbon-rich Palaeozoic‒Mesozoic passive margin shelf,” Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Mem. 55, 309‒339 (1992).
C. M. Burberry, J. W. Cosgrove, and J.-G. Liu, “Spatial arrangement of fold types in the Zagros simply folded belt, Iran, indicated by landform morphology and drainage pattern characteristics,” J. Maps 4 (1), 417‒430 (2008).
S. P. Colman-Sadd, “Fold development in Zagros simply folded belt, Southwest Iran,” Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Bull. 62 (6), 984–1003 (1978).
N. Dehbashi Ghanavati, Geometry of Folding Style Analysis in the Coastal Fars and Effects of Nezamabad Fault in the Structures Region, PhD Thesis Struct. Geol. (Islamic Azad Univ., Sci. Res. Branch of Tehran. 2009).
J. Ehsani and M. Arian, “Quantitative analysis of relative tectonic activity in the Jarahi‒Hendijan basin area, Zagros, Iran,” Geosci. J. 19, 1‒15 (2015).
N. Falcon, “Southern Iran: Zagros Mountains,” in Mesozoic–Cenozoic Orogenic Belts, Ed. by A. Spencer (Spec. Publ.—Geol. Soc. London, 1974, Vol. 4), pp. 199–211.
M. Furst, “Tektonik und diapirismus der östlichen Zagros ketten,” Z. Dtsch. Geol. Ges. 127, 183‒225 (1976).
M. Furst, “Strike-slip faults and diapirism of the south- eastern Zagros Ranges,” in Proceedings of Symposium on Diapirism (Iran, 1990, Vol. 2), pp. 149‒182.
K. Hessami, “The significance of strike-slip faulting in the basement of the Zagros sold and thrust belt,” J. Petrol. Geol. 24 (1), 5–28 (2001).
W. R. Jamison, “Geometric analysis of fold development in over-thrust terranes,” J. Struct. Geol. 9, 207–219 (1987).
R. Khavari, M. Arian, and M. Ghorashi, “Neotectonics of the South Central Alborz drainage basin, in NW Tehran, North of Iran,” J. Appl. Sci. 9, 4115‒4126 (2009).
P. E. Kent, “The salt of the Persian Gulf region,” Trans. Leicester Lit. Phil. Soc. 64, 56–88 (1970).
J. Letouzey, “Detachment folding in the central Eastern Zagros fold-belt (Iran): Salt mobility, multiple detachments and late basement control,” J. Struct. Geol. 27, 1680–1696 (2005).
J. Letouzey and S. Sherkati, “Salt movement, tectonic events, and structural style in the Central Zagros fold-and-thrust belt (Iran),” in Proceedings of 24th Annual GCSSEP, Foundation, Interactions and Bob F. Perkins Research Conference on Salt Sediments Hydrocarbon Prospectivity, December 5–8, 2004 (Houston, Texas, USA, 2004), pp. 67‒76.
E. Mansouri, F. Feizi, A. Jafari Rad, and M. Arian, “A comparative analysis of index overlay and topsis (based on AHP weight) for Iron Skarn Mineral prospectivity mapping, a case study in Sarvian Area, Markazi Province, Iran,” Bull. Miner. Res. Explor. 155, 147‒160 (2017).
E. Mansouri, F. Feizi, A. Jafari Rad, and M. Arian, “Remote-sensing data processing with the multivariate regression analysis method for iron mineral resource potential mapping: A case study in the Sarvian area, Central Iran,” Solid Earth 9 (2), 373‒384 (2018).
N. McQuarrie, “Crustal scale geometry of the Zagros fold-and-thrust belt, Iran,” J. Struct. Geol. 26, 519–535 (2004).
H. McQuillan, “The role of basement tectonics in the control of sedimentary facies, structural patterns and salt plug emplacements in the Zagros fold belt of southwest Iran,” J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 5 (1), 453‒463 (1991).
S. Mitra, “A unified kinematic model for the evolution of detachment folds,” J. Struct. Geol. 25 (10), 1659‒1673 (2003)
S. Mitra, “Fold accommodation faults,” AAPG Bull. 86 (4), 671‒693 (2002).
P. Molnar and J. M. Stock, “Slowing of India’s convergence with Eurasia since 20 Ma and its implications for Tibetan mantle dynamics,” Tectonics 28, TC3001 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1029/2008TC002271
H. Motamedi, M. Sepehr, S. Sherkati, and M. Pourkermani, “Multi-phase Hormuz Salt Diapirism in the Southern Zagros, SW IRAN,” J. Petrol. Geol. 34, 29–44(2010).
H. Motiei, “Stratigraphy of Zagros,” in Treatise on the Geology of Iran, Ed.by A. Houshmandzadeh (Ministry of Mines and Metals, Geol. Surv. Iran, Tehran, 1993).
M. Nabilou, M. Arian, P. Afzal, A. Adib, and A. Kazemi, “Determination of relationship between basement faults and alteration zones in Bafq-Esfordi region, Central Iran,” IUGS Episodes 41 (3), 143‒159 (2018).
M. A. A. Nogole-Sadat and M. Almasian, Tectonic Map of Iran. Scale 1 : 1 000 000 (Geol. Surv. Iran, Tehran, 1993).
R. Nouri and M. Arian, “Multifractal modeling of the gold mineralization in the Takab area (NW Iran),” Arab. J. Geosci. 10 (5), 105‒110 (2017).
R. Nouri, M. R. Jafari, M. Arian, S. Feizi, and P. Afzal, “Correlation between Cu mineralization and major faults using multifractal modelling in the Tarom area (NW Iran),” Geol. Carpathica 64, 409‒416 (2013).
R. Nouri, M. R. Jafari, M. Arian, S. Feizi, and P. Afzal, “Prospection for copper mineralization with contribution of remote sensing, geochemical and mineralographical data in Abhar. Scale 1 : 100 000. Sheet NW Iran,” Arch. Mining Sci. 58, 1071–1084 (2013).
C. A. E. O’Brien, “Tectonic problems of the oil field belt of southwest Iran,” in Proceedings of 18th International Geological Congress (GB, 1950, Pt. 6), pp. 45–58.
R. A. Player, The Hormuz Salt Plugs of Southern Iran, MS, PhD. Thesis (Reading Univ., UK, 1969).
D. M. Ragan, Structural Geology, 3rd ed. (John Wiley, Cambridge Univ. Press, UK, 1985), pp. 210‒215.
J. D. Ramsay, Folding and Fracturing of Rocks (McGraw-Hill, NY, USA, 1967).
G. Razaghian, A. Beitollahi, M. Pourkermani, and M. Arian, “Determining seismotectonic provinces based on seismicity coefficients in Iran,” J. Geodynam. 119, 29‒46 (2018).
M. J. A. Rickard, “A classification diagram for fold orientation,” Geol. Mag. 108, 23‒26 (1971).
C. M. Setchell, J. W. Cosgrove, and J. -G. Liu, The Distribution of Fold Types in the Zagros Simply Folded Belt, Iran. Map Scale 1 : 100 000 (Imperial College London, UK, 2007).
A. Setudehnia and J. T. Perry, Geological map of SE‒SE Fars. Scale 1 : 250 000 (Natl. Iranian Oil Comp., Tehran, 1965).
M. Shamshiri, The Exploration Project of Fars Region (Natl. Iranian Oil Comp., Tehran, 2001, Geol. Rep. No. 53).
S. Sherkati and J. Letouzey, “Variation of structural style and basin evolution in the central Zagros (Izeh zone and Dezful embayment), Iran,” Mar. Petrol. Geol. 21, 535‒554 (2004).
S. Sherkati. M. Molinaro, D. Frizon de Lamotte, and J. Lettouzey, “Detachment folding in the central-eastern Zagros fold belt (Iran): Salt mobility, multiple detachments and late basement control,” J. Struct. Geol. 27, 1680‒1696 (2005).
J. Suppe, “Geometry and kinematics of fault-bend folding,” Am. J. Sci. 283 (7), 684‒721 (1985).
C. J. Talbot and M. Alavi, “The past of a future syntaxis across the Zagros,” in Salt Tectonics, Ed. by G. I. Alsop, D. J. Blundell, and I. Davison (Spec. Publ.—Geol. Soc. London, 1996, Vol. 100), pp. 89‒109.
V. Taesiri, M. Pourkermani, A. Sorbi, M. Almasian, and M. Arian, “Morphotectonics of Alborz Province (Iran): A case study using GIS method,” Geotectonics 54 (5), 691‒704 (2020).
R. J. Twiss and E. M. Moores, Structural Geology (W.H. Freeman, NY, USA, 1992).
A. Yassaghi, “Integration of Landsat imagery interpretation and geomagnetic data on verification of deep-seated transvers fault lineaments in SE Zagros,” Int. J. Remote Sens. 27, 1‒16 (2006).
Tectonics FP Software, http://www.tectonicsfp.com/ (Accessed May 23, 2022).
Global Mapper Software, https://www.bluemarblegeo. com/global-mapper-download/ (Accessed February 21, 2022).
Digital Elevation Model (DEM), https://gisgeography. com/free-global-dem-data-sources/ (Accessed September 12, 2022).
Geological Map in Scale 1 : 100 000, 1 : 250 000 and 1 : 1 000 000 (Natl. Oil Comp. Geol. Surv. Iran), https://gsi.ir/en/page/2269/maps (Accessed June 13, 2022).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors acknowledge from the department of geology, Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch (Tehran, Iran) for funded this project and we thank Vice-President for Research in Science and Research Branch (Tehran, Iran). The authors thank the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) for continuing support this project. The authors are thankful to reviewer Dr. M.P. Antipov (GIN RAS, Moscow, Russia) and anonymous reviewer for helpful comments, and to editor M. N. Shoupletsova (GIN RAS, Moscow, Russia) for thorough editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghalandari, S., Maleki, Z., Arian, M. et al. Basement Faults Effect on the Folding Style: A Case Study from Hendurabi Fault, Zagros, Iran. Geotecton. 57, 513–523 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016852123040064
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016852123040064