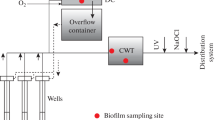
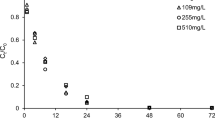
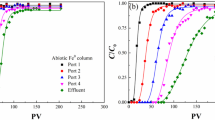
Abstract—The paper is devoted to the biogeochemical aspects of the treatment of iron-bearing groundwater, which are associated with the formation of biofouling in the pore space around wells after aeration of the aquifer and on technological equipment. Structure and activity characteristics of microbial complexes as a result of pumping groundwater from production and observation wells under changing redox conditions are presented. Scanning electron microscopy was used to study the microstructure and elemental composition of biofilm growths. It has been established that the accumulation of iron and manganese by microbial biomass occurs due to the encrustation of the surface of bacterial cells immersed in a polymer matrix represented by a constant base of three elements: Al, Si, and Ca. The survival of microbial complexes in biofouling is due to the high natural potential and ability to carry out biogeochemical processes in a wide range of oxygen concentrations (aerobic and anaerobic conditions).







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
K. A. Boldyrev, V. V. Kuzmin, N. P. Kuranov, and F. Bilek, “Geochemical modeling of stratal deferrification and demanganation of groundwaters,” Vodosnab. Sanitar. Tekhnika, No. 4, 49–55 (2012).
B. Braun, J. Schröder, H. Knecht, and U. Szewzyk, “Unraveling the microbial community of a cold groundwater catchment system,” Water Res. 107 (15), 113–126 (2016).
T. Das, S. Sehar, L. Koop, Y. K. Wong, and S. Ahmed, “Influence of calcium in extracellular DNA mediated bacterial aggregation and biofilm formation,” Plos One 9 (3), 1–11 (2014).
P. Desmond, K. T. Huisman, H. Sanawar, N. M. Farhat, et al., “Controlling the hydraulic resistance of membrane biofilms by engineering biofilm physical structure,” Water Res. 210, e–118031 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.118031
H. -C. Flemming and S. Wuertz, “Bacteria and archaea on Earth and their abundance in biofilms,” Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 17 (4), 247–260 (2019).
D. Ghernaout, N. Elboughdiri, and S. Ghareba, “Fenton technology for wastewater treatment: dares and trends,” Open Access Libr. J. 7, 1–28 (2020).
E. M. Golubeva, L. M. Kondrateva, V. S. Komarova, and A. V. Abrazhevich, “Biogeochemical factors of the formation of iron-bearing biominerals,” Litosfera, No. 2, 115–124 (2017).
S. Goode and D. G. Allen, “Effect of calcium on moving-bed biofilm reactor biofilms,” Water Environ. Res. 83 (3), 220–232 (2011).
R. Hallberg and F. G. Ferris, “Biomineralization by Gallionella,” Geomicrobiol. J. 21, 325–330 (2004).
J. Herlitzius, H. Sumpf, and T. Grischek, “German–Russian cooperation for clean drinking water,” Int. J. Water Manag. Bluefacts. 76–81 (2012).
A. Kappler, B. Schink, and D. K. Newman, “Fe(III) mineral formation and cell encrustation by the nitrate-dependent Fe(II)-oxidizing strain BoFeN1,” Geobiology, No. 3, 235–245 (2005).
N. Khatri, S. Tyagi, and D. Rawtani, “Recent strategies for the removal of iron from water: A review,” J. Water Process Eng. 19, 291–304 (2017).
C. R. Kokare, S. Chakraborty, A. N. Khopade, and K. R. Mahadik, “Biofilm: importance and applications,” Ind. J. Biotechnol. 8, 159–168 (2009).
L. M. Kondratyeva, E. M. Golubeva, and Z. N. Litvinenko, “Microbiological factors of the formation of biominerals,” Sibirsk Ekol. Zh., No. 3, 377–389 (2016).
Z. N. Kondratyeva, L.M. Litvinenko, and N. S. Konovalova, “Study of formation and composition in the terrestrial system of water preparation of iron-bearing groundwaters,” Biotekhnologiya 38 (3), 70–81 (2022).
I. Krupińska, “Importance of humic substances for methods of groundwater treatment,” Pol. J. Soil Sci. 48, 161–172 (2015).
I. Krupińska, “Effect of organic substances on the efficiency of Fe(II) to Fe(III) oxidation and removal of iron compounds from groundwater in the sedimentation process,” CEER 26, 15–29 (2017).
I. Krupińska, “Impact of the oxidant type on the efficiency of the oxidation and removal of iron compounds from groundwater containing humic substances,” Molecules 25 (15), 3380 (2020).
M. I. Kucher, E. E. Frenkel, and S. G. Kucher, “Coevolution biosphere as fundamental ecological modern concept,” Aktual. Probl. Gumanitarn. Sotsial.-Ekon. Nauk, No. 5, 64–66 (2011).
V. V. Kulakov and L. M. Kondrateva, “Biogeochemical aspects of purification of groundwaters of the Amur region,” Tikhookean. Geol. 27 (1), 109–118 (2008).
V. V. Kulakov and V. I. Steblevskii, “Introduction in exploitation of alternative underground source of the Khabarovsk water supply,” Vodosnabzh. Sanitar. Tekhn., No. 7, 41–44 (2012).
A. N. Kvartenko and Zh. M. Govorova, “Modernization of technology of complex conditioning of groundwaters,” Vestn. MGSU, No. 5, 118–123 (2013).
J. Li, X. Peng, H Zhou, J. Li, and Sun Z. and, “Molecular evidence for microorganisms participating in Fe, Mn and S biogeochemical cycling in two low-temperature hydrothermal fields at the Southwest Indian Ridge,” J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 118, 665–679 (2013).
G. Liu, Y. Zhang, W. J. Knibbe, C. Feng, W. Liu, G. Medema, and W. van der Meer, “Potential impacts of changing supply-water quality on drinking water distribution: A review,” Water Res. 116, 135–148 (2017).
K. C. Makris, S. S. Andra, and G. Botsaris, “Pipe scales and biofilms in drinking-water distribution systems: undermining finished water quality,” Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 1477–1523 (2014).
R. Munter, P. Overbeck, and J. Sutt, “Which is the best oxidant for complexed iron removal from groundwater: The Kogalym case,” Ozone-Sci. Eng. 30, 73–80 (2008).
S. Paufler, T. Grischek, Y. Adomat, J. Herlitzius, K. Hiller, and Y. Metelica, “Effective range of chlorine transport in an aquifer during disinfection of wells: from laboratory experiments to field application,” J. Hydrology 559, 711–720 (2018).
C. Y. Peng, G. V. Korshin, R. L. Valentine, A. S. Hill, M. J. Friedman, and S. H. Reiner, “Characterization of elemental and structural composition of corrosion scales and deposits formed in drinking water distribution systems,” Water Res. 44 (15), 4570–4580 (2010).
A. Perez, S. Rossano, N. Trcera, D. Huguenot, C. Fourdrin, A. Vernery-Carron, et al., “Bioalteration of synthetic Fe(III)-, Fe(II)-bearing basaltic glasses and Fe-free glass in the presence of the heterotrophic bacteria strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa: impact of siderophores,” Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 188, 147–162 (2016).
B. N. Ryzhenko, S. R. Krainov, and Yu. V. Shvarov, “Physicochemical factors forming the composition of natural waters: verification of the rock–water model,” Geochem. Int. 41 (6), 565–575 (2003).
B. N. Ryzhenko, M. V. Mironenko, and O. A. Limantseva, “Equilibrium and kinetic simulation of groundwater deironing and demanganation,” Geochem. Int. 57 (12), 1306–1319 (2019).
P. S. Stewart, “Diffusion in biofilms,” J. Bacteriol. 185, 1485–1491 (2003).
L. A. Sudek, G. Wanger, A. S. Templeton, H. Staudigel, and B. M. Tebo, “Submarine basaltic glass colonization by the heterotrophic Fe(II)-oxidizing and siderophore-producing deep-sea bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeri VS–10: the potential role of basalt in enhancing growth,” Front. Microbiol. 8, 363 (2017).
Z. M. Summers, J. A. Gralnick, and D. R. Bond, “Cultivation of an obligate Fe(II)-oxidizing lithoautotrophic bacterium using electrodes,” MBio 4, e 420–12 (2013).
V. I. Vernadsky, Biosphere and Noosphere (Nauka, Moscow, 1989) [in Russian].
Z. Wang L. Liu, J. Yao, and W. Cai, “Effects of extracellular polymeric substances on aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactors,” Chemosphere 63 (10), 1728–1735 (2006).
M. Wolska, “Removal of precursors of chlorinated organic compounds in selected water treatment processes,” Desalin. Water Treat. 52, 3938–3946 (2018).
B. Wu, W. Amelung, Y. Xing, R. Bol, and A. E. Berns, “Iron cycling and isotope fractionation in terrestrial ecosystems,” Earth-Sci. Rev. 190, 323–352 (2019).
M. V. Zhurina, A. V. Gannesen, V. K. Plakunov, and E. L. Zdorovenko, “Composition and functions of the extracellular polymer matrix of bacterial biofilms,” Microbiol. 83 (6), 713–722 (2014).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are deeply grateful to V.V. Ermakov, Zh.M. Govorova, and V.N. Bashkin for valuable recommendations and proposition for the preparation of graphical material.
Funding
This work was made in the framework of the government-financed task of Institute of the Water and Ecology Problems, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences no. 121021500060-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by M. Bogina
The paper continues a previous issue of the journal devoted to biogeochemistry and the 160th anniversary of its founder Academician V.I. Vernadsky (Geochemistry International, 2023, Vol. 61, No. 10).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Litvinenko, Z.N., Kondratyeva, L.M. Role of Biogeochemical Processes during Groundwater Deferrization. Geochem. Int. 61, 1196–1204 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702923100075
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702923100075