Abstract
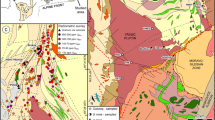
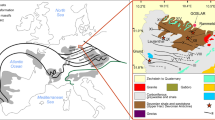
The Pohrenk fluorite mineralisation which makes up Central Anatolia’s most extensive fluorite region is Lutetian aged, and hosted in carbonate rocks that have undergone occasional karstification and silicification along a N–S fault trend. Fluid inclusion values and the position of fluorites in the Tb/La–Tb/Ca diagram show that mineralisation occurred in a hydrothermal environment with homogenisation temperatures ranging from 78.1–363°C. The presence of fluorite as a space filler in carbonate rocks and its association with silicification indicates that the solutions contained considerable amounts of Si alongside F (fluorine). The Pohrenk fluorite samples have 143Nd/144Nd values of between 0.512349 and 0.512497, whilst 87Sr/86Sr values vary between 0.708161 and 0.708772. These values indicate a mantle origin where continental contamination could occur. When the Nd–Sr values are compared to magmatic and young volcanics, the Pohrenk fluorites are seen to be enriched and exhibit similar isotopic signatures to Upper Cretaceous aged magmatics, Early-Middle Miocene volcanics and Mio-Quaternary volcanics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Aldanmaz, “Petrogenesis of late cenozoic collision volcanism in western Anatolia, Turkey”, Durham theses, (Durham University, 1998). http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/4658/
R. J. Bodnar “Revised equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H2O–NaCl solutions” Geochim. Cosmochim Acta 57, 683–684 (1993).
R. Chakrabarti, A. R. Basu, A. Ghatak, “Chemical geodynamics of Western Anatolian” Int. Geol. Rev., iFirst article, 1–22 (2011).
V. Chernyshev, N. I. Serdyuk, D. Z. Zhuravlev, et al., “High-Precision Strontium Isotopic Analysis Using One-Filament Ionization Mode,” in Mass Spectrometry and Isotopic Geology (Nauka, Moscow, 1983), pp. 30–43 [in Russian].
J. Constantopoulos, “Fluid inclusion and REE geochemistry of fluorite from south–central Idaho,” Econ. Geol. 83, 626–636 (1988).
Y. Dilek, S. Altunkaynak, “Geochemistry of Neogene–Quaternary alkaline volcanism in western Anatolia, Turkey, and implications for the Aegean mantle” Int. Geol. Rev. 52 (4–6), 631–655 (2010).
R. G. Eppinger, “Trace and REE variation in fluorites collected from skarn and epithermal mineral deposits in the Sierra Cuchillo area, southcentral New Mexico,” U.S. Geol. Surv., Open_File Rept. 88_0566 (1988).
G. E. Eppinger and L. G. Closs, “Variation of trace elements and rare earth elements in fluorite: a possible tool for exploration,” Econ. Geol. 85, 1896–1907 (1990).
N. M. Evensen, P. J. Hamilton, and R. K. O’Nions, “Rare earth abundances in chondritic meteorite,” Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 42, 1199–1212 (1978).
G. T. Hill, A. R. Campbell, and P. R. Kyle, “Geochemistry of southwestern New Mexico fluorite occurrences: implications for precious metals exploration in fluorite bearing systems,” J. Geochem. Explor. 8, 1–20 (2000).
N. İlbeyli, J.A. Pearce, M. F. Thirlwall, and J. G. Mitchell, “Petrogenesis Of Collision-Related Plutonics In Central Anatolia, Turkey”, Lithos 72, 163–182 (2004)
S. Koc and A. Recber, “Fluid inclusion studies and geochemistry of rare earth elements (REE) of hydrothermal fluorites from Pöhrenk (Kırşehir, Central, Turkey),” Acta Geol. Sinica Geol. Soc. China 75 (1), 59–65 (2001).
P. Möller and G. Morteani, “On the chemical fractionation of REE during the formation of Ca minerals and its application to problems of the genesis of ore deposits,” in The Significance of Trace Elements innSolving Petro_-Genetic Problems, Ed. by S. Augustithis (Athens, 1983), pp. 747–791.
P. Möller, P. P. Parekh, and H. J. Schneider, “The application of Tb/Ca–Tb/La abundance ratios to problems of flourspar genesis,” Miner. Deposita 11, 111–116 (1976).
MTA. (General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration) Türkiye Jeoloji Haritası 1: 100000 ölçekli Kırşehir G 18 Paftası Maden Tetkik ve Arama Genel Müdürlüğü Sf 1–12 (1991)
A. V. Nikiforova, H. Öztürkb, S. Altuncuc, and V. A. Lebedeva, “Kizilcaören orebearing complex with carbonatites (Northwestern Anatolia, Turkey): formation time and mineralogy of rocks” Geol. Ore Deposits, 56 (1), 35–60 (2014).
F. Y Oktay, Savcılı (KAMAN) Cevresinde Orta Anadolu Masifi Tortul Örtüsünün Jeolojisi ve Sedimentolojisi (İ.T.Ü Maden Fakültesi, Docentlik Tezi, İstanbul 1981).
D. A. S. Palmer and A. E. Williams-Jones, “Genesis of the carbonatite-hosted fluorite deposit at Amba Dongar, India: Evidence from fluid inclusions, stable isotopes and whole rock_mineral geochemistry,” Econ. Geol. 91, 934–950 (1996).
H. Rollinson, Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation (Harlow, Longman, 1993).
A. Sasmaz, F. Yavuz, A. Sagιroglu, and B. Akgül, “Geochemical patterns of the Akda madeni (Yozgat, Central Turkey) fluorite deposits and implications,” J. Asian Earth Sci. 24, 469–479 2005).
H.-J. Schneider, P. Möller, and P. P. Parekh, “Rare earth elements distribution in fluorites and carbonate sediments of the East-Alpine mid-Triassic sequences in the Nordliche Kalkalpen,” Miner. Deposita 10, 330–344 (1975).
Y. Uras and C. B. Ersu, F. Oner, “Environmental implications of a hydrogeochemical survey for drinking water in Kirsehir region” Geochem. Int. 49 (11), 1145–1153 (2011).
Y. Uras, Feke (Adana) ve Bayιndιr (Kaman) Fluoritlerinin Nadir Toprak Elementlerinin Karsιlatιrιlmasι (Çukurova University, 2002).
Y. Uras and V. Caliskan, “Geochemical patterns of the Buyukkizilcik (Kahramanmaras) fluorite deposits,” Geochem. Int. 52 (12), 1087–1100 (2014)
S. Yaman, “Bayιndιr (Kaman) Florid filonlarιnda nadir toprak elementleri,” Jeokimyasι, (Jeoloji mühendisligi 25, 39–44 (1985).
A. E. Williams-Jones, I. M. Samson, and G.R. Olivo, “The genesis of hydrothermal fluorite_REE deposits in the Gallinas Mountains, New Mexico,” Econ. Geol. 95, 327–342 (2000).
D. Z. Zhuravlev, I. V. Chernyshov, A. A. Agapova, and N. I. Serdyuk, “High-precision neodymium isotopic analysis of rocks,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Geol., No. 12, 23–40 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uras, Y., Nikiforov, A.V., Oner, F. et al. Geochemistry and Nd, Sr isotopes of the Pohrenk fluorites (Kırsehir-Turkey). Geochem. Int. 55, 263–281 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702917030090
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702917030090