Abstract
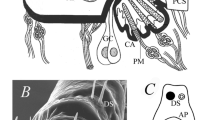
The structure of Haller’s organ, the main sensory organ of hard ticks, studied by methods of scanning electron microscopy, was analyzed in 43 species of the genus Ixodes Latreille, 1795, the solitary genus of the subfamily Ixodinae, on the basis of own and literary data. The structure of Haller’s organ was described in representatives of 13 subgenera: Ixodes s. str. (14 species), Pholeoixodes Schulze, 1942 (3 species), Ixodiopsis Filippova, 1957 (4 species), Ceratixodes Neumann, 1902 (1 species), Scaphixodes Schulze 1941 (2 species), Trichotoixodes Reznik, 1961 (2 species), Partipalpiger Hoogstraal, Clifford, Saito and Keirans 1973 (1 species), Pomerantzevella Feider, 1965 (1 species), Eschatocephalus Frauenfeld, 1851 (2 species), Afrixodes Morel, 1966 (1 species), Sternalixodes Schulze, 1938 (8 species), Multidentatus Clifford, Sonenshine, Keirans and Kohls, 1973 (3 species), Endopalpiger Schulze (1935) (1 species). The main taxonomic characters were distinguished, including the number and topography of sensilla in different parts of the organ; the presence and shape of the capsular orifice; the shape of the anterior trough, etc. It was shown that the structure of Haller’s organ is specific of separate subgenera, whereas differences between species (within each subgenus) are virtually absent. The data obtained were compared with the existing views on the taxonomy of the genus Ixodes.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ash, A., Elliot, A., Godfrey, S., Burmej, H., Abdad, M.Y., Northover, A., Wayne, A., Morris, K., Clode, P., Lymbery, A., and Thompson, R.C.A., Morphological and molecular description of Ixodes woyliei n. sp. (Ixodidae) with consideration for co-extinction with its critically endangered marsupial host, Parasit. Vectors, 2017, vol. 10, article number 70.
Barker, S. C. and Murrell, A., Systematics and evolution of ticks with a list of valid genus and species names, Parasitology, 2004, vol. 129, p. 15. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182004005207
Barros-Battesti, D.M., Arzua, M., Pichorim, M., and Keirans, J.E., Ixodes (Multidentatus) paranaensis n. sp. (Acari: Ixodidae) a parasite of Streptoprocne biscutata (Sclater 1865) (Apodiformes: Apodidae) birds in Brazil, Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 2003, vol. 98, no. 1. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0074-02762003000100013
Belozerov, V.N., Kok, D.J., Fourie, L.J., and Leonovich, S.A., The external structure of Haller’s sensory organ in the Karoo paralysis tick Ixodes (Afrixodes) rubicundus Neum. (Ixodidae), Proceedings of IX International Congress of Acarology (Michigan), 1996, p. 397.
Buczek, A., Bartosik, K., Olszewski, T., Stepien, K., Kubrak, Т., and Sałata, М., Host specificity of ticks (Acari: Ixodida), in Arthropods. Epidemiological Importance, Lublin: Koliber, 2006, p. 37.
Charrier, N.P., Hermouet, A., Hervet, C., Agoulon, A., Barker, S.C., Heylen, D., Toty, C., McCoy, K.D., Plantard, O., and Rispe, C., A transcriptome-based phylogenetic study of hard ticks (Ixodidae), Scientific Reports, 2019, vol. 9, article number 12923.
Clifford, C.M., Sonenshine, D.E., Keirans, J.E., and Kohls, G.M., Systematics of the Subfamily Ixodinae (Acarina: Ixodidae). 1. The subgenera of Ixodes. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Amer., 1973, vol. 66, no. 3, p. 489. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/66.3.489
Darsie, R.F. and Anastos, G., Geographical distribution and hosts of Ixodes texanus Banks (Acarina, Ixodidae), Ann. Entomol. Soc. Amer., 1957, vol. 50, no. 3, p. 295. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/50.3.295
Filippova, N.A., Ixodovye kleshchi podsemeistva Ixodinae. Fauna SSSR. Paukoobraznye (Ixodid Ticks of the Subfamily Ixodinae. Fauna of the USSR, Arachnidae), vol. 4, no. 4, Leningrad: Nauka, 1977.
Haller, G., Vorlaufige Bemerkungen Uber das Gehurorgan der Ixodiden, Zool. Anz., 1881, vol. 4, p. 165.
Hayashi, F. and Hasegawa, M., Immature stages and reproductive characteristics of the lizard tick, Ixodes asanumai (Acarina: Ixodidae), Appl. Entomol. Zool., 1983, vol. 18, no. 3, p. 315. https://doi.org/10.1303/aez.18.315
Heylen, D.J.A., Van Oosten, A.R., Devriendt, N., and Elst, J., Seasonal feeding activity of the tree-hole tick, Ixodes arboricola, Parasitology, 2014, vol. 141, no. 8, p. 1044. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182014000225
Homsher, P.J. and Sonenshine, D.E., Scanning electron microscopy of ticks for systematic studies: fine structure of Haller’s organ in ten species of Ixodes, Trans. Am. Micros. Soc., 1975, vol. 94, no. 3, p. 368. https://doi.org/10.2307/3225501
Homsher, P.J. and Sonenshine, D.E., Scanning electron microscopy of ticks for systematic studies 2. Structure of Hallerʼs organ in Ixodes brunneus and Ixodes frontalis, J. Med. Entomol., 1977, vol. 14, no. 1, p. 93. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/14.1.93
Homsher, P.J. and Sonenshine, D.E., Scanning electron microscopy of ticks for systematic studies: 3. Structure of Haller’s organ in five species of the subgenus Multidentatus of the genus Ixodes, in Recent Advances in Acarology, 1979, vol. 2, N.Y.: Academic Press, 1979, p. 485.
Homsher, P.J. and Sonenshine, D.E., Scanning electron microscopy of ticks for systematic studies 2. Structure of Hallerʼs organ in Ixodes brunneus and Ixodes frontalis, J. Med. Entomol., 1977, vol. 14, no. 1, p. 93. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/14.1.93
Homsher, P.J., Keirans, J.E, Robbins, R.G., Irwin-Pinkley, L., and Sonenshine, D.E., 1988. Scanning electron microscopy of ticks for systematic studies: structure of Haller’s organ in eight species of the subgenus Sternalixodes of the genus Ixodes (Acari: Ixodidae), J. Med. Entomol., 1988, vol. 25, no. 5, p. 348. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/25.5.348
Honzаkovа, E., Sixl, W., and Waltinger, H., Scanning electron microscopy of the ticks Ixodes laguri and Ixodes arboricola: surface structures of Haller’s organ, Folia Parasitol., 1975, vol. 22, p. 241.
Hoogstraal, H. and Aeschlimann, A., Tick-host specificity, Bull. Soc. Entomol. Suisse, 1982, vol. 55, p. 5.
Hornok, S., Kontschán, J., Estrada-Peña, A., de Mera, I.G.F., Tomanović, S., and de la Fuente J., Contributions to the morphology and phylogeny of the newly discovered bat tick species, Ixodes ariadnae in comparison with I. vespertilionis and I. simplex, Parasit. Vectors, 2015, vol. 8, p. 47.
Kwak, M.L., Beveridge, I., Koehler, A.V., Malipatil, M., Gasser, R.B.., and Jabbar A., Phylogenetic analysis of the Australasian paralysis ticks and their relatives (Ixodidae: Ixodes: Sternalixodes), Parasit. Vectors, 2017, vol. 10, article number 122.
Leonovich, S.A. and Belozerov, V.N., Regeneration of Haller’s sensory organ in the tick Ixodes ricinus L., Exp. Appl. Acarol., 1992, vol. 15, p. 59.
Leonovich, S.A. and Dimov, I., Sense organs on palps and fore tarsi of gamasid mites (Parasitiformes, Rhinonyssidae), parasites of the nasal cavity of the great tit, the rock dove, and the Eurasian coot, Entomol. Rev., 2012, vol. 92, no. 46, p. 1012. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0013873812090084
Leonovich, S.A. and Stanyukovich, M.K., Sensory organs of mesostigmatic mites (Acarina, Mesostigmata) dwelling in body cavities of mammals and birds, Proceedings of the Zoological Institute RAS, 2011, vol. 315, no. 3, p. 263.
Leonovich, S.A., Electron microscopic studies of Haller’s organ in the tick Ixodes persulcatus (Ixodidae), Parazitologiya, 1977, vol. 11, no. 4, p. 340.
Leonovich, S.A., Morphology of Haller’s organ in ticks of the family Ixodidae (Acarina: Ixodoidea). Studies in a scanning electron microscope, in Problemy zoologii (Problems of Zoology), Leningrad: Nauka, 1976, p. 59.
Leonovich, S.A., On types of parasitism in hard ticks, Parazitologiya, 2019, vol. 53, no. 5, p. 416. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031184719050053
Leonovich, S.A., Phenol and lactone receptors in the distal sensilla of Haller’s organ in Ixodes ricinus ticks and their possible role in host perception, Exp. Appl. Acarol., 2004. vol. 32, nos. 1–2, p. 89. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:APPA.0000018200.24760.78
Leonovich, S.A., Sense organs, in Taezhnyi kleshch Ixodes persulcatus Sch. (Acarina, Ixodidae). Morfologiya, systematika, ekologiya, meditsinskoe znachenie (Taiga Tick Ixodes persulcatus Sch. (Acarina, Ixodidae). Morphology, Systematics, Ecology, Medical Importance), Leningrad: Nauka, 1985, p. 77.
Leonovich, S.A., Sensornye sistemy paraziticheskikh kleshchei (Sensory Systems of Parasitic Ticks and Mites), St. Petersburg: Nauka, 2005.
Onofrio, V.C., Labruna, M.B., Faccini, J.L.H., and Barros-Battesti, D.M., Description of immature stages and redescription of adults of Ixodes luciae Sénevet (Acari: Ixodidae), Zootaxa, 2010, vol. 2495, p. 53.
Ronghang, B. and Roy, B., A scanning electron microscopic observations on sensilla of Ixodes acutitarsus recovered from semi-wild cattle Bos frontalis Lambert, Entomol. Appl. Sci. Lett., 2014, vol. 1, no. 4, p. 8.
Shao, R., Barker, S.C., Mitani, H., Aoki, Y., and Fukunaga, M., Evolution of duplicate control regions in the mitochondrial genomes of Metazoa: a case study with Australasian Ixodes ticks, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2005, vol. 22, no. 3, p. 620. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msi047
Smith, C.N., Biology of Ixodes dentatus Neumann (Ixodidae), Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 1945, vol. 38, no. 2, p. 223. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/38.2.223
Xu, G., Fang, Q.Q., Keirans, J.E., and Durden, L.A., Molecular phylogenetic analyses indicate that the Ixodes ricinus complex is a paraphyletic group, J. Parasitol., 2003, vol. 89, no. 3, p. 4452. https://doi.org/10.1645/0022-3395(2003)089[0452:MPAITT]2.0.CO;2
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The study was performed according to the State program “Diversity of Parasitic Systems, Adaptations, and Evolutionary Trends of Parasites” (theme no. АААА-А19-119020690109-2). Material from the collection of the Zoological Institute RAS (UFC ZIN reg. no. 2-2.20) was used in the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leonovich, S.A. Structure of Haller’s Organ and Taxonomy of Hard Ticks of the Subfamily Ixodinae (Family Ixodidae). Entmol. Rev. 100, 1387–1401 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0013873820090122
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0013873820090122