Abstract
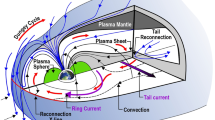
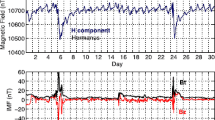
In a magnetic cloud, which is part of a sporadic solar wind on the Earth orbit, against the background of a constant solar wind velocity, abrupt jumps in the solar wind density and antiphase, highly correlated (correlation coefficient R∼−0.9) variations of the magnitude of the strength of the interplanetary magnetic field were detected. Analysis has shown that these jumps, which represent fibers or eruptive protuberances, result, when interacting with the Earth magnetosphere, in the development of a high-latitude magnetic disturbance, starting on the dayside and propagating into the morning and evening sides of the magnetosphere. The processes, developing in the auroral region during this disturbance, are similar to processes occurring during the substorm, but they are characterized by a shorter duration and lower value of released energy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eselevich, V.G., Kaigorodov, A.P., and Fainshtein, V.G., Some peculiarities of solar plasma fluxes from coronal holes, Planet. Space Sci., 1990, vol.38, no. 4, p. 459.
Schwenn, R. and Marsch, E., Physics of the Inner Heliosphere, vols. I, II, Berlin Heidelberg: SpringerVerlag, 1991.
McComas, D.J., Elliott, H.A., and von Steiger, R., Solar wind from high latitude CH at solar maximum, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2002, vol.29, no. 9, p. 28. doi 10.1029/2001GL013940
Svalgaard, L.J., Wilcox, W., and Duvall, T.L., A model combining the solar magnetic field, Solar Phys., 1974, vol.37, p. 157.
Eselevich, M.V., Eselevich, V.G., and Fujiki, K., Streamer belt and chains as the main sources of quasistationary slow solar wind, Solar Phys., 2007, vol.240, p. 135.
Eselevich, V.G., Fainshtein, V.G., and Rudenko, G.V., Study of the structure of streamer belts and chains in the solar corona, Solar Phys., 1999, vol.188, no. 2, p. 277.
Wang, Y.M., Sheeley N.R., and Rich, N.B., Coronal pseudostreamers, Astrophys. J., 2007, vol.685, p. 1340.
Khabarova, O. and Zastenker, G., Sharp changes of solar wind ion flux and density within and outside current sheets, Solar. Phys., 2011, vol.270, no. 1, p. 311. doi 10.1007/s11207-011-9719-4
Parkhomov, V.A., Riazantseva, M.O., and Zastenker, G.N., Local amplification of auroral electrojet as response to a sharp solar wind pressure pulse, Planet. Space Sci., 2005, vol.53, no. 1–3, p. 265.
Borodkova, N.L., Effect of large and sharp changes of solar wind dynamic pressure on the Earth’s magnetosphere: Analysis of several events, Cosmic Res., 2010, vol.48, no. 1, p. 41.
Parkhomov, V.A., Borodkova, N.L., Dmitriev, A.V., et al., The role of solar wind pressure jumps in the initiation and control processes of magnetospheric substorms, Geomagn. Aeron., 2011, vol.51, no. 7, p. 979.
Safrankova, J., Zastenker, G., Nemecek, Z., et al., Small scale observation of magnetopause motion: Preliminary results of the INTERBALL project, Ann. Geophys., 1997, vol.15, p. 562.
Klimov, S.I., Romanov, S.A., Amata, E., et al., ASPI experiment: measurements of fields and waves onboard the INTERBALL-1 spacecraft, Ann. Geophys., 1997, vol.15, no. 5, p. 514.
Burlaga, L., Sitteler, E, Mariani, F., and Schwenn, R., Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock: Voyager, Helios, and IMP8 observations, J. Geophys. Res., 1981, vol.86, no. 8, p. 6673.
Burlaga, L., Klein, L., Sheeley, M., Jr., et al., A magnetic cloud and a coronal mass ejection, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1982, vol.9, no. 12, p. 1317.
Burlaga, L., Micro-scale structure in the interplanetary medium, Solar Phys., 1968, no. 4, p. 67.
Tung-Shin Hsu and McPherron, R.L., An evaluation of statistical significance of the association between northward turning of the interplanetary magnetic field and substorm expansion onsets, J. Geophys. Res., 2002. vol. 107, no. A11, p. 1308. doi 10.1029/2000JA000125
Xiaoyan, Zh. and Tsurutani, B.T., Interplanetary shock triggering of nightside geomagnetic activity: Substorms, pseudobreakups, and quiescent events, J. Geophys. Res., 2001. vol. 106, no. A9, p. 18957.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.A. Parkhomov, N.L. Borodkova, V.G. Eselevich, M.V. Eselevich, 2015, published in Kosmicheskie Issledovaniya, 2015, Vol. 53, No. 6, pp. 449–460.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parkhomov, V.A., Borodkova, N.L., Eselevich, V.G. et al. Abrupt changes of density in sporadic solar wind and their effect on Earth magnetosphere. Cosmic Res 53, 411–422 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952515050093
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952515050093