Abstract
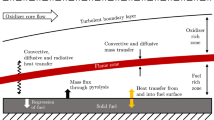
Combustion of solid propellants in rocket propulsion systems usually occurs in an intense cross-flow of combustion products (solid rocket motor), gaseous oxidizer (hybrid rocket motor) or air (ramjet and air-breathing engines). This leads to the so-called erosive burning effects, resulting in a change in the burning law under the influence of the gas flow. The main approaches to modeling the erosive burning of solid propellants in a high-velocity cross-flow of gases are considered. Methods for the criterial description of the results of experimental studies of the erosive burning of solid propellants under transonic and supersonic flow conditions are analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. I. Leipunskii, “On the Physical Basis of the Interior Ballistics of Missiles,” Doct. Dissertation in Phys.-Math. Sci. (Inst. of Chem. Phys., Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Moscow, 1945). Published in Theory of Combustion of Propellants and Explosives (Nauka, Moscow, 1982), pp. 226–277 [in Russian].
M. K. Razdan, K. K. Kuo, “Erosive Burning of Solid Propellants,” in Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics, Vol. 90 (4): Fundamentals of Solid Propellant Combustion, Ed. by K. K. Kuo and M. Summerfield (New York, 1994).
L. K. Gusachenko and V. E. Zarko, “Erosive Burning. Modeling Problems,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 43 (3), 47–58 (2007) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 43 (3), 286–296 (2007)].
V. K. Bulgakov and A. M. Lipanov, Theory of Erosive Burning of Solid Propellants (Nauka, Moscow, 2001) [in Russian].
H. Muraour, “Sur la Théorie des Réactions Explosives. Cas Particulier des Explosifs D‘amourcage,” Bull. Soc. Chem. Fr. 51, 1152–1166 (1932).
I. P. Grave, Interior Ballistics: Pyrodynamics (Artakademiya Dzerzhinskogo, Leningrad, 1934) [in Russian].
Yu. I. Dimitrienko and I. D. Dimitrienko, “Thermomechanical Model of Erosive Burning of Energetic Materials,” Vestn. MSTU Baumana, Ser. Estestv. Nauki, 96–112 (2012).
Ya. B. Zel’dovich, “Theory of Propellant Combustion in a Gas Flow,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 7 (4), 463–476 (1971) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 7 (4), 399–408 (1971)].
V. N. Vilyunov, “On Theory of Erosive Burning of Propellants,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 136 (2), 381 (1961).
H. Schlichting, Boundary-Layer Theory (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1968).
S. S. Kutateladze and A. I. Leont’ev, Turbulent Boundary Layer of a Compressible Gas (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1962) [in Russian].
Ya. I. Shapiro, G. Yu. Mazing, and N. E. Prudnikov, Theory of Solid Propellant Rocket Motors (Voenizdat, Moscow, 1966) [in Russian].
S. S. Kutateladze, Heat Transfer and Hydrodynamic Resistance: Handbook (Energoatomizdat, Moscow, 1990) [in Russian].
V. N. Vilyunov and A. D. Kolmakov, “Burning Rate of Propellants in a Turbulent Flow of Gases,” Tr. Sib. Fizikotekh. Inst., No. 3 (1963).
V. N. Vilyunov, A. A. Dvoryashin, A. D. Margolin, S. K. Ordzhonikidze, and P. F. Pokhil, “Burning of Ballistite Type H in Sonic Flow,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 8 (4), 501–505 (1972) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 8 (4), 410–413 (1972)].
V. N. Vilyunov and Yu. M. Isaev, “Erosive Burning in Supersonic Flow,” in Chemical Physics of Combustion and Explosion. Combustion of Condensed Systems, Proc. IX All-Union Symp. on Combustion and Explosion (Chernogolovka, 1989), pp. 12–15.
V. A. Arkhipov, D. A. Zimin, E. A. Kozlov, and N. S. Tret’yakov, “Experimental Study of the Erosive Burning of Solid Propellants,” Khim. Fiz. 16 (9), 101–106 (1997).
V. A. Arkhipov and D. A. Zimin, “Erosive Burning of a Solid Propellant in a Supersonic Flow,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 34 (1), 61–64 (1998) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 34 (1), 55–57 (1998)].
V. A. Arkhipov, E. A. Zverev, and D. A. Zimin, “Solving an Inverse Problem of Erosive Burning Rate Reconstruction,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 38 (1), 73–79 (2002) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 38 (1), 65–70 (2002)].
V. A. Arkhipov and N. S. Tretyakov “Erosive Burning of Solid Propellants,” in Rocket Motors and Problems of Space Exploration (Torus Press, Moscow, 2005), pp. 220–230 [in Russian].
V. N. Aleksandrov, V. M. Bytskevich, V. K. Verkholomov, et al., Integral Solid Propellant Ramjets (Fundamentals of Theory and Calculation) (Akademkniga, Moscow, 2006) [in Russian].
Yu. M. Kochetkov, M. L. Kuranov, and M. L. Filimonov, “Methodical Bases of Gas Dynamics and Interior Ballistics of Nozzleless SRM, Prospects for Use,” Polet: Aviatsiya, Raket. Tekh. Kosmonavt., No. 11, 4–12 (2002).
J. M. Lenoir and G. A. Robillard, “A Mathematical Method to Predict the Effects of Erosive Burning in Solid Propellant Rockets,” in Sixth Symp. (Int.) on Combustion (1957), pp. 663–667.
C. A. Saderholm, R. A. Biddle, L. H. Caveny, and M. Summerfield, “Combustion Mechanisms of Fuel-Rich Propellants in Flow Fields,” in AIAA 8th Propulsion Conf., AIAA Paper No. 72-1145 (1972).
G. Lengelle, “Model Describing the Erosive Burningand Velocity Response of Composite Propellants,” AIAA J. 13 (3), 315–322 (1975).
J. C. Godon, J. Duterque, and G. Lengelle, “Solid-Propellant Erosive Burning,” J. Propul. Power 8 (4), (1992).
M. K. Razdan and K. K. Kuo, “Erosive Burning Study of Composite Solid Propellants by Turbulent Boundary-Layer Approach,” AIAA J. 17 (11), (1979).
M. J. Chiaverini, K. K. Kuo, A. Peretz, et al., “Regression-Rate and Heat-Transfer Correlations for Hybrid Rocket Combustion,” J. Propul. Power 17 (1), 99–110 (2001).
W. H. Heiser and D. T. Pratt, Hypersonic Airbreathing Propulsion (Washington, DC, 1994); ISBN 1-56347-035-7. (AIAA Education Ser.)
P. J. Waltrup, M. E.White, and F. Zarlingo, “History of U. S. Navy Ramjet, Scramjet, and Mixed-Cycle Propulsion Development,” AIAA Paper No. 96-3152 (1996).
Encyclopedia Astronautica; http://www.astronautix.com/lvs/gird09.htm.
G. A. Marxman, C. E. Wooldridge, and R. J. Muzzy, “Fundamentals of Hybrid Boundary-Layer Combustion,” in Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics, Vol. 15: Heterogeneous Combustion (Academic Press, 1964).
G. P. Sutton and O. Biblarz, Rocket Propulsion Elements (Wiley and Sons, New York, 2001).
M. Grosse, “Effect of a Diaphragm on Performance and Regression of a Laboratory Scale Hybrid Rocket Motor Using Nitrous Oxide and Paraffin,” in 45th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, AIAA Paper No. 2009-5113 (2009).
N. Bellomo, M. Marta Lazzarin, and F. Barato, “Numerical Investigation of the Effect of a Diaphragm on the Performance of a Hybrid Rocket Motor,” AIAA Paper No. 2010-7033 (2010).
Yu. A. Kustov and S. S. Rybanin, “Effect of Chemical Kinetics on the Burning Rate of a Propellant Slab in a Turbulent Oxidizer Flow,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 6 (1), 54–64 (1970) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 6 (1), 50–59 (1970)].
D. R. Greatrix, “Regression Rate Estimation for Standard-Flow Hybrid Rocket Engines,” Aerospace Sci. Technol. 13, 358–363 (2009).
L. Fanton, C. Paravan, and L. T. DeLuca, “Testing and Modeling Fuel Regression Rate in a Miniature Hybrid Burner,” Int. J. Aerospace Eng. 15, (2012); ID 673838 2012.
A. Karabeyoglu, G. Zilliac, and B. J. Cantwell, “Combustion of Liquefying Hybrid Propellants: Part 1. General Theory,” J. Propul. Power 18 (3), (2002).
A. Karabeyoglu, D. Altman, and B. J. Cantwell, “Scale-Up Tests of High Regression Rate Paraffin-Based Hybrid Rocket Fuels,” J. Propul. Power. 20 (6), 1037–1045 (2004).
A. Antoniou and K. M. Akyuzlu, “A Physics Based Comprehensive Mathematical Model to Predict Motor Performance in Hybrid Rocket Propulsion Systems,” AIAA Paper 2005-3541, (2005).
N. Serin and Y. A. Gögüs, “A Fast Computer Code for Hybrid Motor Configuration, Eulec, and Results Obtained for HTPB/O2 Combination,” AIAA Paper No. 2003-4747 (2003).
N. Gascoin and P. Gillard, “Preliminary Pyrolysis and Combustion Study for the Hybrid Propulsion,” AIAA Paper No. 2010-6871 (2010).
R. Hilbert, F. Tap, H. El-Rabii, and D. Thévenin, “Impact of Detailed Chemistry and Transport Models on Turbulent Combustion Simulations,” Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 30, 61–117 (2004).
D. Bianchi, B. Betti, and F. Nasuti, “Simulation of Gaseous Oxygen/Hydroxyl-Terminated Polybutadiene Hybrid Rocket Flowfields and Comparison with Experiments,” J. Propul. Power 31 (3), 919–929 (2015).
H. Arisawa and T. B. Brill, “Flash Pyrolysis of Hydroxyl-Terminated Poly-Butadiene (HTPB) II: Implications of the Kinetics to Combustion of Organic Polymers,” Combust. Flame 106 (1–2), 144–154 (1996); DOI: 10.1016/0010-2180(95)00254-5.
D. Bianchi, F. Nasuti, and D. Delfini, “Modeling of Gas-Surface Interface for Paraffin-Based Hybrid Rocket Fuels in CFD Simulations,” in 6th Eur. Conf. for Aerospace Sciences (Krakow, 2015), FP EUCASS-368.
M. Faenza, F. Barato, and M. Lazzarin, et al., “Hybrid Rocket Motors Regression Rate Prediction Through CFD Simulations,” in 6th Eur. Conf. for Aerospace Sciences (Krakow, 2015), FP EUCASS-074.
S. May and O. Bozic, “CFD Simulation of Chemical Non-Equilibrium Reacting Flow within AHRES Hybrid Rocket Engine,” in 6th Eur. Conf. for Aerospace Sciences (Krakow, 2015), FP EUCASS-215.
P. Milova, R. Blanchard, and L. Galfetti, “A Parametric Study of the Effect of Liquid Entrainment on the Combustion Characteristics of a Paraffin Based Hybrid Rocket Motor,” in 6th Eur. Conf. for Aerospace Sciences (Krakow, 2015), FP EUCASS-327.
A. M. Gubertov, V. V. Mironov, and R. G. Gollender, et al., Processes in Hybrid Rocket Motors (Nauka, Mocsow, 2008) [in Russian].
D. W. Netzer, “Modeling Solid-Fuel Ramjet Combustion,” J. Spacecraft Rockets 14 (12), (1977).
D. W. Netzer, “Model Application to Solid-Fuel Ramjet Combustion,” J. Spacecraft Rockets 15 (5), (1978)
C. A. Stevenson and D. W. Netzer, “Primitive Variable Model Application to Solid-Fuel Ramjet Combustion,” J. Spacecraft and Rockets 28 (1), (1981).
G. Schulte, “Fuel Regression and Flame Stabilization Studies of Solid-Fuel Ramjets,” J. Propul. Power 2 (4), (1986).
G. Schulte, R. Pein, and A. Hogl, “Temperature and Concentration Measurements in a Solid-Fuel Ramjet Combustion Chamber,” J. Propul. 3 (2), (1987).
P. Korting, H. Schoyer, and Y. Timnat, “Advanced Hybrid Rocket Motor Experiments,” Acta Astronaut. 15 (2), 97–104 (1987).
C. Carmicino and S. A. Russo, “Performance Comparison between Two Different Injector Configurations in a Hybrid Rocket,” Aerospace Sci. Technol. 11, 61–67 (2007).
L. T. DeLuca, L. Galfetti, F. Maggi, et al., “Characterization of HTPB-Based Solid Fuel Formulations: Performance, Mechanical Properties, and Pollution,” Acta Astronaut. 92, 150–162 (2013).
P. Tadini, C. Paravan, and L. T. DeLuca, “Ballistic Characterization of Mettallized HTPB-Based Fuels with Swirling Oxidizer in Lab-Scale Hybrid Burner,” in Proc. 9th Int. Conf. on High Energy Materials (HEMs-2013) (Sagamihara, Japan, 2013), pp. 1–9.
V. E. Zarko and K. K. Kuo, “Critical Review of Methods for Regression Rate Measurements of Condensed Phase Systems,” in Non-Intrusive Combustion Diagnostics, Ed. by K. K. Kuo and T. Parr (Begel House, New York, 1994), pp. 600–623.
M. Chiaverini, N. Serin, D. K. Johnson, et al., “Regression Rate Behavior of Hybrid Rocket Solid Fuels,” J. Propul. Power 16 (1), 125–132 (2000).
B. Evans et al., “Characterization of Nano-Sized Energetic Particle Enhancement of Solid-Fuel Burning Rates in an X-ray Transparent Hybrid Rocket Engine,” AIAA Paper No. 2004-3821 (2004).
B. Evan, N. A. Favorito, E. Boyer, et al., “Characterization of Solid Fuel Mass Burning Enhancement Utilizing an X-ray Transparent Hybrid Rocket Motor,” in Advancements in Energetic Materials and Chemical Propulsion, Ed. by K. K. Kuo and J. de R. Rivera (Begell House, New York, 2007), pp. 705–724.
J. Y. Lestrade, “Liquefying Fuel Regression Rate Modeling in Hybrid Propulsion,” Aerospace Sci. Technol. 42, 80–87 (2015).
C. Paravan, A. Reina, A. Sossi, et al., “Time-Resolved Regression Rate of Innovative Hybrid Solid Fuel Formulations,” Prog. Propul. Phys., No. 4, 75–98 (2013); DOI: 10.1051/eucass/201304075.
A. Gany, “Accomplishments and Challenges in Solid Fuel Ramjets and Scramjets,” Int. J. Energ. Mater. Chem. Propul. 8 (5), 421–446 (2009).
A. Rekakavas, L. Litterio, M. Boiocchi, and L. Galfetti, “Experimental Visualizations of Entrainment Phenomena in Wax-Based Fuels for Hybrid Space Propulsion,” in 6th Europ. Conf. for Aerospace Sciences (Krakow, 2015), FP EUCASS-569.
V. V. Perov, V. E. Zarko, and C. Zhukov, “New Microwave Method for Measuring Unsteady Mass Gasification Rate of Condensed Systems,” Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 50 (6), 130–133 (2014) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 50 (6), 739–741 (2014)].
V. Perov, V. Zarko, V. Zvegintsev, and D. Nalivaichenko, “New Method for Measuring Transient Mass Gasification Rate of Condensed Systems,” in Proc. 56th Israel Ann. Conf. on Aerospace Sciences, Tel Aviv, March 9–10, 2016, WeL2T5.3.
I. S. Tseng and V. Yang, “Combustion of a Double-Base Homogeneous Propellant in a Rocket Motor,” Combust. Flame 96, 325–342 (1994).
S. Apte and V. Yang, “Unsteady Flow Evolution and Combustion Dynamics of Homogeneous Solid Propellant in a Rocket Motor,” Combust. Flame 131, 110–131 (2002).
W. D. Cai, P. Thakre, and V. Yang, “A Model of AP/HTPB Composite Propellant Combustion in Rocket Motor Environments,” Combust. Sci. Technol. 180, 2143–2169 (2008).
D. Pastrone, “Approaches to Low Fuel Regression Rate in Hybrid Rocket Engines,” Int. J. Aerospace Eng. (2012); Article ID 649753; http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/649753.
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/SpaceShipOne.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.A. Arkhipov, V.E. Zarko, I.K. Zharova, A.S. Zhukov, E.A. Kozlov, D.D. Aksenenko, A.V. Kurbatov
Published in Fizika Goreniya i Vzryva, Vol. 52, No. 5, pp. 3–22, September–October, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arkhipov, V.A., Zarko, V.E., Zharova, I.K. et al. Solid propellant combustion in a high-velocity cross-flow of gases (review). Combust Explos Shock Waves 52, 497–513 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508216050014
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508216050014