Abstract
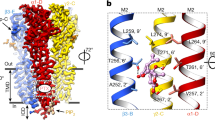
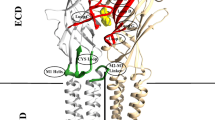
The permeability of ion channels for ions and substances that bind inside the pore depends on the cross-sectional area of the pore. We have constructed models of the closed, open, and desensitized α1β2γ2 GABAA receptor on the basis of known structures of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic ligand-gated channels. We employed Monte Carlo energy minimization to optimize the model structures. We have found significant pore constrictions, whose diameter depends on the functional state of the receptor in the cytoplasmic, middle, and extracellular parts of the pore-forming M2 segments. It is known that the constrictions in the middle (the 9' ring of residues) and cytoplasmic (the 2' ring of residues) parts of the M2 helices form the activation and desensitization gates of the GABAA receptor. Our computations predict that the constriction in the extracellular part of the M2 helices (the 20' ring of residues) may also serve as a gate in the GABAA receptor, whose physiological role is still unclear. Our results imply that the structures of a number of prokaryotic and eukaryotic ligand-gated channels that have been found in bacteria and lower organisms can be used for homology modeling of the pore region of the human GABAA receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Hille, Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes, 3rd ed. (Sinauer Assoc., Sunderland, MA, 2001).
W. Sieghart, Adv. Pharmacol. 54, 231 (2006).
W. Hevers and H. Luddens, Mol. Neurobiol. 18 (1), 35 (1998).
J. L. Galzi, A. Devillers-Thiery, N. Hussy, et al., Nature 359 (6395), 500 (1992).
A. Keramidas, A. J. Moorhouse, P. R. Schofield, et al., Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 86 (2), 161 (2004).
C. Miller, Neuron 2 (3), 1195 (1989).
R. W. Olsen, Neurochem. Res. 39 (10), 1924 (2014).
L. Chen, K. A. Durkin, and J. E. Casida, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103 (13), 5185 (2006).
A. V. Rossokhin, I. N. Sharonova, J. V. Bukanova, et al., Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 63, 72 (2014).
B. E. Erkkila, A. V. Sedelnikova, and D. S. Weiss, Biophys. J. 94 (11), 4299 (2008).
B. S. Zhorov and P. D. Bregestovski, Biophys. J. 78 (4), 1786 (2000).
O. S. Smart, J. G. Neduvelil, X. Wang, et al., J. Mol. Graph. 14 (6), 354 (1996).
E. Chovancova, A. Pavelka, P. Benes, et al., PLoS Comput. Biol. 8 (10), e1002708 (2012).
M. Petrek, P. Kosinova, J. Koca, et al., Structure 15 (11), 1357 (2007).
E. Yaffe, D. Fishelovitch, H. J. Wolfson, et al., Proteins 73 (1), 72 (2008).
P. S. Miller and A. R. Aricescu, Nature 512 (7514), 270 (2014).
X. Huang, H. Chen, K. Michelsen, et al., Nature 526 (7572), 277 (2015).
J. Du, W. Lu, S. Wu, et al., Nature 526 (7572), 224 (2015).
N. Bocquet, H. Nury, M. Baaden, et al., Nature 457 (7225), 111 (2009).
R. E. Hibbs and E. Gouaux, Nature 474 (7349), 54 (2011).
R. J. Hilf and R. Dutzler, Nature 452 (7185), 375 (2008).
I. Zimmermann and R. Dutzler, PLoS Biol. 9 (6), e1001101 (2011).
R. Spurny, J. Ramerstorfer, K. Price, et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 109 (44), E3028 (2012).
N. Bocquet, L. Prado de Carvalho, J. Cartaud, et al., Nature 445 (7123), 116 (2007).
R. J. Howard, J. R. Trudell, and R. A. Harris, Pharmacol. Rev. 66 (2), 396 (2014).
Z. Li and H. A. Scheraga, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 84 (19), 6611 (1987).
J. Weiner, P. A. Kollman, D. A. Case, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 106, 765 (1984).
D. P. Garden and B. S. Zhorov, J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 24 (2), 91 (2010).
R. D. Shannon, Acta Crystallogr. A 32 (5), 751 (1976).
P. F. Lang and B. C. Smith, Dalton Trans. 39 (33), 7786 (2010).
D. E. Conway, Ionic Hydration in Chemistry and Biophysics (Elsevier, New York, 1981).
N. Unwin, J. Mol. Biol. 229 (4), 1101 (1993).
A. Miyazawa, Y. Fujiyoshi, and N. Unwin, Nature 423 (6943), 949 (2003).
N. Unwin, J. Mol. Biol. 346 (4), 967 (2005).
M. O’Mara, B. Cromer, M. Parker, et al., Biophys. J. 88 (5), 3286 (2005).
M. Ernst, S. Bruckner, S. Boresch, et al., Mol. Pharmacol. 68 (5), 1291 (2005).
R. Hawthorne, B. A. Cromer, H. L. Ng, et al., J. Neurochem. 98 (2), 395 (2006).
P. J. Corringer, M. Baaden, N. Bocquet, et al., J. Physiol. 588 (Pt 4), 565 (2010).
A. Rossokhin, G. Teodorescu, S. Grissmer, et al., Mol. Pharmacol. 69 (4), 1356 (2006).
A. Rossokhin, T. Dreker, S. Grissmer, et al., Mol. Pharmacol. 79 (4), 681 (2011).
G. Hu, L. Y. Chen, and J. Wang, J. Mol. Model. 18 (8), 3731 (2012).
A. V. Rossokhin and B. S. Zhorov, J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 30 (7), 559 (2016).
P. S. Miller and T. G. Smart, Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 31 (4), 161 (2010).
G. D. Cymes, Y. Ni, and C. Grosman, Nature 438 (7070), 975 (2005).
J. E. Carland, A. J. Moorhouse, P. H. Barry, et al., J. Biol. Chem. 279 (52), 54153 (2004).
M. Gielen, P. Thomas, and T. G. Smart, Nat. Commun. 6, 6829 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Rossokhin, 2017, published in Biofizika, 2017, Vol. 62, No. 5, pp. 866–875.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossokhin, A.V. Homology modeling of the transmembrane domain of the GABAA receptor. BIOPHYSICS 62, 708–716 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350917050190
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350917050190