Abstract
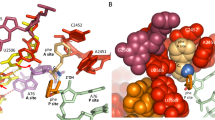
Class I release factors (RFs) recognize stop codons in the sequences of mRNAs and are required for the hydrolysis of peptidyl-tRNA in the ribosomal P site during the final step of protein synthesis in bacteria, resulting in the release of a complete polypeptide chain from the ribosome. A key role in this process belongs to the highly conserved GGQ motif in RFs. Mutations in this motif can reduce the hydrolysis rate or even completely inhibit the reaction. Previously, it was hypothesized that the amino acid residues of GGQ (especially glutamine) are essential for the proper coordination of the water molecule for subsequent hydrolysis of the ester bond. However, available structures of the 70S ribosome termination complex do not allow unambiguous identification of the exact orientation of the carbonyl group in peptidyl-tRNA relative to the GGQ, as well as of the position of the catalytic water molecule in the peptidyl transferase center (PTC). This mini-review summarizes key facts and hypotheses on the role of GGQ in the catalysis of peptide release, as well as suggests and discusses future experiments aimed to produce high-quality structural data for deciphering the precise mechanism of RF-mediated catalysis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PTC:
-
peptidyl transferase center
- RF:
-
release factor
References
Capecchi, M. R. (1967) Polypeptide chain termination in vitro: isolation of a release factor, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 58, 1144-1151, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.58.3.1144.
Capecchi, M. R., and Klein, H. A. (1969) Characterization of three proteins involved in polypeptide chain termination, Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol., 34, 469-477, https://doi.org/10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.053.
Scolnick, E., Tompkins, R., Caskey, T., and Nirenberg, M. (1968) Release factors differing in specificity for terminator codons, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 61, 768-774.
Petry, S., Brodersen, D. E., Murphy, F. V., Dunham, C. M., Selmer, M., et al. (2005) Crystal structures of the ribosome in complex with release factors RF1 and RF2 bound to a cognate stop codon, Cell, 123, 1255-1266, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.039.
Laurberg, M., Asahara, H., Korostelev, A., Zhu, J., Trakhanov, S., and Noller, H. F. (2008) Structural basis for translation termination on the 70S ribosome, Nature, 454, 852-857, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07115.
Frolova, L. Y., Tsivkovskii, R. Y., Sivolobova, G. F., Oparina, N. Y., Serpinsky, O. I., et al. (1999) Mutations in the highly conserved GGQ motif of class 1 polypeptide release factors abolish ability of human eRF1 to trigger peptidyl-tRNA hydrolysis, RNA, 5, 1014-1020.
Seit-Nebi, A., Frolova, L., Justesen, J., and Kisselev, L. (2001) Class-1 translation termination factors: invariant GGQ minidomain is essential for release activity and ribosome binding but not for stop codon recognition, Nucleic Acids Res., 29, 3982-3987.
Mora, L., Heurgue-Hamard, V., Champ, S., Ehrenberg, M., Kisselev, L. L., and Buckingham, R. H. (2003) The essential role of the invariant GGQ motif in the function and stability in vivo of bacterial release factors RF1 and RF2, Mol. Microbiol., 47, 267-275.
Shaw, J. J., and Green, R. (2007) Two distinct components of release factor function uncovered by nucleophile partitioning analysis, Mol. Cell, 28, 458-467, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2007.09.007.
Freistroffer, D. V., Pavlov, M. Y., MacDougall, J., Buckingham, R. H., and Ehrenberg, M. (1997) Release factor RF3 in E. coli accelerates the dissociation of release factors RF1 and RF2 from the ribosome in a GTP-dependent manner, EMBO J., 16, 4126-4133, https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/16.13.4126.
Zavialov, A. V., Buckingham, R. H., and Ehrenberg, M. (2001) A posttermination ribosomal complex is the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for peptide release factor RF3, Cell, 107, 115-124, https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00508-6.
Baranov, P. V., Vestergaard, B., Hamelryck, T., Gesteland, R. F., Nyborg, J., and Atkins, J. F. (2006) Diverse bacterial genomes encode an operon of two genes, one of which is an unusual class-I release factor that potentially recognizes atypical mRNA signals other than normal stop codons, Biol. Direct., 1, 28, https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6150-1-28.
Heurgue-Hamard, V., Champ, S., Mora, L., Merkulova-Rainon, T., Kisselev, L. L., and Buckingham, R. H. (2005) The glutamine residue of the conserved GGQ motif in Saccharomyces cerevisiae release factor eRF1 is methylated by the product of the YDR140w gene, J. Biol. Chem., 280, 2439-2445, https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M407252200.
Weixlbaumer, A., Jin, H., Neubauer, C., Voorhees, R. M., Petry, S., et al. (2008) Insights into translational termination from the structure of RF2 bound to the ribosome, Science, 322, 953-956, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1164840.
Korostelev, A., Asahara, H., Lancaster, L., Laurberg, M., Hirschi, A., et al. (2008) Crystal structure of a translation termination complex formed with release factor RF2, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 105, 19684-19689, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0810953105.
Korostelev, A., Zhu, J., Asahara, H., and Noller, H. F. (2010) Recognition of the amber UAG stop codon by release factor RF1, EMBO J., 29, 2577-2585, https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2010.139.
Santos, N., Zhu, J., Donohue, J. P., Korostelev, A. A., and Noller, H. F. (2013) Crystal structure of the 70S ribosome bound with the Q253P mutant form of release factor RF2, Structure, 21, 1258-1263, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2013.04.028.
Pierson, W. E., Hoffer, E. D., Keedy, H. E., Simms, C. L., Dunham, C. M., and Zaher, H. S. (2016) Uniformity of peptide release is maintained by methylation of release factors, Cell Rep., 17, 11-18, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.085.
Jin, H., Kelley, A. C., Loakes, D., and Ramakrishnan, V. (2010) Structure of the 70S ribosome bound to release factor 2 and a substrate analog provides insights into catalysis of peptide release, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 107, 8593-8598, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1003995107.
Rawat, U. B., Zavialov, A. V., Sengupta, J., Valle, M., Grassucci, R. A., et al. (2003) A cryo-electron microscopic study of ribosome-bound termination factor RF2, Nature, 421, 87-90, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01224.
Rawat, U., Gao, H., Zavialov, A., Gursky, R., Ehrenberg, M., and Frank, J. (2006) Interactions of the release factor RF1 with the ribosome as revealed by cryo-EM, J. Mol. Biol., 357, 1144-1153, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.01.038.
Graille, M., Heurgue-Hamard, V., Champ, S., Mora, L., Scrima, N., et al. (2005) Molecular basis for bacterial class I release factor methylation by PrmC, Mol. Cell, 20, 917-927, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2005.10.025.
Dincbas-Renqvist, V., Engstrom, A., Mora, L., Heurgue-Hamard, V., Buckingham, R., and Ehrenberg, M. (2000) A post-translational modification in the GGQ motif of RF2 from Escherichia coli stimulates termination of translation, EMBO J., 19, 6900-6907, https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.24.6900.
Heurgue-Hamard, V., Champ, S., Engstrom, A., Ehrenberg, M., and Buckingham, R. H. (2002) The hemK gene in Escherichia coli encodes the N(5)-glutamine methyltransferase that modifies peptide release factors, EMBO J., 21, 769-778, https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/21.4.769.
Schmeing, T. M., Huang, K. S., Strobel, S. A., and Steitz, T. A. (2005) An induced-fit mechanism to promote peptide bond formation and exclude hydrolysis of peptidyl-tRNA, Nature, 438, 520-524, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04152.
Polikanov, Y. S., Steitz, T. A., and Innis, C. A. (2014) A proton wire to couple aminoacyl-tRNA accommodation and peptide-bond formation on the ribosome, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 21, 787-793, https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2871.
Svetlov, M. S., Syroegin, E. A., Aleksandrova, E. V., Atkinson, G. C., Gregory, S. T., et al. (2021) Structure of Erm-modified 70S ribosome reveals the mechanism of macrolide resistance, Nat. Chem. Biol., 17, 412-420, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-020-00715-0.
Brunelle, J. L., Shaw, J. J., Youngman, E. M., and Green, R. (2008) Peptide release on the ribosome depends critically on the 2′-OH of the peptidyl-tRNA substrate, RNA, 14, 1526-1531, https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.1057908.
Youngman, E. M., Brunelle, J. L., Kochaniak, A. B., and Green, R. (2004) The active site of the ribosome is composed of two layers of conserved nucleotides with distinct roles in peptide bond formation and peptide release, Cell, 117, 589-599.
Polacek, N., Gomez, M. J., Ito, K., Xiong, L., Nakamura, Y., and Mankin, A. (2003) The critical role of the universally conserved A2602 of 23S ribosomal RNA in the release of the nascent peptide during translation termination, Mol. Cell, 11, 103-112.
Zaher, H. S., Shaw, J. J., Strobel, S. A., and Green, R. (2011) The 2′-OH group of the peptidyl-tRNA stabilizes an active conformation of the ribosomal PTC, EMBO J., 30, 2445-2453, https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2011.142.
Gamper, H., and Hou, Y. M. (2018) tRNA 3′-amino-tailing for stable amino acid attachment, RNA, 24, 1878-1885, https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.068015.118.
Funding
This work was supported by the Illinois State Start-up Funds and by the National Science Foundation (grant no. MCB-1907273).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interests in financial or any other sphere. This article does not contain a description of studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balasanyants, S.M., Aleksandrova, E.V. & Polikanov, Y.S. The Role of Release Factors in the Hydrolysis of Ester Bond in Peptidyl-tRNA. Biochemistry Moscow 86, 1122–1127 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297921090078
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297921090078