Abstract
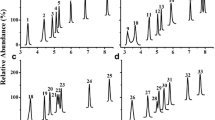
An optimized method for analysis of free amino acids using a modified lithium-citrate buffer system with a Hitachi L-8800 amino acid analyzer is described. It demonstrates clear advantages over the sodium-citrate buffer system commonly used for the analysis of protein hydrolysates. A sample pretreatment technique for amino acid analysis of brain extracts is also discussed. The focus has been placed on the possibility of quantitative determination of the reduced form of glutathione (GSH) with simultaneous analysis of all other amino acids in brain extracts. The method was validated and calibration coefficient (K GSH) was determined. Examples of chromatographic separation of free amino acids in extracts derived from different parts of the brain are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DTNB:
-
5,5′-dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid
- GSH:
-
reduced glutathione
- GSSG:
-
oxidized glutathione
References
Halliwell, B. (1996) Antioxidants in human health and disease, Ann. Rev. Nutr., 16, 33–50.
Perry, T. L., Stedman, D., and Hansen, S. (1968) A versatile lithium buffer elution system for single column automatic amino acid chromatography, J. Chromatogr., 38, 460–466.
Trofimova, L., Ksenofontov, A., Mkrtchyan, G., Graf, A., Baratova, L., and Bunik, V. I. (2016) Quantification of rat brain amino acids: analysis of the data consistency, Curr. Anal. Chem., 11, 1–8.
Ellman, G. L. (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 82, 70–77.
Sedlak, J., and Lindsay, R. H. (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent, Anal. Biochem., 25, 192–205.
Moore, S., Spackman, D. H., and Stein, W. H. (1958) Automatic recording apparatus for use in the chromatography of amino acids, Fed. Proc., 17, 1107–1115.
Smith, A. M. (1951) The determination of amino-acids colorimetrically by the ninhydrin reaction, Analyst, 76, 623–627.
Hamilton, P. B. (1963) Ion exchange chromatography of amino acids, Anal. Chem., 35, 2055–2064.
Tsepkova, P. M., Artiukhov, A. V., Boyko, A. I., Aleshin, V. A., Mkrtchyan, G. V., Zvyagintseva, M. A., Ryabov, S. I., Ksenofontov, A. L., Baratova, L. A., Graf, A. V., and Bunik, V. I. (2017) Thiamine induces long-term changes in amino acid profiles and activities of 2-oxoglutarate and 2-oxoadipate dehydrogenases in rat brain, Biochemistry (Moscow), 82, 723–736.
Riddles, P. W., Blakeley, R. L., and Zerner, B. (1983) Reassessment of Ellman’s reagent, Methods Enzymol., 91, 49–60.
Bland, J. M., and Altman, D. G. (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement, Lancet, 1, 307–310.
Bunce, C. (2009) Correlation, agreement, and Bland–Altman analysis: statistical analysis of method comparison studies, Am. J. Ophthalmol., 148, 4–6.
Giavarina, D. (2015) Understanding bland altman analysis, Biochem. Med., 25, 141–151.
Thompson, J. W. (1926) Glutathione content of normal animals, J. Biol. Chem., 70, 793–800.
Anderson, M. E. (1985) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide in biological samples, Methods Enzymol., 113, 548–555.
Reed, D. J., Babson, J. R., Beatty, P. W., Brodie, A. E., Ellis, W. W., and Potter, D. W. (1980) High-performance liquid chromatography analysis of nanomole levels of glutathione, glutathione disulfide, and related thiols and disulfides, Anal. Biochem., 106, 55–62.
Newton, G. L., Dorian, R., and Fahey, R. C. (1981) Analysis of biological thiols: derivatization with mono-bromobimane and separation by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography, Anal. Biochem., 114, 383–387.
Rahman, I., Kode, A., and Biswas, S. K. (2006) Assay for quantitative determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide levels using enzymatic recycling method, Nat. Protoc., 1, 3159–3165.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A. L. Ksenofontov, A. I. Boyko, G. V. Mkrtchyan, V. N. Tashlitsky, A. V. Timofeeva, A. V. Graf, V. I. Bunik, L. A. Baratova, 2017, published in Biokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 82, No. 10, pp. 1538-1549.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ksenofontov, A.L., Boyko, A.I., Mkrtchyan, G.V. et al. Analysis of free amino acids in mammalian brain extracts. Biochemistry Moscow 82, 1183–1192 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629791710011X
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629791710011X