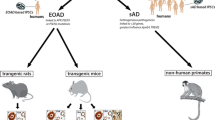
Abstract
In this review, recent data are presented on molecular and cellular mechanisms of pathogenesis of the most widespread (about 95%) sporadic forms of Alzheimer’s disease obtained on in vivo rodent models. Although none of the available models can fully reproduce the human disease, several key molecular mechanisms (such as dysfunction of neurotransmitter systems, especially of the acetylcholinergic system, β-amyloid toxicity, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, disturbances in neurotrophic systems) are confirmed with different models. Injection models, olfactory bulbectomy, and senescence accelerated OXYS rats are reviewed in detail. These three approaches to in vivo modeling of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease have demonstrated a considerable similarity in molecular and cellular mechanisms of pathology development. Studies on these models provide complementary data, and each model possesses its specific advantages. A general analysis of the data reported for the three models provides a multifaceted and the currently most complete molecular picture of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. This is highly relevant also from the practical viewpoint because it creates a basis for elaboration and preclinical studies of means for treatment of this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Irizarry, M. C., McNamara, M., Fedorchak, K., Hsiao, K., and Hyman, B. T. (1997) APPSw transgenic mice develop age-related A beta deposits and neurophil abnormalities, but no neuronal loss in CA1, J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 56, 965–973.
Shinohara, M., Fujioka, S., Murray, M. E., Wojtas, A., Baker, M., Rovelet-Lecrux, A., Rademakers, R., Das, P., Parisi, J. E., Graff-Radford, N. R., Petersen, R. C., Dickson, D. W., and Bu, G. (2014) Regional distribution of synaptic markers and APP correlate with distinct clinico-pathological features in sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s disease, Brain, 137, 1533–1549.
Coyle, J. T., Price, D. L., and DeLong, M. R. (1983) Alzheimer’s disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation, Science, 219, 1184–1190.
Winkler, J., Thal, L. J., Gage, F. H., and Fisher, L. J. (1998) Cholinergic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease, J. Mol. Med., 76, 555–567.
McDonald, M. P., and Overmier, J. B. (1998) Present imperfect: a critical review of animal models of the mnemonic impairments in Alzheimer’s disease, Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 22, 99–120.
Hanin, A., Fisher, A., Hortnagl, H., Leventer, S. M., Potter, P. E., and Walsh, T. J. (1987) Ethylcholine aziridini-um (AF64A; ECMA) and other potential cholinergic neu-ron-specific neurotoxins, in Psychopharmacology: The Third Generation of Progress (Meltzer, H. Y., ed.) Raven Press, N. Y., pp. 341–349.
Chrobak, J. J., Hanin, I., Schmechel, D. E., and Walsh, T. J. (1988) AF64A-induced working memory impairment: behavioral, neurochemical and histological correlates, Brain Res., 463, 107–117.
Lorens, S. K., Kindel, G., Dong, X. W., Lee, J. M., and Hanin, I. (1991) Septal choline acetyltransferase immunoreactive neurons: dose-dependent effects of AF64A, Brain Res. Bull., 26, 965–971.
Hanin, I. (1996) The AF64A model of cholinergic hypo-function: an update, Life Sci., 58, 1955–1964.
Eva, C., Fabrazzo, M., and Costa, E. (1987) Changes of cholinergic, noradrenergic and serotonergic synaptic transmis-sion indices by ethylcholine aziridinium ion (AF64A) infused intraventricularly, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 222, 181–186.
Walsh, T. J., Tilson, H. A., DeHaven, D. L., Mailman, R. B., Fisher, A., and Hanin, I. (1984) AF64A, a cholinergic neurotoxin, selectively depletes acetylcholine in hippocampus and cortex, and produces long-term passive avoidance and radial-arm maze deficits in the rat, Brain Res., 321, 91–102.
Gulyaeva, N. V., Lazareva, N. A., Libe, M. L., Mitrokhina, O. S., Onufriev, M. V., Stepanichev, M. Y., Chernysevskaya, I. A., and Walsh, T. J. (1996) Oxidative stress in the brain following intraventricular administration of ethylcholine aziridinium (AF64A), Brain Res., 726, 174–180.
Stepanichev, M. Y., and Gulyaeva, N. V. (2014) Injection models of Alzheimer’s disease as an approach to investiga-tion of cellular mechanisms of pathogenesis: neurodegen-erative changes, inflammation, neurogenesis disorders, in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From the Genome to the Whole Organism (Ugryumov, M. V., ed.) [in Russian], Vol. 2, Nauchnyi Mir, Moscow, pp. 352–379.
Hanin, I. (1997) Molecular mechanisms of AF64A toxicity in the cholinergic neuron, in Progress in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases (Fisher, A., ed.) Plenum Press, N. Y.-London, pp. 675–680.
Rinner, W. A., Pifl, C., Lassmann, H., and Hortnagl, H. (1997) Induction of apoptosis in vitro and in vivo by the cholinergic neurotoxin ethylcholine aziridinium, Neuroscience, 79, 535–542.
Simon, H. U., Haj-Yehia, A., and Levi-Schaffer, F. (2000) Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction, Apoptosis, 5, 415–418.
Wortwein, G., Stackman, R. W., and Walsh, T. J. (1994) Vitamin E prevents the place learning deficit and the cholinergic hypofunction induced by AF64A, Exp. Neurol., 125, 15–21.
Emerich, D. F., and Walsh, T. J. (1990) Ganglioside AGF2 promotes task-specific recovery and attenuates the cholinergic hypofunction induced by AF64A, Brain Res., 572, 299–307.
Emerich, D. F., Black, B. A., Kesslak, J. P., Cotman, C. W., and Walsh, T. J. (1992) Transplantation of fetal cholinergic neurons into the hippocampus attenuates the cognitive and neurochemical deficits induced by AF64A, Brain Res. Bull., 28, 219–226.
Moiseeva, Y. V., Onufriev, M. V., Lazareva, N. A., Stepanichev, M. Y., and Gulyaeva, N. V. (2001) Free radical mechanisms of septo-hippocampal neurodegeneration caused by cholinotoxin AF64A in rats in vivo, Neirokhimiya, 18, 287–289.
Lautenschlager, M., Onufriev, M. V., Gulyaeva, N. V., Harms, C., Freyer, D., Sehmsdorf, U., Ruscher, K., Moiseeva, Y. V., Arnswald, A., Victorov, I., Dirnagl, U., Weber, J. R., and Hortnagl, H. (2000) Role of nitric oxide in the ethylcholine aziridinium model of delayed apoptotic neurodegeneration in vivo and in vitro, Neuroscience, 97, 383–393.
Stepanichev, M. Y., Libe, M. L., Chernyshevskaya, I. A., Moiseenok, A. G., and Gulyaeva, N. V. (2007) Delayed expression of NADPH-diaphorase in rat brain after administration of the cholinotoxin AF64A, Neurochem. J., 1, 244–248.
Lautenshlager, M., Arnswald, A., Freyer, D., Weber, J. R., and Hortnagl, H. (1997) The AF64A model of cholinergic hypofunction: role of nitric oxide in AF64A-mediated neu-rodegeneration, in Progress in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases (Fisher, A., ed.) Plenum Press, N. Y.-London, pp. 681–686.
Wiley, R. G., Oeltmann, T. N., and Lappi, D. A. (1991) Immunolesioning: selective destruction of neurons using immunotoxin to rat NGF receptor, Brain Res., 562, 149–153.
Waite, J. J., Chen, A. D., Wardlow, M. L., Wiley, R. G., Lappi, D. A., and Thal, L. J. (1995) 192-Immunoglobulin G-saporin produces graded behavioral and biochemical changes accompanying the loss of cholinergic neurons of the basal forebrain and cerebellar Purkinje cells, Neuroscience, 65, 463–476.
Rossner, S., Hartig, W., Schliebs, R., Bruckner, G., Brauer, K., Perez-Polo, J. R., Wiley, R. G., and Bigl, V. (1995) 192IgG-saporin immunotoxin-induced loss of cholinergic cells differentially activates microglia in rat basal forebrain nuclei, J. Neurosci. Res., 41, 335–346.
Seeger, G., Hartig, W., Rossner, S., Schliebs, R., Bruckner, G., Bigl, V., and Brauer, K. (1997) Electron microscopic evidence for microglial phagocytic activity and cholinergic cell death after administration of the immunotoxin 192IgG-saporin in rat, J. Neurosci. Res., 48, 465–476.
Baxter, M. G., Bucci, D. J., Sobel, T. J., Williams, M. J., Gorman, L. K., and Gallagher, M. (1996) Intact spatial learning following lesions of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons, Neuroreport, 7, 1417–1420.
Bassant, M. H., Jouvenceau, A., Apartis, E., Poindessous-Jazat, F., Dutar, P., and Billard, J. M. (1998) Immunolesion of the cholinergic basal forebrain: effects on functional properties of hippocampal and septal neurons, Int. J. Dev. Neurosci., 16, 613–632.
Cooper-Kuhn, C. M., Winkler, J., and Kuhn, H. G. (2004) Decreased neurogenesis after cholinergic forebrain lesion in the adult rat, J. Neurosci. Res., 77, 155–165.
Wrenn, C. C., and Wiley, R. G. (1998) The behavioral functions of the cholinergic basal forebrain: lessons from 192IgG-saporin, Int. J. Dev. Neurosci., 16, 595–602.
Berchtold, N. C., Kesslak, J. P., and Cotman, C. W. (2002) Hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene regu-lation by exercise and the medial septum, J. Neurosci. Res., 68, 511–521.
Paban, V., Farioli, F., Romier, B., Chambon, C., and Alescio-Lautier, B. (2010) Gene expression profile in rat hippocampus with and without memory deficit, Neurobiol. Learning Memory, 94, 42–56.
Paban, V., Chambon, C., Manrique, C., Touzet, C., and Alescio-Lautier, B. (2011) Neurotrophic signaling molecules associated with cholinergic damage in young and aged rats: environmental enrichment as potential therapeutic agent, Neurobiol. Aging, 32, 470–485.
Paban, V., Chambon, C., Farioli, F., and Alescio-Lautier, B. (2011) Gene regulation in the rat prefrontal cortex after learning with or without cholinergic insult, Neurobiol. Learning Memory, 95, 441–452.
Santamaria, J., Khalfallah, O., Sauty, C., Brunet, I., Sibieude, M., Mallet, J., Berrard, S., and Lecomte, M. J. (2009) Silencing of choline acetyltransferase expression by lentivirus-mediated RNA interference in cultured cells and in the adult rodent brain, J. Neurosci. Res., 87, 532–544.
Kamenetz, F., Tomita, T., Hsieh, H., Seabrook, G., Borchelt, D., Iwatsubo, T., Sisodia, S., and Malinow, R. (2003) APP processing and synaptic function, Neuron, 37, 925–937.
Walsh, D. M., Klyubin, I., Fadeeva, J. V., Cullen, W. K., Anwyl, R., Wolfe, M. S., Rowan, M. J., and Selkoe, D. J. (2002) Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid beta protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo, Nature, 416, 535–539.
Morgan, D. (2007) Amyloid, memory and neurogenesis, Exp. Neurol., 205, 330–335.
Hardy, J. (2009) The amyloid hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease: a critical reappraisal, J. Neurochem., 110, 1129–1134.
Gulyaeva, N. V., and Stepanichev, M. Yu. (2010) Abeta(25-35) as proxyholder for amyloidogenic peptides: in vivo evidence, Exp. Neurol., 222, 6–9.
Chen, S. Y., Harding, J. W., and Barnes, C. D. (1996) Neuropathology of synthetic beta-amyloid peptide analogs in vivo, Brain Res., 715, 44–50.
Kowall, N., McKee, A., Yankner, B., and Beal, M. F. (1992) In vivo neurotoxicity of beta-amyloid [beta(1-40)] and the beta(25-35) fragment, Neurobiol. Aging, 13, 537–542.
Stepanichev, M. Y., Zdobnova, I. M., Yakovlev, A. A., Onufriev, M. V., Lazareva, N. A., Zarubenko, I. I., and Gulyaeva, N. V. (2003) Effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha central administration on hippocampal damage in rat induced by amyloid beta-peptide (25-35), J. Neurosci. Res., 71, 110–120.
Maurice, T., Lockhart, B., and Privat, A. (1996) Amnesia induced in mice by centrally administered β-amyloid peptides involves cholinergic dysfunction, Brain Res., 706, 181–189.
Delobette, S., Privat, A., and Maurice, T. (1997) In vitro aggregation facilities beta-amyloid peptide-(25-35)-induced amnesia in the rat, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 319, 1–4.
Yamaguchi, Y., and Kawashima, S. (2001) Effects of β-amyloid-(25-35) on passive avoidance, radial-arm maze learning and choline acetyltransferase activity in the rat, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 412, 265–272.
Stepanichev, M., Lazareva, N., Tukhbatova, G., Salozhin, S., and Gulyaeva, N. (2014) Transient disturbances in con-textual fear memory induced by Aβ(25-35) in rats are accompanied by cholinergic dysfunction, Behav. Brain Res., 259, 152–157.
Berrard, S., Varoqui, H., Cervini, R., Israel, M., Mallet, J., and Diebler, M. F. (1995) Coregulation of two embedded gene products, choline acetyltransferase and the vesicular acetylcholine transporter, J. Neurochem., 65, 939–942.
Gordon, R. Y., Makarova, E. G., Podolski, I. Y., Rogachevsky, V. V., and Kordonets, O. L. (2012) Impairment of protein synthesis is an early effect of amy-loid-β in neurons, Neurochem. J., 29, 139–150.
Ding, Q., Markesbery, W. R., Chen, Q., Li, F., and Keller, J. N. (2005) Ribosome dysfunction is an early event in Alzheimer’s disease, J. Neurosci., 25, 9171–9175.
Shan, X., Chang, Y., and Lin, C. L. (2007) Messenger RNA oxidation is an early event preceding cell death and causes reduced protein expression, FASEB J., 21, 2753–2764.
Stepanichev, M. Y., Zdobnova, I. M., Zarubenko, I. I., Lazareva, N. A., and Gulyaeva, N. V. (2004) Amyloid-beta(25-35)-induced memory impairments correlate with cell loss in rat hippocampus, Physiol. Behav., 80, 647–655.
Virok, D. P., Simon, D., Bozso, Z., Rajko, R., Datki, Z., Balint, E., Szegedi, V., Janaky, T., Penke, B., and Fulop, L. (2011) Protein array based interactome analysis of amyloid-β indicates an inhibition of protein translation, J. Proteome Res., 10, 1538–1547.
Frautschy, S. A., Cole, G. M., and Baird, A. (1992) Phagocytosis and deposition of vascular beta-amyloid in rat brains injected with Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid, Am. J. Pathol., 140, 1389–1399.
Hickman, S. E., Allison, E. K., and El Khoury, J. (2008) Microglial dysfunction and defective beta-amyloid clear-ance pathways in aging Alzheimer’s disease mice, J. Neurosci., 28, 8354–8360.
Qiu, W. Q., Ye, Z., Kholodenko, D., Seubert, P., and Selkoe, D. J. (1997) Degradation of amyloid beta-protein by a metalloprotease secreted by microglia and other neural and non-neural cells, J. Biol. Chem., 272, 6641–6646.
Weldon, D., Rogers, S. D., Ghilardi, J. R., Finke, M. P., Cleary, J. P., O’Hare, E., Esler, W. P., Maggio, J. E., and Mantyh, P. W. (1998) Fibrillar β-amyloid induces microglial phagocytosis, expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, and loss of a selected population of neurons in rat CNS in vivo, J. Neurosci., 18, 2161–2173.
Rogers, J., and Lue, L. F. (2001) Microglial chemotaxis, activation, and phagocytosis of amyloid β-peptide as linked phenomena in Alzheimer’s disease, Neurochem. Int., 39, 333–340.
Sigurdsson, E. M., Lee, J. M., Dong, X. W., Hejna, M. J., and Lorens, S. A. (1997) Bilateral injections of amyloid-beta 25-35 into the amygdala of young Fischer rats: behavioral, neurochemical, and time dependent histopathological effects, Neurobiol. Aging, 18, 591–608.
Sigurdsson, E. M., Lee, J. M., Dong, X. W., Hejna, M. J., and Lorens, S. A. (1997) Laterality in the histological effects of injections of amyloid-beta 25-35 into the amygdala of young Fischer rats, J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 56, 714–725.
Stepanichev, M. Y., Zdobnova, I. M., Yakovlev, A. A., Onufriev, M. V., Lazareva, N. A., Zarubenko, I. I., and Gulyaeva, N. V. (2003) Effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha central administration on hippocampal damage in rat induced by amyloid beta-peptide (25-35), J. Neurosci. Res., 71, 110–120.
Stepanichev, M. Y., Flegontova, O. V., Lazareva, N. A., Egorova, L. K., and Gulyaeva, N. V. (2006) Influence of anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-4 on neurodegeneration I rats induced by beta-amyloid peptide, Neirokhimiya, 23, 67–72.
Mitrokhina, O. S., Stepanichev, M., Lazareva, N. A., Moiseeva, Y. V., Onufriev, M. V., and Gulyaeva, N. V. (1999) Effect of intracerebroventricular administration of the (25-35) fragment of beta-amyloid peptide on the lipid peroxidation level in rat brain structures and blood, Dokl. Akad. Nauk, 368, 711–713.
Stepanichev, M. Y., Onufriev, M. V., Yakovlev, A. A., Khrenov, A. I., Peregud, D. I., Vorontsova, O. N., Lazareva, N. A., and Gulyaeva, N. V. (2008) Amyloid-beta (25-35) increases activity of neuronal NO-synthase in rat brain, Neurochem. Int., 52, 1114–1124.
Jin, K., Peel, A. L., Mao, X. O., Xie, L., Cottrell, B. A., Henshall, D. C., and Greenberg, D. A. (2004) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 343–347.
Hamilton, L. K., Joppe, S. E., Cochard, L., and Fernandes, K. J. (2013) Aging and neurogenesis in the adult forebrain: what we have learned and where we should go from here, Eur. J. Neurosci., 37, 1978–1986.
Lazarov, O., Mattson, M. P., Peterson, D. A., Pimplikar, S. W., and Van Praag, H. (2010) When neurogenesis encounters aging and disease, Trends Neurosci., 33, 569–579.
Haughey, N. J., Nath, A., Chan, S. L., Borchard, A. C., Rao, M. S., and Mattson, M. P. (2002) Disruption of neurogenesis by amyloid beta-peptide, and perturbed neural progenitor cell homeostasis, in models of Alzheimer’s disease, J. Neurochem., 83, 1509–1524.
Sotthibundhu, A., Li, Q. X., Thangnipon, W., and Coulson, E. J. (2009) Abeta(1-42) stimulates adult SVZ neurogenesis through the p75 neurotrophin receptor, Neurobiol. Aging, 30, 1975–1985.
Li, X., and Zuo, P. (2005) Effects of Abeta25-35 on neurogenesis in the adult mouse subventricular zone and dentate gyrus, Neurol. Res., 27, 218–222.
Stepanichev, M. Y., Moiseeva, Y. V., Lazareva, N. A., Onufriev, M. V., and Gulyaeva, N. V. (2009) Changes of the cell proliferation in the subventricular zone of the brain of adult rats on injection of β-amyloid peptide (25-35), Morfologiya, 135, 13–16.
Estrada, C., and Murillo-Carretero, M. (2005) Nitric oxide and adult neurogenesis in health and disease, Neuroscientist, 11, 294–307.
Moreno-Lopez, B., Noval, J. A., Gonzalez-Bonet, L., and Estrada, C. (2000) Morphological bases for a role of nitric oxide in adult neurogenesis, Brain Res., 869, 244–250.
Jaffrey, S. R., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Ferris, C. D., Tempst, P., and Snyder, S. H. (2001) Protein S-nitrosylation: a physiological signal for neuronal nitric oxide, Nat. Cell Biol., 3, 193–197.
Murillo-Carretero, M., Ruano, M. J., Matarredona, E. R., Villalobo, A., and Estrada, C. (2002) Antiproliferative effect of nitric oxide on epidermal growth factor-responsive human neuroblastoma cells, J. Neurochem., 83, 119–131.
Salkovic-Petrisic, M., Knezovic, A., Hoyer, S., and Riederer, P. (2013) What have we learned from the strepto-zotocin-induced animal model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease, about the therapeutic strategies in Alzheimer’s research, J. Neural Transm. (Vienna), 120, 233–252.
Genrikhs, E. E., Stelmashook, E. V., Golyshev, S. A., Aleksandrova, O. P., and Isaev, N. K. (2017) Streptozotocin causes neurotoxic effect in cultured cerebellar granule neurons, Brain. Res. Bull., 130, 90–94.
Halawany, A. M., Sayed, N. S., Abdallah, H. M., and Dine, R. S. (2017) Protective effects of gingerol on streptozo-tocin-induced sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: emphasis on inhibition of β-amyloid, COX-2, alpha-, beta-secretases and APH1a, Sci. Rep., 7, 2902.
Bassani, T. B., Bonato, J. M., Machado, M. M. F., Coppola-Segovia, V., Moura, E. L. R., Zanata, S. M., Oliveira, R. M., and Vital, M. A. (2017) Decrease in adult neurogenesis and neuroinflammation are involved in spatial memory impairment in the streptozotocin-induced model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease in rats, Mol. Neurobiol., 16.
Zakaria, R., Wan Yaacob, W. M., Othman, Z., Long, I., Ahmad, A. H., and Al-Rahbi, B. (2017) Lipopolysaccha-ride-induced memory impairment in rats: a model of Alzheimer’s disease, Physiol. Res., 12.
Houdek, H. M., Larson, J., Watt, J. A., and Rosenberger, T. A. (2014) Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces a dose-dependent activation of neuroglia and loss of basal fore-brain cholinergic cells in the rat brain, Inflamm. Cell Signal., 1, 47.
Willard, L. B., Hauss-Wegrzyniak, B., and Wenk, G. L. (1999) Pathological and biochemical consequences of acute and chronic neuroinflammation within the basal forebrain cholinergic system of rats, Neuroscience, 88, 193–200.
Arai, H., Furuya, T., Yasuda, T., Miura, M., Mizuno, Y., and Mochizuki, H. (2004) Neurotoxic effects of lipopolysaccha-ride on nigral dopaminergic neurons are mediated by microglial activation, interleukin-1beta, and expression of caspase-11 in mice, J. Biol. Chem., 279, 51647–51653.
Desai, R. A., Davies, A. L., Tachrount, M., Kasti, M., Laulund, F., Golay, X., and Smith, K. J. (2016) Cause and prevention of demyelination in a model multiple sclerosis lesion, Ann. Neurol., 79, 591–604.
Stepanichev, M., Dygalo, N. N., Grigoryan, G., Shishkina, G. T., and Gulyaeva, N. (2014) Rodent models of depres-sion: neurotrophic and neuroinflammatory biomarkers, Biomed. Res. Int., 932757.
Attems, J., Lintner, F., and Jellinger, K. A. (2005) Olfactory involvement in aging and Alzheimer’s disease: an autopsy study, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 7, 149–157.
Van Hoesen, G. W., Augustinack, J. C., Dierking, J., Redman, S. J., and Thangavel, R. (2000) The parahippocampal gyrus in Alzheimer’s disease. Clinical and pre-clinical neuroanatomical correlates, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. USA, 911, 254–274.
Kovacs, T., Cairns, N. J., and Lantos, P. L. (1999) Beta-amyloid deposition and neurofibrillary tangle formation in the olfactory bulb in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease, Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol., 25, 481–491.
Kus, L., Borys, E., Ping, Chu, Y., Ferguson, S. M., Blakely, R. D., Emborg, M. E., Kordower, J. H., Levey, A. I., and Mufson, E. J. (2003) Distribution of high affinity choline transporter immunoreactivity in the primate central nervous system, J. Comp. Neurol., 463, 341–357.
Wang, H. Y., Lee, D. H., D’Andrea, M. R., Peterson, P. A., Shank, R. P., and Reitz, A. B. (2000) Beta-amyloid(1-42) binds to alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor with high affinity. Implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathology, J. Biol. Chem., 275, 5626–5632.
Nagele, R. G., D’Andrea, M. R., Anderson, W. J., and Wang, H. Y. (2002) Intracellular accumulation of beta-amyloid(1-42) in neurons is facilitated by the alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in Alzheimer’s disease, Neuroscience, 110, 199–211.
Christen-Zaech, S., Kraftsik, R., Pillevuit, O., Kiraly, M., Martins, R., Khalili, K., and Miklossy, J. (2003) Early olfactory involvement in Alzheimer’s disease, Can. J. Neurol. Sci., 30, 20–25.
Ferreyra-Moyano, H., and Barragan, E. (1989) The olfactory system and Alzheimer’s disease, Int. J. Neurosci., 49, 157–197.
Pearson, R. C., Esiri, M. M., Hiorns, R. W., Wilcock, G. K., and Powell, T. P. (1985) Anatomical correlates of the distribution of the pathological changes in the neocortex in Alzheimer’s disease, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 82, 4531–4534.
Brunjes, P. C., and Frazier, L. L. (1986) Maturation and plasticity in the olfactory system of vertebrates, Brain Res., 396, 1–45.
Ruitenberg, M. J., and Vukovic, J. (2008) Promoting central nervous system regeneration: lessons from cranial nerve I, Restor. Neurol. Neurosci., 26, 183–196.
Gomez, C., Brinon, J. G., Orio, L., Colado, M. I., Lawrence, A. J., Zhou, F. C., Vidal, M., Barbado, M. V., and Alonso, J. R. (2007) Changes in the serotonergic system in the main olfactory bulb of rats unilaterally deprived from birth to adulthood, J. Neurochem., 100, 924–938.
Gomez, C., Brinon, J. G., Colado, M. I., Orio, L., Vidal, M., Barbado, M. V., and Alonso, J. R. (2006) Differential effects of unilateral olfactory deprivation on noradrenergic and cholinergic systems in the main olfactory bulb of the rat, Neuroscience, 141, 2117–2128.
Loopuijt, L. D., and Sebens, J. B. (1990) Loss of dopamine receptors in the olfactory bulb of patients with Alzheimer’s disease, Brain Res., 529, 239–234.
Damulin, I. V. (1999) Alzheimer’s disease, Ross. Med. Zh., 6, 45–48.
Gavrilova, S. I. (2002) Alzheimer’s disease: current concepts about diagnosis and therapy, Ross. Med. Zh., 10, 36.
Aleksandrova, I. Y., Kuvichkin, V. V., Kashparov, I. V., Medvinskaya, N. I., Nesterova, I. V., Lunin, S. M., Samokhin, A. N., and Bobkova, N. V. (2004) Increased level of β-amyloid in the brain of bulbectomized mice, Biochemistry (Moscow), 69, 176–180.
Nesterova, I. V., Gurevich, E. V., Nesterov, V. I., Otmakhova, N. A., and Bobkova, N. V. (1997) Bulbectomy-induced loss of raphe neurons is counteracted by antidepressant treatment, Prog. Neuropsychopharm. Biol. Psychiatry, 21, 127–140.
Bobkova, N. V., Nesterova, I. V., and Nesterov, V. I. (2001) The state of cholinergic structures in forebrain of bulbectomized mice, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 131, 427–431.
Kamynina, A. V., Volpina, O. M., Medvinskaya, N. I., Aleksandrova, I. J., Volkova, T. D., Koroev, D. O., Samokhin, A. N., Nesterova, I. V., Shelukhina, I. V., Kryukova, E. V., Tsetlin, V. I., Ivanov, V. T., and Bobkova, N. V. (2010) Vaccination with peptide 173-193 of acetylcholine receptor α7-subunit prevents memory loss in olfactory bulbectomized mice, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 21, 249–261.
Bobkova, N. V., Kamynina, A. V., Medvinskaya, N. I., Koroev, D. O., Nesterova, I. V., Aleksandrova, I. J., Samokhin, A. N., Volkova, T. D., and Volpina, O. M. (2009) Influence of passive immunization with antibodies to the extracellular fragment of α7-ACHR on the Alzheimer’s type neurodegenerative process, Vestn. Nov. Med. Tekhnol., 16, 214–216.
Koliatsos, V. E., Dawson, T. M., Kecojevic, A., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y. F., and Huang, K. X. (2004) Cortical interneurons become activated by deafferentation and instruct the apoptosis of pyramidal neurons, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 14264–14269.
Bobkova, N. V., Nesterova, I. V., Dana, R., Dana, E., Nesterov, V. I., Aleksandrova, I. Y., Medvinskaya, N. I., and Samokhin, A. N. (2004) Morphofunctional changes in neurons in the temporal cortex of the brain in relation to spatial memory in bulbectomized mice after treatment with mineral ascorbates, Neurosci. Behav. Physiol., 34, 671–676.
Han, F., Shioda, N., Moriguchi, S., Qin, Z.-H., and Fukunaga, K. (2008) The vanadium (IV) compound rescues septo-hippocampal cholinergic neurons from neu-rodegeneration in olfactory bulbectomized mice, Neuroscience, 151, 671–679.
Broekkamp, C. L., O’Connor, W. T., Tonnaer, J. A., Rijk, H. W., and Van Delet, A. M. (1986) Corticosterone, choline acetyltransferase and noradrenaline levels in olfactory bulbectomized rats in relation to changes in passive avoidance acquisition and open field activity, Physiol. Behav., 37, 429–434.
Bobkova, N., Vorobyov, V., Medvinskaya, N., Nesterova, I., Tatarnikova, O., Nekrasov, P., Samokhin, A., Deev, A., Sengpiel, F., Koroev, D., and Volpina, O. (2016) Immunization against specific fragments of neurotrophin p75 receptor protects forebrain cholinergic neurons in the olfac-tory bulbectomized mice, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 53, 289–301.
Beck, M., Bigl, V., and Rossner, S. (2003) Guinea pigs as a nontransgenic model for APP processing in vitro and in vivo, Neurochem. Res., 28, 637–644.
Battaglia, F., Wang, H. Y., Ghilardi, M. F., Gashi, E., Quartarone, A., Friedman, E., and Nixon, R. A. (2007) Cortical plasticity in Alzheimer’s disease in humans and rodents, Biol. Psychiatry, 62, 1405–1412.
Reddy, P. H., Mani, G., Park, B. S., Jacques, J., Murdoch, G., Whetsell, W., Jr., Kaye, J., and Manczak, M. (2005) Differential loss of synaptic proteins in Alzheimer’s disease: implications for synaptic dysfunction, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 7, 103–117.
Novoselova, E. B., Bobkova, N. V., Sinotova, O. A., Ogai, V. B., Glushkova, E. B., Medvinskaya, N. I., and Samokhin, A. N. (2003) The immune status of bulbectomized mice, Dokl. Biol. Sci., 393, 505–507.
Wynn, Z. J., and Cummings, J. L. (2004) Cholinesterase inhibitor therapies and neuropsychiatric manifestations of Alzheimer’s disease, Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord., 17, 100–108.
Yamamoto, T., Jin, J., and Watanabe, S. (1997) Characteristics of memory dysfunction in olfactory bulbectomized rats and the effects of cholinergic drugs, Behav. Brain Res., 83, 57–62.
Upton, N., Chuang, T. T., Hunter, A. J., and Virley, D. J. (2008) 5-HT(6) receptor antagonists as novel cognitive enhancing agents for Alzheimer’s disease, Neurotherapeutics, 5, 458–469.
Avetisyan, A. V., Samokhin, A. N., Alexandrova, I. Y., Zinovkin, R. A., Simonyan, R. A., and Bobkova, N. V. (2016) Mitochondrial dysfunction in neocortex and hippocampus of olfactory bulbectomized mice, a model of Alzheimer’s disease, Biochemistry (Moscow), 81, 615–623.
Smith, D. H., Chen, X. H., Iwata, A., and Graham, D. I. (2003) Amyloid beta accumulation in axons after traumatic brain injury in humans, J. Neurosurg., 8, 1072–1077.
Selkoe, D. (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy, Physiol. Rev., 81, 741–766.
Vetrivel, K. S., and Thinakaran, G. (2006) Amyloidogenic processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein in intracellu-lar compartments, Neurology, 66, 69–73.
Chyung, J. H., and Selkoe, D. J. (2003) Inhibition of receptor-mediated endocytosis demonstrates generation of amyloid β-protein at the cell surface, J. Biol. Chem., 278, 51035–51043.
Marin, N., Romero, B., Bosch-Morell, F., Llansola, M., Felipo, V., Roma, J., and Romero, F. J. (2000) Beta-amyloid-induced activation of caspase-3 in primary cultures of rat neurons, Mech. Ageing Dev., 119, 63–67.
Pentzek, M., Grass-Kapanke, B., and Ihl, R. (2007) Odor identification in Alzheimer’s disease and depression, Aging Clin. Exp. Res., 19, 255–258.
Song, C., and Leonard, B. E. (2005) The olfactory bulbectomized rat as a model of depression, Neurosci. Biobeh. Rev., 29, 627–647.
Meyerson, L. R., Wennogle, L. P., Abel, M. S., Coupet, J., Lippa, A. S., Rauh, C. E., and Beer, B. (1982) Human brain receptor alterations in suicide victims, Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 17, 159–163.
Otmakhova, N. A., Gurevich, E. V., Katkov, Y. A., Nesterova, I. V., and Bobkova, N. V. (1992) Dissociation of multiple behavioral effects between olfactory bulbectomized C57Bl/6J and DBA/2J mice, Physiol. Behav., 52, 441–448.
Gurevich, E. V., Aleksandrova, I. A., Otmakhova, N. A., Katkov, Y. A., Nesterova, I. V., and Bobkova, N. V. (1993) Effects of bulbectomy and subsequent antidepressant treatment on brain 5-HT2 and 5-HT1A receptors in mice, Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 45, 65–70.
Sheline, Y. I., West, T., Yarasheski, K., Swarm, R., Jasielec, M. S., Fisher, J. R., Ficker, W. D., Yan, P., Xiong, C., Frederiksen, C., Grzelak, M. V., Chott, R., Bateman, R. J., Morris, J. C., Mintun, M. A., Lee, J. M., and Cirrito, J. R. (2014) An antidepressant decreases CSF Aβ production in healthy individuals and in transgenic AD mice, Sci. Transl. Med., 14, 236.
Marine, N., and Boriana, A. (2014) Olfactory markers of depression and Alzheimer’s disease, Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 45, 262–270.
Djordjevic, J., Jones-Gotman, M., De Sousa, K., and Chertkow, H. (2008) Olfaction in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease, Neurobiol. Aging, 29, 693–706.
Saiz-Sanchez, D., De La Rosa-Prieto, C., Ubeda-Banon, I., and Martinez-Marcos, A. (2013) Interneurons and beta-amyloid in the olfactory bulb, anterior olfactory nucleus and olfactory tubercle in APPxPS1 transgenic mice model of Alzheimer’s disease, Anat. Rec., 296, 1413–1423.
Saiz-Sanchez, D., Flores-Cuadrado, A., Ubeda-Banon, I., De la Rosa-Prieto, C., and Martinez-Marcos, A. (2016) Interneurons in the human olfactory system in Alzheimer’s disease, Exp. Neurol., 276, 13–21.
Wu, N., Rao, X., Gao, Y., Wang, J., and Xu, F. (2013) Amyloid-β deposition and olfactory dysfunction in an Alzheimer’s disease model, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 37, 699–712.
Zelaya, M. V., Perez-Valderrama, E., De Morentin, X. M., Tunon, T., Ferrer, I., Luquin, M. R., Fernandez-Irigoyen, J., and Santamaria, E. (2015) Olfactory bulb proteome dynamics during the progression of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: identification of common and distinct olfactory targets across Alzheimer-related co-pathologies, Oncotarget, 24, 39437–39456.
Doorn, K. J., Goudriaan, A., Blits-Huizinga, C., Bol, J. G., Rozemuller, A. J., Hoogland, P. V., Lucassen, P. J., Drukarch, B., Van de Berg, W. D., and Van Dam, A. M. (2014) Increased amoeboid microglial density in the olfactory bulb of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s patients, Brain Pathol., 24, 152–165.
Morley, J. E., Armbrecht, H. J., Farr, S. A., and Kumar, V. B. (2012) The senescence accelerated mouse (SAMP8) as a model for oxidative stress and Alzheimer’s disease, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1822, 650–656.
Ito, K. (2013) Frontiers of model animals for neuro-science: two prosperous aging model animals for promot-ing neuroscience research, Exp. Anim., 62, 275–280.
Kolosova, N. G., Stefanova, N. A., Korbolina, E. E., Fursova, A. Z., and Kozhevnikova, O. S. (2014) Senescence-accelerated OXYS rats: a genetic model of premature aging and age-related diseases, Adv. Gerontol., 4, 294–298.
Beregovoy, N. A., Sorokina, N. S., Starostina, M. V., and Kolosova, N. G. (2011) Age-specific peculiarities of formation of long-term post-tetanic potentiation in OXYS rats, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 151, 71–73.
Stefanova, N. A., Kozhevnikova, O. S., Vitovtov, A. O., Maksimova, K. Y., Logvinov, S. V., Rudnitskaya, E. A., Korbolina, E. E., Muraleva, N. A., and Kolosova, N. G. (2014) Senescence-accelerated OXYS rats: a model of age-related cognitive decline with relevance to abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease, Cell Cycle, 13, 898–909.
Stefanova, N. A., Muraleva, N. A., Skulachev, V. P., and Kolosova, N. G. (2014) Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in senescence-accelerated OXYS rats can be partially retarded with mitochondria-targeted antioxidant SkQ1, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 38, 681–694.
Stefanova, N. A., Muraleva, N. A., Maksimova, K. Y., Rudnitskaya, E. A., Kiseleva, E., Telegina, D. V., and Kolosova, N. G. (2016) An antioxidant specifically targeting mitochondria delays progression of Alzheimer’s dis-ease-like pathology, Aging (Albany NY), 11, 2713–2733.
Kolosova, N. G., Tyumentsev, M. A., Muraleva, N. A., Kiseleva, E. V., Vitovtov, A. O., and Stefanova, N. A. (2017) Antioxidant SkQ1 alleviates signs of Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in old OXYS rats by reversing mito-chondrial deterioration, Curr. Alzheimer Res., doi: 10.2174/1567205014666170621111033.
Stefanova, N. A., Muraleva, N. A., Skulachev, V. P., and Kolosova, N. G. (2014) Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in senescence-accelerated OXYS rats can be partially retarded with mitochondria-targeted antioxidant SkQ1, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 38, 681–694.
Stefanova, N. A., Korbolina, E. E., Ershov, N. I., Rogaev, E. I., and Kolosova, N. G. (2015) Changes in the transcriptome of the prefrontal cortex of OXYS rats as the signs of Alzheimer’s disease development, Vavilov J. Genet. Breed., 19, 74–82.
Stefanova, N. A., Muraleva, N. A., Korbolina, E. E., Kiseleva, E., Maksimova, K., and Kolosova, N. G. (2015) Amyloid accumulation is a late event in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in nontransgenic rats, Oncotarget, 6, 1396–1413.
Swerdlow, R. H., and Khan, S. M. (2004) A “mitochondrial cascade hypothesis” for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease, Med. Hypotheses, 63, 8–20.
Gerschutz, A., Heinsen, H., and Grunblatt, E., Wagner, A. K., Bartl, J., Meissner, C., Fallgatter, A. J., Al-Sarray, S., Troakes, C., Ferrer, I., Arzberger, N., Deckert, J., Riederer, P., Fischer, T., Tatschner, T., and Monoranu, C. M. (2013) Neuron-specific mitochondrial DNA deletion levels in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease, Curr. Alzheimer Res., 10, 1041–1046.
Loshchenova, P. S., Sinitsyna, O. I., Fedoseeva, L. A., Stefanova, N. A., and Kolosova, N. G. (2015) Influence of antioxidant SkQ1 on accumulation of mitochondrial DNA deletions in the hippocampus of senescence accelerated OXYS rats, Biochemistry (Moscow), 80, 596–603.
Mawuenyega, K. G., Sigurdson, W., Ovod, V., Munsell, L., Kasten, T., Morris, J. C., Yarasheski, K. E., and Bateman, R. J. (2013) Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease, Science, 330, 1774.
Kanemitsu, H., Tomiyama, T., and Mori, H. (2003) Human neprilysin is capable of degrading amyloid beta peptide not only in the monomeric form but also the pathological oligomeric form, Neurosci. Lett., 350, 113–116.
Rudnitskaya, E. A., Maksimova, K. Y., Muraleva, N. A., Logvinov, S. V., Yanshole, L. V., Kolosova, N. G., and Stefanova, N. A. (2015) Beneficial effects of melatonin in a rat model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease, Biogerontology, 16, 303–316.
Rudnitskaya, E. A., Muraleva, N. A., Maksimova, K. Y., Kiseleva, E., Kolosova, N. G., and Stefanova, N. A. (2015) Melatonin attenuates memory impairment, amyloid-β accumulation, and neurodegeneration in a rat model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease, J. Alzheimer’s Dis., 47, 103–116.
Fefanova, N. A., Maksimova, K. Y., Kiseleva, E., Rudnitskaya, E. A., Muraleva, N. A., and Kolosova, N. G. (2015) Melatonin attenuates impairments of structural hippocampal neuroplasticity in OXYS rats during active progression of Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology, J. Pineal. Res., 59, 163–177.
Tan, D. X., Manchester, L. C., Qin, L., and Reiter, R. J. (2016) Melatonin: a mitochondrial targeting molecule involving mitochondrial protection and dynamics, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 16, 17.
Rudnitskaya, E. A., Kolosova, N. G., and Stefanova, N. A. (2017) Impact of changes in neurotrophic supplementation on development of Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in OXYS rats, Biochemistry (Moscow), 82, 318–329.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N. V. Gulyaeva, N. V. Bobkova, N. G. Kolosova, A. N. Samokhin, M. Yu. Stepanichev, N. A. Stefanova, 2017, published in Biokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 82, No. 10, pp. 1427-1443.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gulyaeva, N.V., Bobkova, N.V., Kolosova, N.G. et al. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: Studies on rodent models in vivo . Biochemistry Moscow 82, 1088–1102 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917100029
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917100029