Abstract
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin protein, one of the key components of cytoskeleton. They are polar filaments whose plus-ends usually oriented toward the cell periphery are more dynamic than their minus-ends, which face the center of the cell. In cells, microtubules are organized into a network that is being constantly rebuilt and renovated due to stochastic switching of its individual filaments from growth to shrinkage and back. Because of these dynamics and their mechanical properties, microtubules take part in various essential processes, from intracellular transport to search and capture of chromosomes during mitosis. Microtubule dynamics are regulated by many proteins that are located on the plus-ends of these filaments. One of the most important and abundant groups of plus-end-interacting proteins are EB-family proteins, which autonomously recognize structures of the microtubule growing plus-ends, modulate their dynamics, and recruit multiple partner proteins with diverse functions onto the microtubule plus-ends. In this review, we summarize the published data about the properties and functions of EB-proteins, focusing on analysis of their mechanism of interaction with the microtubule growing ends.
Similar content being viewed by others
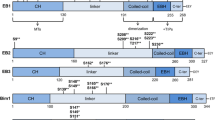
Abbreviations
- APC:
-
adenomatous polyposis coli (tumor suppressor protein)
- Bim1:
-
binding microtubules protein 1 (yeast S. cerevisiae EB analog)
- CH:
-
calponin homology domain
- EB-proteins:
-
end-binding proteins (family of proteins binding to growing microtubule ends)
- EBH:
-
EB-homology domain
- Mal3:
-
microtubule integrity protein (yeast S. pombe EB analog)
- XMAP215:
-
Xenopus microtubule-associated protein 215 kDa
References
Hawkins, T., Mirigian, M., Selcuk Yasar, M., and Ross, J. L. (2010) Mechanics of microtubules, J. Biomech., 43, 23–30.
Cassimeris, L., Pryer, N. K., and Salmon, E. D. (1988) Realtime observations of microtubule dynamic instability in living cells, J. Cell Biol., 107, 2223–2231.
Mitchison, T., and Kirschner, M. (1984) Dynamic instability of microtubule growth, Nature, 312, 237–242.
Desai, A., and Mitchison, T. J. (1997) Microtubule poly-merization dynamics, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 13, 83–117.
Satir, P., and Christensen, S. T. (2007) Overview of structure and function of mammalian cilia, Annu. Rev. Physiol., 69, 377–400.
Tanaka, E. M., and Kirschner, M. W. (1991) Microtubule behavior in the growth cones of living neurons during axon elongation, J. Cell Biol., 115, 345–363.
Tvorogova, A. V., and Vorob’ev, I. A. (2012) Microtubules suppress blebbing and stimulate lamellae extension in spreading fibroblasts, Tsitologiya, 54, 742–753.
Li, R., and Gundersen, G. G. (2008) Beyond polymer polarity: how the cytoskeleton builds a polarized cell, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 9, 860–873.
McIntosh, J. R., Grishchuk, E. L., and West, R. R. (2002) Chromosome-microtubule interactions during mitosis, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 18, 193–219.
Walker, R. A., O’Brien, E. T., Pryer, N. K., Soboeiro, M. F., Voter, W. A., Erickson, H. P., and Salmon, E. D. (1988) Dynamic instability of individual microtubules analyzed by video light microscopy: rate constants and transition frequencies, J. Cell Biol., 107, 1437–1448.
Akhmanova, A., and Steinmetz, M. O. (2008) Tracking the ends: a dynamic protein network controls the fate of micro-tubule tips, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 9, 309–322.
Akhmanova, A., and Hoogenraad, C. C. (2005) Micro-tubule plus-end-tracking proteins: mechanisms and func-tions, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 17, 47–54.
Kumar, P., and Wittmann, T. (2012) +TIPs: SxIPping along microtubule ends, Trends Cell Biol., 22, 418–428.
Al-Bassam, J., and Chang, F. (2011) Regulation of micro-tubule dynamics by TOG-domain proteins XMAP215/ Dis1 and CLASP, Trends Cell Biol., 21, 604–614.
Varga, V., Helenius, J., Tanaka, K., Hyman, A. A., Tanaka, T. U., and Howard, J. (2006) Yeast kinesin-8 depolymerizes microtubules in a length-dependent manner, Nat. Cell Biol., 8, 957–962.
Gudimchuk, N., Vitre, B., Kim, Y., Kiyatkin, A., Cleveland, D. W., Ataullakhanov, F. I., and Grishchuk, E. L. (2013) Kinetochore kinesin CENP-E is a processive bi-directional tracker of dynamic microtubule tips, Nat. Cell Biol., 15, 1079–1088.
Chen, Y., and Hancock, W. O. (2015) Kinesin-5 is a micro-tubule polymerase, Nat. Commun., 6, 8160.
Moore, A. T., Rankin, K. E., von Dassow, G., Peris, L., Wagenbach, M., Ovechkina, Y., Andrieux, A., Job, D., and Wordeman, L. (2005) MCAK associates with the tips of polymerizing microtubules, J. Cell Biol., 169, 391–397.
Lampert, F., Hornung, P., and Westermann, S. (2010) The Dam1 complex confers microtubule plus end-tracking activity to the Ndc80 kinetochore complex, J. Cell Biol., 189, 641–649.
Lansbergen, G., and Akhmanova, A. (2006) Microtubule plus end: a hub of cellular activities, Traffic, 7, 499–507.
Van de Willige, D., Hoogenraad, C. C., and Akhmanova, A. (2016) Microtubule plus-end tracking proteins in neuronal development, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 73, 2053–2077.
Su, L. K., and Qi, Y. (2001) Characterization of human MAPRE genes and their proteins, Genomics, 71, 142–149.
De Groot, C. O., Jelesarov, I., Damberger, F. F., Bjelic, S., Scharer, M. A., Bhavesh, N. S., Grigoriev, I., Buey, R. M., Wüthrich, K., Capitani, G., Akhmanova, A., and Steinmetz, M. O. (2010) Molecular insights into mammalian end-binding protein heterodimerization, J. Biol. Chem., 285, 5802–5814.
Komarova, Y., De Groot, C. O., Grigoriev, I., Gouveia, S. M., Munteanu, E. L., Schober, J. M., Honnappa, S., Buey, R. M., Hoogenraad, C. C., Dogterom, M., Borisy, G. G., Steinmetz, M. O., and Akhmanova, A. (2009) Mammalian end binding proteins control persistent microtubule growth, J. Cell Biol., 184, 691–706.
Slep, K. C., and Vale, R. D. (2007) Structural basis of microtubule plus end tracking by XMAP215, CLIP-170 and EB1, Mol. Cell, 27, 976–991.
Honnappa, S., John, C. M., Kostrewa, D., Winkler, F. K., and Steinmetz, M. O. (2005) Structural insights into the EB1–APC interaction, EMBO J., 24, 261–269.
Slep, K. C., Rogers, S. L., Elliott, S. L., Ohkura, H., Kolodziej, P. A., and Vale, R. D. (2005) Structural determinants for EB1-mediated recruitment of APC and spectraplakins to the microtubule plus end, J. Cell Biol., 168, 587–598.
Maurer, S. P., Fourniol, F. J., Bohner, G., Moores, C. A., and Surrey, T. (2012) EBs recognize a nucleotide-dependent structural cap at growing microtubule ends, Cell, 149, 371–382.
Zhang, R., Alushin, G. M., Brown, A., and Nogales, E. (2015) Mechanistic origin of microtubule dynamic instability and its modulation by EB proteins, Cell, 162, 849–859.
Hayashi, I., and Ikura, M. (2003) Crystal structure of the aminoterminal microtubule-binding domain of end-binding protein 1 (EB1), J. Biol. Chem., 278, 36430–36434.
Gimona, M., Djinovic-Carugo, K., Kranewitter, W. J., and Winder, S. J. (2002) Functional plasticity of CH domains, FEBS Lett., 513, 98–106.
Buey, R. M., Mohan, R., Leslie, K., Walzthoeni, T., Missimer, J. H., Menzel, A., Bjelic, S., Bargsten, K., Grigoriev, I., Smal, I., Meijering, E., Aebersold, R., Akhmanova, A., and Steinmetz, M. O. (2011) Insights into EB1 structure and the role of its C-terminal domain for discriminating microtubule tips from the lattice, Mol. Biol. Cell, 22, 2912–2923.
Alberico, E. O., Zhu, Z. C., Wu, Y.-F. O., Gardner, M. K., Kovar, D. R., and Goodson, H. V. (2016) Interactions between the microtubule binding protein EB1 and Factin, J. Mol. Biol., 428, 1304–1314.
Dougherty, G. W., Adler, H. J., Rzadzinska, A., Gimona, M., Tomita, Y., Lattig, M. C., Merritt, R. C., and Kachar, B. (2005) CLAMP, a novel microtubule-associated protein with EB-type calponin homology, Cell Motil. Cytoskelet., 62, 141–156.
Wei, R. R., Al-Bassam, J., and Harrison, S. C. (2007) The Ndc80/HEC1 complex is a contact point for kinetochore-microtubule attachment, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 14, 54–59.
Des Georges, A., Katsuki, M., Drummond, D. R., Osei, M., Cross, R. A., and Amos, L. A. (2008) Mal3, the Schizosaccharomyces pombe homolog of EB1, changes the microtubule lattice, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 15, 1102–1108.
Honnappa, S., Gouveia, S. M., Weisbrich, A., Damberger, F. F., Bhavesh, N. S., Jawhari, H., Grigoriev, I., van Rijssel, F. J. A., Buey, R. M., Lawera, A., Jelesarov, I., Winkler, F. K., Wuthrich, K., Akhmanova, A., and Steinmetz, M. O. (2009) An EB1-binding motif acts as a microtubule tip localization signal, Cell, 138, 366–376.
Coy, D. L., Hancock, W. O., Wagenbach, M., and Howard, J. (1999) Kinesin’s tail domain is an inhibitory regulator of the motor domain, Nat. Cell Biol., 1, 288–292.
Hayashi, I., Wilde, A., Mal, T. K., and Ikura, M. (2005) Structural basis for the activation of microtubule assembly by the EB1 and p150Glued complex, Mol. Cell, 19, 449–460.
Kanaba, T., Maesaki, R., Mori, T., Ito, Y., Hakoshima, T., and Mishima, M. (2013) Microtubule-binding sites of the CH domain of EB1 and its autoinhibition revealed by NMR, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1834, 499–507.
Sen, I., Veprintsev, D., Akhmanova, A., and Steinmetz, M. O. (2013) End binding proteins are obligatory dimers, PLoS One, 8, e74448.
Skube, S. B., Chaverri, J. M., and Goodson, H. V. (2010) Effect of GFP tags on the localization of EB1 and EB1 fragments in vivo, Cytoskelet. Hoboken NJ, 67, 1–12.
Jiang, K., Toedt, G., Montenegro Gouveia, S., Davey, N. E., Hua, S., Van der Vaart, B., Grigoriev, I., Larsen, J., Pedersen, L. B., Bezstarosti, K., Lince-Faria, M., Demmers, J., Steinmetz, M. O., Gibson, T. J., and Akhmanova, A. (2012) A proteome-wide screen for mammalian SxIP motif-containing microtubule plus-end track-ing proteins, Curr. Biol., 22, 1800–1807.
Ramirez-Rios, S., Denarier, E., Prezel, E., Vinit, A., Stoppin-Mellet, V., Devred, F., Barbier, P., Peyrot, V., Sayas, C. L., Avila, J., Peris, L., Andrieux, A., Serre, L., Fourest-Lieuvin, A., and Arnal, I. (2016) Tau antagonizes end-binding protein tracking at microtubule ends through a phosphorylation-dependent mechanism, Mol. Biol. Cell, 27, 2924–2934.
Velot, L., Molina, A., Rodrigues-Ferreira, S., Nehlig, A., Bouchet, B. P., Morel, M., Leconte, L., Serre, L., Arnal, I., Braguer, D., Savina, A., Honore, S., and Nahmias, C. (2015) Negative regulation of EB1 turnover at microtubule plus ends by interaction with microtubule-associated pro-tein ATIP3, Oncotarget, 6, 43557–43570.
Nakamura, M., Zhou, X. Z., and Lu, K. P. (2001) Critical role for the EB1 and APC interaction in the regulation of microtubule polymerization, Curr. Biol., 11, 1062–1067.
Green, R. A., Wollman, R., and Kaplan, K. B. (2005) APC and EB1 function together in mitosis to regulate spindle dynamics and chromosome alignment, Mol. Biol. Cell, 16, 4609–4622.
Stypula-Cyrus, Y., Mutyal, N. N., Cruz, M. A. D., Kunte, D. P., Radosevich, A. J., Wali, R., Roy, H. K., and Backman, V. (2014) End-binding protein 1 (EB1) up-regulation is an early event in colorectal carcinogenesis, FEBS Lett., 588, 829–835.
Wen, Y., Eng, C. H., Schmoranzer, J., Cabrera-Poch, N., Morris, E. J. S., Chen, M., Wallar, B. J., Alberts, A. S., and Gundersen, G. G. (2004) EB1 and APC bind to mDia to stabilize microtubules downstream of Rho and promote cell migration, Nat. Cell Biol., 6, 820–830.
Zhang, J., Ahmad, S., and Mao, Y. (2007) BubR1 and APC/EB1 cooperate to maintain metaphase chromosome alignment, J. Cell Biol., 178, 773–784.
Rosenberg, M. M., Yang, F., Mohn, J. L., Storer, E. K., and Jacob, M. H. (2010) The postsynaptic adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) multiprotein complex is required for localizing neuroligin and neurexin to neuronal nicotinic synapses in vivo, J. Neurosci., 30, 11073–11085.
Chen, Y., Tian, X., Kim, W.-Y., and Snider, W. D. (2011) Adenomatous polyposis coli regulates axon arborization and cytoskeleton organization via its N-terminus, PLoS One, 6, e24335.
Votin, V., Nelson, W. J., and Barth, A. I. M. (2005) Neurite outgrowth involves adenomatous polyposis coli protein and ß-catenin, J. Cell Sci., 118, 5699–5708.
Eom, T.-Y., Stanco, A., Guo, J., Wilkins, G., Deslauriers, D., Yan, J., Monckton, C., Blair, J., Oon, E., Perez, A., Salas, E., Oh, A., Ghukasyan, V., Snider, W. D., Rubenstein, J. L. R., and Anton, E. S. (2014) Differential regulation of microtubule severing by APC underlies distinct patterns of projection neuron and interneuron migration, Dev. Cell, 31, 677–689.
Purro, S. A., Ciani, L., Hoyos-Flight, M., Stamatakou, E., Siomou, E., and Salinas, P. C. (2008) Wnt regulates axon behavior through changes in microtubule growth directionality: a new role for adenomatous polyposis coli, J. Neurosci., 28, 8644–8654.
Koester, M. P., Muller, O., and Pollerberg, G. E. (2007) Adenomatous polyposis coli is differentially distributed in growth cones and modulates their steering, J. Neurosci., 27, 12590–12600.
Shi, S.-H., Cheng, T., Jan, L. Y., and Jan, Y.-N. (2004) APC and GSK-3ß are involved in mPar3 targeting to the nascent axon and establishment of neuronal polarity, Curr. Biol., 14, 2025–2032.
Vaughan, P. S., Miura, P., Henderson, M., Byrne, B., and Vaughan, K. T. (2002) A role for regulated binding of p150Glued to microtubule plus ends in organelle transport, J. Cell Biol., 158, 305–319.
Brouhard, G. J., Stear, J. H., Noetzel, T. L., Al-Bassam, J., Kinoshita, K., Harrison, S. C., Howard, J., and Hyman, A. A. (2008) XMAP215 is a processive microtubule polymerase, Cell, 132, 79–88.
Zanic, M., Widlund, P. O., Hyman, A. A., and Howard, J. (2013) Synergy between XMAP215 and EB1 increases microtubule growth rates to physiological levels, Nat. Cell Biol., 15, 688–693.
Su, A. I., Wiltshire, T., Batalov, S., Lapp, H., Ching, K. A., Block, D., Zhang, J., Soden, R., Hayakawa, M., Kreiman, G., Cooke, M. P., Walker, J. R., and Hogenesch, J. B. (2004) A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 6062–6067.
Tirnauer, J. S., O’Toole, E., Berrueta, L., Bierer, B. E., and Pellman, D. (1999) Yeast Bim1p promotes the G1-specific dynamics of microtubules, J. Cell Biol., 145, 993–1007.
Schwartz, K., Richards, K., and Botstein, D. (1997) BIM1 encodes a microtubule-binding protein in yeast, Mol. Biol. Cell, 8, 2677–2691.
Beinhauer, J. D., Hagan, I. M., Hegemann, J. H., and Fleig, U. (1997) Mal3, the fission yeast homologue of the human APC-interacting protein EB-1 is required for microtubule integrity and the maintenance of cell form, J. Cell Biol., 139, 717–728.
Asakawa, K., Toya, M., Sato, M., Kanai, M., Kume, K., Goshima, T., Garcia, M. A., Hirata, D., and Toda, T. (2005) Mal3, the fission yeast EB1 homologue, cooperates with Bub1 spindle checkpoint to prevent monopolar attachment, EMBO Rep., 6, 1194–1200.
Berrueta, L., Kraeft, S.-K., Tirnauer, J. S., Schuyler, S. C., Chen, L. B., Hill, D. E., Pellman, D., and Bierer, B. E. (1998) The adenomatous polyposis coli-binding protein EB1 is associated with cytoplasmic and spindle micro-tubules, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 10596–10601.
Morrison, E. E., Wardleworth, B. N., Askham, J. M., Markham, A. F., and Meredith, D. M. (1998) EB1, a pro-tein which interacts with the APC tumour suppressor, is associated with the microtubule cytoskeleton throughout the cell cycle, Oncogene, 17, 3471–3477.
Piehl, M., Tulu, U. S., Wadsworth, P., and Cassimeris, L. (2004) Centrosome maturation: measurement of micro-tubule nucleation throughout the cell cycle by using GFP-tagged EB1, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 1584–1588.
Cheeseman, I. M., and Desai, A. (2008) Molecular architecture of the kinetochore–microtubule interface, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 9, 33–46.
Bruning-Richardson, A., Langford, K. J., Ruane, P., Lee, T., Askham, J. M., and Morrison, E. E. (2011) EB1 is required for spindle symmetry in mammalian mitosis, PLoS One,6.
Lomakin, A. J., Semenova, I., Zaliapin, I., Kraikivski, P., Nadezhdina, E., Slepchenko, B. M., Akhmanova, A., and Rodionov, V. (2009) CLIP-170-dependent capture of membrane organelles by microtubules initiates minus-end directed transport, Dev. Cell, 17, 323–333.
Morrison, E. E., Moncur, P. M., and Askham, J. M. (2002) EB1 identifies sites of microtubule polymerization during neurite development, Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res., 98, 145–152.
Jaworski, J., Kapitein, L. C., Gouveia, S. M., Dortland, B. R., Wulf, P. S., Grigoriev, I., Camera, P., Spangler, S. A., Stefano, P. D., Demmers, J., Krugers, H., Defilippi, P., Akhmanova, A., and Hoogenraad, C. C. (2009) Dynamic microtubules regulate dendritic spine morphology and synaptic plasticity, Neuron, 61, 85–100.
Alves-Silva, J., Sanchez-Soriano, N., Beaven, R., Klein, M., Parkin, J., Millard, T. H., Bellen, H. J., Venken, K. J. T., Ballestrem, C., Kammerer, R. A., and Prokop, A. (2012) Spectraplakins promote microtubule-mediated axonal growth by functioning as structural microtubule-associated proteins and EB1-dependent +TIPs (tip inter-acting proteins), J. Neurosci., 32, 9143–9158.
Arens, J., Duong, T.-T., and Dehmelt, L. (2013) A morphometric screen identifies specific roles for microtubule-regulating genes in neuronal development of P19 stem cells, PLoS One,8.
Akhmanova, A., and Steinmetz, M. O. (2015) Control of microtubule organization and dynamics: two ends in the limelight, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 16, 711–726.
Vitre, B., Coquelle, F. M., Heichette, C., Garnier, C., Chretien, D., and Arnal, I. (2008) EB1 regulates micro-tubule dynamics and tubulin sheet closure in vitro, Nat. Cell Biol., 10, 415–421.
Bieling, P., Laan, L., Schek, H., Munteanu, E. L., Sandblad, L., Dogterom, M., Brunner, D., and Surrey, T. (2007) Reconstitution of a microtubule plus-end tracking system in vitro, Nature, 450, 1100–1105.
Maurer, S. P., Cade, N. I., Bohner, G., Gustafsson, N., Boutant, E., and Surrey, T. (2014) EB1 accelerates two conformational transitions important for microtubule maturation and dynamics, Curr. Biol., 24, 372–384.
Mohan, R., Katrukha, E. A., Doodhi, H., Smal, I., Meijering, E., Kapitein, L. C., Steinmetz, M. O., and Akhmanova, A. (2013) End-binding proteins sensitize microtubules to the action of microtubule-targeting agents, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110, 8900–8905.
Doodhi, H., Prota, A. E., Rodriguez-Garcia, R., Xiao, H., Custar, D. W., Bargsten, K., Katrukha, E. A., Hilbert, M., Hua, S., Jiang, K., Grigoriev, I., Yang, C.-P. H., Cox, D., Horwitz, S. B., Kapitein, L. C., Akhmanova, A., and Steinmetz, M. O. (2016) Termination of protofilament elongation by eribulin induces lattice defects that promote microtubule catastrophes, Curr. Biol., 26, 1713–1721.
Moriwaki, T., and Goshima, G. (2016) Five factors can reconstitute all three phases of microtubule polymerization dynamics, J. Cell Biol., 215, 357–368.
Srayko, M., Kaya, A., Stamford, J., and Hyman, A. A. (2005) Identification and characterization of factors required for microtubule growth and nucleation in the early C. elegans embryo, Dev. Cell, 9, 223–236.
Nakamura, S., Grigoriev, I., Nogi, T., Hamaji, T., Cassimeris, L., and Mimori-Kiyosue, Y. (2012) Dissecting the nanoscale distributions and functions of microtubule-end-binding proteins EB1 and ch-TOG in interphase HeLa cells, PLoS One,7.
Maurer, S. P., Cade, N. I., Bohner, G., Gustafsson, N., Boutant, E., and Surrey, T. (2014) EB1 accelerates two conformational transitions important for microtubule maturation and dynamics, Curr. Biol., 24, 372–384.
Matsuo, Y., Maurer, S. P., Yukawa, M., Zakian, S., Singleton, M. R., Surrey, T., and Toda, T. (2016) An unconventional interaction between Dis1/TOG and Mal3/EB1 in fission yeast promotes the fidelity of chromosome segregation, J. Cell Sci., 129, 4592–4606.
Bieling, P., Kandels-Lewis, S., Telley, I. A., Van Dijk, J., Janke, C., and Surrey, T. (2008) CLIP-170 tracks growing microtubule ends by dynamically recognizing composite EB1/tubulin-binding sites, J. Cell Biol., 183, 1223–1233.
Dixit, R., Barnett, B., Lazarus, J. E., Tokito, M., Goldman, Y. E., and Holzbaur, E. L. F. (2009) Microtubule plus-end tracking by CLIP-170 requires EB1, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 106, 492–497.
Mandelkow, E. M., Mandelkow, E., and Milligan, R. A. (1991) Microtubule dynamics and microtubule caps: a time-resolved cryo-electron microscopy study, J. Cell Biol., 114, 977–991.
Tran, P. T., Joshi, P., and Salmon, E. D. (1997) How tubulin subunits are lost from the shortening ends of micro-tubules, J. Struct. Biol., 118, 107–118.
Muller-Reichert, T., Chretien, D., Severin, F., and Hyman, A. A. (1998) Structural changes at microtubule ends accompanying GTP hydrolysis: information from a slowly hydrolyzable analogue of GTP, guanylyl (alpha,beta)methylenediphosphonate, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 3661–3666.
Zovko, S., Abrahams, J. P., Koster, A. J., Galjart, N., and Mommaas, A. M. (2008) Microtubule plus-end conformations and dynamics in the periphery of interphase mouse fibroblasts, Mol. Biol. Cell, 19, 3138–3146.
Chretien, D., Fuller, S. D., and Karsenti, E. (1995) Structure of growing microtubule ends: two-dimensional sheets close into tubes at variable rates, J. Cell Biol., 129, 1311–1328.
Guesdon, A., Bazile, F., Buey, R. M., Mohan, R., Monier, S., Garcia, R. R., Angevin, M., Heichette, C., Wieneke, R., Tampe, R., Duchesne, L., Akhmanova, A., Steinmetz, M. O., and Chretien, D. (2016) EB1 interacts with out-wardly curved and straight regions of the microtubule lattice, Nat. Cell Biol., 18, 1102–1108.
Hoog, J. L., Huisman, S. M., Sebo-Lemke, Z., Sandblad, L., McIntosh, J. R., Antony, C., and Brunner, D. (2011) Electron tomography reveals a flared morphology on growing microtubule ends, J. Cell Sci., 124, 693–698.
Carlier, M. F., and Pantaloni, D. (1981) Kinetic analysis of guanosine 5'-triphosphate hydrolysis associated with tubulin polymerization, Biochemistry, 20, 1918–1924.
Walker, R. A., Inoue, S., and Salmon, E. D. (1989) Asymmetric behavior of severed microtubule ends after ultraviolet-microbeam irradiation of individual micro-tubules in vitro, J. Cell Biol., 108, 931–937.
Tran, P. T., Walker, R. A., and Salmon, E. D. (1997) A metastable intermediate state of microtubule dynamic instability that differs significantly between plus and minus ends, J. Cell Biol., 138, 105–117.
Hyman, A. A., Salser, S., Drechsel, D. N., Unwin, N., and Mitchison, T. J. (1992) Role of GTP hydrolysis in micro-tubule dynamics: information from a slowly hydrolyzable analogue, GMPCPP, Mol. Biol. Cell, 3, 1155–1167.
O’Brien, E. T., Voter, W. A., and Erickson, H. P. (1987) GTP hydrolysis during microtubule assembly, Biochemistry, 26, 4148–4156.
Stewart, R. J., Farrell, K. W., and Wilson, L. (1990) Role of GTP hydrolysis in microtubule polymerization: evidence for a coupled hydrolysis mechanism, Biochemistry, 29, 6489–6498.
Caplow, M., and Shanks, J. (1996) Evidence that a single monolayer tubulin-GTP cap is both necessary and sufficient to stabilize microtubules, Mol. Biol. Cell, 7, 663–675.
Drechsel, D. N., and Kirschner, M. W. (1994) The minimum GTP cap required to stabilize microtubules, Curr. Biol., 4, 1053–1061.
Zanic, M., Stear, J. H., Hyman, A. A., and Howard, J. (2009) EB1 recognizes the nucleotide state of tubulin in the microtubule lattice, PLoS One,4.
Maurer, S. P., Bieling, P., Cope, J., Hoenger, A., and Surrey, T. (2011) GTPγS microtubules mimic the growing microtubule end structure recognized by end-binding proteins (EBs), Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 108, 3988–3993.
Bechstedt, S., Lu, K., and Brouhard, G. J. (2014) Doublecortin recognizes the longitudinal curvature of the microtubule end and lattice, Curr. Biol., 24, 2366–2375.
Caplow, M., and Fee, L. (2003) Concerning the chemical nature of tubulin subunits that cap and stabilize micro-tubules, Biochemistry, 42, 2122–2126.
Duellberg, C., Cade, N. I., Holmes, D., and Surrey, T. (2016) The size of the EB cap determines instantaneous microtubule stability, eLife,5.
Gardner, M. K., Charlebois, B. D., Janosi, I. M., Howard, J., Hunt, A. J., and Odde, D. J. (2011) Rapid microtubule self-assembly kinetics, Cell, 146, 582–592.
Brouhard, G. J. (2015) Dynamic instability 30 years later: complexities in microtubule growth and catastrophe, Mol. Biol. Cell, 26, 1207–1210.
Mimori-Kiyosue, Y., Grigoriev, I., Lansbergen, G., Sasaki, H., Matsui, C., Severin, F., Galjart, N., Grosveld, F., Vorobjev, I., Tsukita, S., and Akhmanova, A. (2005) CLASP1 and CLASP2 bind to EB1 and regulate micro-tubule plus-end dynamics at the cell cortex, J. Cell Biol., 168, 141–153.
Bjelic, S., De Groot, C. O., Scharer, M. A., Jaussi, R., Bargsten, K., Salzmann, M., Frey, D., Capitani, G., Kammerer, R. A., and Steinmetz, M. O. (2012) Interaction of mammalian end binding proteins with CAP-Gly domains of CLIP-170 and p150(glued), J. Struct. Biol., 177, 160–167.
Tortosa, E., Galjart, N., Avila, J., and Sayas, C. L. (2013) MAP1B regulates microtubule dynamics by sequestering EB1/3 in the cytosol of developing neuronal cells, EMBO J., 32, 1293–1306.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V. V. Mustyatsa, A. V. Boyakhchyan, F. I. Ataullakhanov, N. B. Gudimchuk, 2017, published in Biokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 82, No. 7, pp. 1033–1046.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mustyatsa, V.V., Boyakhchyan, A.V., Ataullakhanov, F.I. et al. EB-family proteins: Functions and microtubule interaction mechanisms. Biochemistry Moscow 82, 791–802 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917070045
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917070045