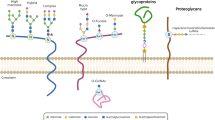
Abstract
Malignant transformation is tightly connected with changes in the glycosylation of proteins and lipids, which in turn are contributing to the invasive and metastatic behavior of tumor cells. One example of such changes is demasking of the otherwise hidden core-1 structure, also known as Thomsen–Friedenreich antigen, which is a highly tumor-specific glycotope and potentially a cancer stem cell marker. This review summarizes what is known about the mechanism(s) of its expression on tumor cells. New data reveal a close connection between tumor metabolism and Golgi function. Based on these data, we suggest that the expression of this antigen is also a marker of aerobic glycolysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TF:
-
Thomsen—Friedenreich antigen
- V-ATPase:
-
vacuolar H+-ATPase
References
Friedenreich, V. (1930) The Thomsen Hemagglutination Phenomenon, Levin & Munksgaard, Copenhagen.
Kim, Z., and Uhlenbruck, G. (1966) Untersuchungen uber T-antigen und T-agglutinin, Z. Immun. Forsch., 130, 8899.
Springer, G. F., Desai, P. R., and Banatwala, I. (1975) Blood group MN antigens and precursors in normal and malignant human breast glandular tissue, J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 54, 335–339.
Springer, G. F. (1997) Immunoreactive T and Tn epitopes in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and immunotherapy, J. Mol. Med., 75, 594–602.
Springer, G. F. (1984) T and Tn, general carcinoma autoantigens, Science, 228, 1198–1206.
Cao, Y., Stosiek, P., Springer, G. F., and Karsten, U. (1996) Thomsen–Friedenreich-related carbohydrate antigens in normal adult human tissues: a systematic and comparative study, Histochem. Cell Biol., 106, 197–207.
Cao, Y., Karsten, U., Liebrich, W., Haensch, W., Springer, G. F., and Schlag, P. M. (1995) Expression of Thomsen–Friedenreich-related antigens in primary and metastatic colorectal carcinomas: a reevaluation, Cancer, 76, 1700–1708.
Takanami, I. (1999) Expression of Thomsen–Friedenreich antigen as a marker of poor prognosis in pulmonary adenocarcinoma, Oncol. Rep., 6, 341–344.
Baldus, S. E., Hanisch, F. G., Monaca, E., Karsten, U., Zirbes, T. K., Thiele, J., and Dienes, H. P. (1999) Immunoreactivity of Thomsen–Friedenreich (TF) antigen in human neoplasms: the importance of carrier-specific glycotope expression on MUC1, Histol. Histopathol., 14, 1153–1158.
Cao, Y., Karsten, U., Otto, G., and Bannasch, P. (1999) Expression of MUC1, Thomsen–Friedenreich antigen, Tn, sialosyl-Tn, and a2,6-linked sialic acid in hepatocellular carcinomas and preneoplastic hepatocellular lesions, Virchows Arch., 434, 503–509.
Veerman, A. J. P., Hogeman, P. H. G., Huismans, D. R., Van Zantwijk, C. H., and Bezemer, P. D. (1985) Peanut agglutinin, a marker for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with a good prognosis, Cancer Res., 45, 1890–1893.
Karsten, U. (2002) CD176 workshop panel report, in Leucocyte Typing VII (Mason, D., ed.) Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 202–203.
Karsten, U., and Goletz, S. (2013) What makes cancer stem cell markers different? Springer Plus, 2, 301.
Brockhausen, I., Yang, J., Burchell, J., Whitehouse, C., and Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. (1995) Mechanism underlying aberrant glycosylation of the MUC1 mucin in breast cancer, Eur. J. Biochem., 233, 607–617.
Ermini, L., Bhattacharjee, J., Spagnoletti, A., Bechi, N., Aldi, S., Ferretti, C., Bianchi, L., Bini, L., Rosati, F., Paulesu, L., and Ietta, F. (2013) Oxygen governs Galß13GalNAc epitope in human placenta, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol., 305, C931–C940.
Brockhausen, I. (1999) Pathways of O-glycan biosynthesis in cancer cells, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1473, 67–95.
Brockhausen, I. (2006) Mucin-type O-glycosylation in human colon and breast cancer: glycodynamics and functions, EMBO Rep., 7, 599–604.
Goletz, S., Cao, Y., Danielczyk, A., Ravn, P., Schoeber, U., and Karsten, U. (2003) Thomsen–Friedenreich antigen: the “hidden” tumor antigen, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 535, 147–162.
Burchell, J. M., Mungul, A., and Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. (2001) O-linked glycosylation in the mammary gland: changes that occur during malignancy, J. Mamm. Gland Biol. Neoplasm, 6, 355–364.
Vavasseur, F., Yang, J., Dole, K., Paulsen, H., and Brockhausen, I. (1995) Synthesis of core 3: characterization of UDP-GlcNAc: GalNAc ß3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity from colonic tissues. Loss of the activity in human cancer cell lines, Glycobiology, 5, 351–357.
Schneider, F., Kemmner, W., Haensch, W., Franke, G., Gretschel, S., Karsten, U., and Schlag, P. M. (2001) Overexpression of sialyltransferase CMP-sialic acid:Galß1,3GalNAc-R a6-sialyltransferase is related to poor patient survival in human colorectal carcinomas, Cancer Res., 61, 4605–4611.
Dalziel, M., Whitehouse, C., McFarlane, I., Brockhausen, I., Gschmeissner, S., Schwientek, T., Clausen, H., Burchell, J. M., and Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. (2001) The relative activities of the C2GnT1 and ST3Gal-I glycosyltransferases determine O-glycan structure and expression of a tumor-associated epitope on MUC1, J. Biol. Chem., 276, 11007–11015.
Gill, D. J., Tham, K. M., Chia, J., Wang, S. C., Steentoft, C., Clausen, H., Bard-Chapeau, E. A., and Bard, F. A. (2013) Initiation of GalNAc-type O-glycosylation in the endoplasmic reticulum promotes cancer cell invasiveness, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110, E3152–E3162.
Radhakrishnan, P., Dabelsteen, S., Madsen, F. B., Francavilla, C., Kopp, K. L., Steentoft, C., Vakhrushev, S. Y., Olsen, J. V., Hansen, L., Bennett, E. P., Woetmann, A., Yin, G., Chen, L., Song, H., Bak, M., Hlady, R. A., Peters, S. L., Opavsky, R., Thode, C., Qvortrup, K., Schjoldager, K. T. -B. G., Clausen, H., Hollingsworth, M. A., and Wandall, H. H. (2014) Immature truncated O-glycophenotype of cancer directly induces oncogenic features, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 111, E4066–E4075.
Ju, T., Otto, V. I., and Cummings, R. D. (2011) The Tn antigen–structural simplicity and biological complexity, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 50, 1770–1791.
Kumamoto, K., Goto, Y., Sekikawa, K., Takenoshita, S., Ishida, N., Kawakita, M., and Kannagi, R. (2001) Increased expression of UDP-galactose transporter RNA in human colon cancer tissues and its implication in synthesis of Thomsen–Friedenreich antigen and sialyl Lewis A/X determinants, Cancer Res., 61, 4620–4627.
Nilsson, T., Slusarewicz, P., Hoe, M. H., and Warren, G. (1993) Kin recognition. A model for the retention of Golgi enzymes, FEBS Lett., 330, 1–4.
De Graffenried, C. L., and Bertozzi, C. R. (2004) The roles of enzyme localization and complex formation of Golgi enzymes, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 16, 356–363.
Engelsberg, A., Hermosilla, R., Karsten, U., Schulein, R., Dorken, B., and Rehm, A. (2003) The Golgi protein RCAS1 controls cell surface expression of tumor-associated O-linked glycan antigens, J. Biol. Chem., 278, 22998–23007.
Egea, G., Franci, C., Gambus, G., Lesuffleur, T., Zweibaum, A., and Real, F. X. (1993) Cis-Golgi resident proteins and O-glycans are abnormally compartmentalized in the RER of colon cancer cells, J. Cell Sci., 105, 819–830.
Sewell, R., Backstrom, M., Dalziel, M., Gschmeissner, S., Karlsson, H., Noll, T., Gatgens, J., Clausen, H., Hansson, G. C., Burchell, J., and Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. (2006) The ST6GalNAc-I sialyltransferase localizes throughout the Golgi and is responsible for the synthesis of the tumorassociated sialyl-Tn-glycan in human breast cancer, J. Biol. Chem., 281, 3586–3594.
Rottger, S., White, J., Wandall, H. H., Olivo, J.-C., Stark, A., Bennett, E. P., Whitehouse, C., Berger, E. G., Clausen, H., and Nilsson, T. (1998) Localization of three human polypeptide GalNAc-transferases in HeLa cells suggests initiation of O-linked glycosylation throughout the Golgi apparatus, J. Cell Sci., 111, 45–60.
Axelsson, M. A. B., Karlsson, N. G., Steel, D. M., Ouwendijk, J., Nilsson, T., and Hansson, G. C. (2001) Neutralization of pH in the Golgi apparatus cause redistribution of glycosyltransferases and changes in the O-glycosylation of mucins, Glycobiology, 11, 633–644.
Campbell, B. J., Rowe, G. E., Leiper, K., and Rhodes, J. M. (2001) Increasing the intra-Golgi pH of cultured LS174T goblet-differentiated cells mimics the decreased mucin sulfation and increased Thomsen–Friedenreich antigen (Galß1-3GalNaca-) expression seen in colon cancer, Glycobiology, 11, 385–393.
Thorens, B., and Vassalli, P. (1986) Chloroquine and ammonium chloride prevent terminal glycosylation of immunoglobulins in plasma cells without affecting secretion, Nature, 321, 618–620.
Caplan, M. J., Stow, J. L., Newman, A. P., Madri, J., Anderson, H. C., Farquhar, M. G., Palade, G. E., and Jamieson, J. D. (1987) Dependence on pH of polarized sorting of secreted proteins, Nature, 329, 632–635.
Kellokumpu, S., Sormunen, R., and Kellokumpu, I. (2002) Abnormal glycosylation and altered Golgi structure in colorectal cancer: dependence on intra-Golgi pH, FEBS Lett., 516, 217–224.
Paroutis, P., Touret, N., and Grinstein, S. (2004) The pH of the secretory pathway: measurement, determinants, and regulation, Physiology, 19, 207–215.
Rivinoja, A., Kokkonen, N., Kellokumpu, I., and Kellokumpu, S. (2006) Elevated Golgi pH in breast and colorectal cancer cells correlates with the expression of oncofetal carbohydrate T-antigen, J. Cell. Physiol., 208, 167–174.
Gawlitzek, M., Ryll, T., Lofgren, J., and Sliwkowski, M. B. (2000) Ammonium alters N-glycan structures of recombinant TNFR-IgG: degradative versus biosynthetic mechanisms, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 68, 637–646.
Rivinoja, A., Hassinen, A., Kokkonen, N., Kauppila, A., and Kellokumpu, S. (2009) Elevated Golgi pH impairs terminal N-glycosylation by inducing mislocalization of Golgi glycosyltransferases, J. Cell. Physiol., 220, 144–154.
Hassinen, A., Pujol, F. M., Kokkonen, N., Pieters, C., Kihlstrom, M., Korhonen, K., and Kellokumpu, S. (2011) Functional organization of the Golgi Nand O-glycosylation pathways involves pH-dependent complex formation that is impaired in cancer cells, J. Biol. Chem., 286, 38329–38340.
Hassinen, A., and Kellokumpu, S. (2014) Organizational interplay of Golgi N-glycosyltransferases involves organelle microenvironment-dependent transitions between enzyme homoand heteromers, J. Biol. Chem., 289, 26937–26948.
Rivinoja, A., Pujol, F. M., Hassinen, A., and Kellokumpu, S. (2012) Golgi pH, its regulation and roles in human disease, Ann. Med., 44, 542–554.
Maeda, Y., Ide, T., Koike, M., Uchiyama, Y., and Kinoshita, T. (2008) GPHR is a novel anion channel critical for acidification and functions of the Golgi apparatus, Nature Cell Biol., 10, 1135–1145.
Marshansky, V., Rubinstein, J. L., and Gruber, G. (2014) Eukaryotic V-ATPase: novel structural findings and functional insights, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1837, 857–879.
Warburg, O., Wind, F., and Negelein, E. (1927) The metabolism of tumors in the body, J. Gen. Physiol., 8, 519–530.
Hanahan, D., and Weinberg, R. A. (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation, Cell, 144, 646–674.
DeBerardinis, R. J., Lum, J. J., Hatzivassiliou, G., and Thompson, C. B. (2008) The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation, Cell Metab., 7, 11–20.
Gillies, R. J., Raghunand, N., Karczmar, G. S., and Bhujwalla, Z. M. (2002) MRI of the tumor microenvironment, J. Magn. Reson. Imag., 16, 430–450.
Damaghi, M., Wojtkowiak, J. W., and Gillies, R. J. (2013) pH sensing and regulation in cancer, Front. Physiol., 4; http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2013.00370.
Gatenby, R. A., Smallbone, K., Maini, P. K., Rose, F., Averill, J., Nagle, R. B., Worrall, L., and Gillies, R. J. (2007) Cellular adaptions to hypoxia and acidosis during somatic evolution of breast cancer, Brit. J. Cancer, 97, 646–653.
Vogelstein, B., and Kinzler, K. W. (2004) Cancer genes and the pathways they control, Nature Med., 10, 789–799.
Kroemer, G., and Pouyssegur, J. (2008) Tumor cell metabolism: cancer’s Achilles heel, Cancer Cell, 13, 472–482.
Cardone, R. A., Casavola, V., and Reshkin, S. J. (2005) The role of disturbed pH dynamics and the Na+/H+ exchanger in metastasis, Nature Rev. Cancer, 5, 786–795.
Wong, N., De Melo, J., and Tang, D. (2013) PKM2, a central point of regulation in cancer metabolism, Int. J. Cell Biol.; http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/242513.
Semenza, G. L. (2013) HIF-1 mediates metabolic responses to intratumoral hypoxia and oncogenic mutations, J. Clin. Invest., 123, 3665–3671.
Soonthornsit, J., Yamaguchi, Y., Tamura, D., Ishida, R., Nakakoji, Y., Osako, S., Yamamoto, A., and Nakamura, N. (2014) Low cytoplasmic pH reduces ER–Golgi trafficking and induces disassembly of the Golgi apparatus, Exp. Cell Res., 328, 325–339.
Finley, L. W. S., Carracedo, A., Lee, J., Souza, A., Egia, A., Zhang, J., Teruya-Feldstein, J., Moreira, P. I., Cardoso, S. M., Clish, C. B., Pandolfi, P. P., and Haigis, M. C. (2011) SIRT3 opposes reprogramming of cancer cell metabolism through HIFa destabilization, Cancer Cell, 19, 416–428.
Schapiro, F., Sparkowski, J., Adduci, A., Suprynowicz, F., Schlegel, R., and Grinstein, S. (2000) Golgi alkalinization by the papillomavirus E5 oncoprotein, J. Cell Biol., 148, 305–315.
Sautin, Y. Y., Lu, M., Gaugler, A., Zhang, L., and Gluck, S. L. (2005) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kianse-mediated effects of glucose on vacuolar H+-ATPase assembly, translocation, and acidification of intracellular compartments in renal epithelial cells, Mol. Cell. Biol., 25, 575–589.
Jeschke, U., Richter, D. U., Hammer, A., Briese, V., Friese, K., and Karsten, U. (2002) Expression of the Thomsen–Friedenreich antigen and of its putative carrier protein mucin 1 in the human placenta and in trophoblast cells in vitro, Histochem. Cell Biol., 117, 219–226.
Ito, K., and Suda, T. (2014) Metabolic requirements for the maintenance of self-renewing stem cells, Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 15, 243–256.
Martinez-Outschoorn, U. E., Lisanti, M. P., and Sotgia, F. (2014) Catabolic cancer-associated fibroblasts transfer energy and biomass to anabolic cancer cells, fueling tumor growth, Seminars Cancer Biol., 25, 47–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2015, Vol. 80, No. 7, pp. 959–966.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karsten, U., Goletz, S. What controls the expression of the core-1 (Thomsen—Friedenreich) glycotope on tumor cells?. Biochemistry Moscow 80, 801–807 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915070019
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915070019