Abstract
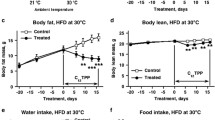
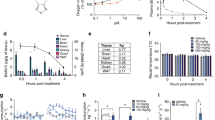
Obesity is associated with premature mortality, impaired quality of life, and large healthcare costs. However, treatment options remain quite limited. Here we studied potential anti-obesity effects of a novel cationic mitochondrial uncoupler, C4R1 (derivative of rhodamine 19) in C57Bl/6 mice. Obesity was induced by long-term (eight weeks) high fat diet feeding at thermoneutrality. The treated group of mice received consecutively two doses of C4R1 in drinking water (30 and 12–14 μmol/kg daily) during 30 days. Effects of C4R1 were dose-dependent. After six days of C4R1 treatment at dose 30 μmol/kg daily, food intake was reduced by 68%, body weight by 19%, and fat mass by 21%. Body weight decrease was explained partly by reduced food intake and partly by increased metabolism, likely resulting from uncoupling. Body fat reduction upon C4R1 treatment was associated with improved lipid utilization estimated from decrease in respiratory quotient to the minimal level (0.7). Interestingly, the classical uncoupler 2,4-dinitrophenol at similar dose (27 μmol/kg daily) did not have any effect. Our results are relevant to the search for substances causing mild uncoupling of mitochondria that could be a promising therapeutic strategy to treat obesity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C4R1:
-
a short-chain alkyl derivative of rhodamine 19
- DNP:
-
2,4-dinitrophenol
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- RMR:
-
resting metabolic rate
- RQ:
-
respiratory quotient
- UCP1:
-
uncoupling protein 1
References
Tseng, Y. H., Cypess, A. M., and Kahn, C. R. (2010) Cellular bioenergetics as a target for obesity therapy, Nature Rev. Drug Discov., 9, 465–482.
Rodgers, R. J., Tschop, M. H., and Wilding, J. P. (2012) Anti-obesity drugs: past, present and future, Dis. Model Mech., 5, 621–626.
Wadden, T. A. (1993) Treatment of obesity by moderate and severe caloric restriction. Results of clinical research trials, Ann. Intern. Med., 119, 688–693.
Harper, J. A., Dickinson, K., and Brand, M. D. (2001) Mitochondrial uncoupling as a target for drug development for the treatment of obesity, Obes. Rev., 2, 255–265.
Nedergaard, J., and Cannon, B. (2010) The changed metabolic world with human brown adipose tissue: therapeutic visions, Cell Metab., 11, 268–272.
Tainter, M. L., Cutting, W. C., and Stockton, A. B. (1934) Use of dinitrophenol in nutritional disorders: a critical survey of clinical results, Am. J. Public Health Nations Health, 24, 1045–1053.
Parascandola, J. (1974) Dinitrophenol and bioenergetics: an historical perspective, Mol. Cell Biochem., 5, 69–77.
Shemano, I., and Nickerson, M. (1963) Mechanisms of thermal responses to 2,4-dinitrophenol, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 139, 88–93.
Schlagowski, A. I., Singh, F., Charles, A. L., Gali Ramamoorthy, T., Favret, F., Piquard, F., Geny, B., and Zoll, J. (2014) Mitochondrial uncoupling reduces exercise capacity despite several skeletal muscle metabolic adaptations, J. Appl. Physiol. (1985), 116, 364–375.
Goldgof, M., Xiao, C., Chanturiya, T., Jou, W., Gavrilova, O., and Reitman, M. L. (2014) The chemical uncoupler 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) protects against diet-induced obesity and improves energy homeostasis in mice at thermoneutrality, J. Biol. Chem., 289, 19341–19350.
Caldeira da Silva, C. C., Cerqueira, F. M., Barbosa, L. F., Medeiros, M. H., and Kowaltowski, A. J. (2008) Mild mitochondrial uncoupling in mice affects energy metabolism, redox balance and longevity, Aging Cell, 7, 552–560.
Quin, C., Robertson, L., McQuaker, S. J., Price, N. C., Brand, M. D., and Hartley, R. C. (2010) Caged mitochondrial uncouplers that are released in response to hydrogen peroxide, Tetrahedron, 66, 2384–2389.
Shabalina, I. G., and Nedergaard, J. (2011) Mitochondrial (“mild”) uncoupling and ROS production: physiologically relevant or not, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 39, 1305–1309.
Hatcher, A. S., Alderson, J. M., and Clements-Jewery, H. (2011) Cardiac mitochondrial uncoupling agents trigger ventricular fibrillation in isolated rat hearts, J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 28, 28.
McFee, R. B., Caraccio, T. R., McGuigan, M. A., Reynolds, S. A., and Bellanger, P. (2004) Dying to be thin: a dinitrophenol related fatality, Vet. Hum. Toxicol., 46, 251–254.
Grundlingh, J., Dargan, P. I., El-Zanfaly, M., and Wood, D. M. (2011) 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP): a weight loss agent with significant acute toxicity and risk of death, J. Med. Toxicol., 7, 205–212.
Severin, F. F., Severina, I. I., Antonenko, Y. N., Rokitskaya, T. I., Cherepanov, D. A., Mokhova, E. N., Vyssokikh, M. Y., Pustovidko, A. V., Markova, O. V., Yaguzhinsky, L. S., Korshunova, G. A., Sumbatyan, N. V., Skulachev, M. V., and Skulachev, V. P. (2010) Penetrating cation/fatty acid anion pair as a mitochondria-targeted protonophore, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 107, 663–668.
Trendeleva, T. A., Sukhanova, E. I., Rogov, A. G., Zvyagilskaya, R. A., Seveina, I. I., Ilyasova, T. M., Cherepanov, D. A., and Skulachev, V. P. (2013) Role of charge screening and delocalization for lipophilic cation permeability of model and mitochondrial membranes, Mitochondrion, 13, 500–506.
Antonenko, Y. N., Avetisyan, A. V., Cherepanov, D. A., Knorre, D. A., Korshunova, G. A., Markova, O. V., Ojovan, S. M., Perevoshchikova, I. V., Pustovidko, A. V., Rokitskaya, T. I., Severina, I. I., Simonyan, R. A., Smirnova, E. A., Sobko, A. A., Sumbatyan, N. V., Severin, F. F., and Skulachev, V. P. (2011) Derivatives of rhodamine 19 as mild mitochondria-targeted cationic uncouplers, J. Biol. Chem., 286, 17831–17840.
Khailova, L. S., Silachev, D. N., Rokitskaya, T. I., Avetisyan, A. V., Lyamsaev, K. G., Severina, I. I., Il’yasova, T. M., Gulyaev, M. V., Dedukhova, V. I., Trendeleva, T. A., Plotnikov, E. Y., Zvyagilskaya, R. A., Chernyak, B. V., Zorov, D. B., Antonenko, Y. N., and Skulachev, V. P. (2014) A short-chain alkyl derivative of rhodamine 19 acts as a mild uncoupler of mitochondria and a neuroprotector, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1837, 1739–1747.
Rokitskaya, T. I., Ilyasova, T. M., Severina, I. I., Antonenko, Y. N., and Skulachev, V. P. (2013) Electrogenic proton transport across lipid bilayer membranes mediated by cationic derivatives of rhodamine 19: comparison with anionic protonophores, Eur. Biophys. J., 42, 477–485.
Lodhi, I. J., and Semenkovich, C. F. (2009) Why we should put clothes on mice, Cell Metab., 9, 111–112.
Nedergaard, J., and Cannon, B. (2014) The browning of white adipose tissue: some burning issues, Cell Metab., 20, 396–407.
Feldmann, H. M., Golozoubova, V., Cannon, B., and Nedergaard, J. (2009) UCP1 ablation induces obesity and abolishes diet-induced thermogenesis in mice exempt from thermal stress by living at thermoneutrality, Cell Metab., 9, 203–209.
Teodoro, J. S., Zouhar, P., Flachs, P., Bardova, K., Janovska, P., Gomes, A. P., Duarte, F. V., Varela, A. T., Rolo, A. P., Palmeira, C. M., and Kopecky, J. (2014) Enhancement of brown fat thermogenesis using chenodeoxycholic acid in mice, Int. J. Obes. (Lond.), 38, 1027–1034.
Watanabe, M., Houten, S. M., Mataki, C., Christoffolete, M. A., Kim, B. W., Sato, H., Messaddeq, N., Harney, J. W., Ezaki, O., Kodama, T., Schoonjans, K., Bianco, A. C., and Auwerx, J. (2006) Bile acids induce energy expenditure by promoting intracellular thyroid hormone activation, Nature, 439, 484–489.
Jacob, M., Bjarnason, I., Rafi, S., Wrigglesworth, J., and Simpson, R. J. (2001) A study of the effects of indometacin on liver mitochondria from rats, mice and humans, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther., 15, 1837–1842.
Connoley, I. P., Liu, Y. L., Frost, I., Reckless, I. P., Heal, D. J., and Stock, M. J. (1999) Thermogenic effects of sibutramine and its metabolites, Br. J. Pharmacol., 126, 1487–1495.
Ryan, D. H. (2000) Use of sibutramine and other noradrenergic and serotonergic drugs in the management of obesity, Endocrine, 13, 193–199.
Halford, J. C., Boyland, E. J., Blundell, J. E., Kirkham, T. C., and Harrold, J. A. (2010) Pharmacological management of appetite expression in obesity, Nature Rev. Endocrinol., 6, 255–269.
Andreyev, A. Y., Bondareva, T. O., Dedukhova, V. I., Mokhova, E. N., Skulachev, V. P., Tsofina, L. M., Volkov, N. I., and Vygodina, T. V. (1989) The ATP/ADP-antiporter is involved in the uncoupling effect of fatty acids on mitochondria, Eur. J. Biochem., 182, 585–592.
Samartsev, V. N., Smirnov, A. V., Zeldi, I. P., Markova, O. V., Mokhova, E. N., and Skulachev, V. P. (1997) Involvement of aspartate/glutamate antiporter in fatty acid-induced uncoupling of liver mitochondria, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1319, 251–257.
Skulachev, V. P. (1999) Anion carriers in fatty acid-mediated physiological uncoupling, J. Bioenerg. Biomembr., 31, 431–445.
Nedergaard, J., Golozoubova, V., Matthias, A., Asadi, A., Jacobsson, A., and Cannon, B. (2001) UCP1: the only protein able to mediate adaptive non-shivering thermogenesis and metabolic inefficiency, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1504, 82–106.
Shabalina, I. G., Jacobsson, A., Cannon, B., and Nedergaard, J. (2004) Native UCP1 displays simple competitive kinetics between the regulators purine nucleotides and fatty acids, J. Biol. Chem., 279, 38236–38248.
Shabalina, I. G., Kramarova, T. V., Nedergaard, J., and Cannon, B. (2006) Carboxyatractyloside effects on brownfat mitochondria imply that the adenine nucleotide translocator isoforms ANT1 and ANT2 may be responsible for basal and fatty-acid-induced uncoupling respectively, Biochem. J., 399, 405–414.
Petrovic, N., Walden, T. B., Shabalina, I. G., Timmons, J. A., Cannon, B., and Nedergaard, J. (2010) Chronic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPAR γ) activation of epididymally derived white adipocyte cultures reveals a population of thermogenically competent, UCP1-containing adipocytes molecularly distinct from classic brown adipocytes, J. Biol. Chem., 285, 7153–7164.
Shabalina, I. G., Ost, M., Petrovic, N., Vrbacky, M., Nedergaard, J., and Cannon, B. (2010) Uncoupling protein-1 is not leaky, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1797, 773–784.
Shabalina, I. G., Petrovic, N., de Jong, J. M., Kalinovich, A. V., Cannon, B., and Nedergaard, J. (2013) UCP1 in brite/beige adipose tissue mitochondria is functionally thermogenic, Cell Rep., 5, 1196–1203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2015, Vol. 80, No. 5, pp. 735–745.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalinovich, A.V., Shabalina, I.G. Novel mitochondrial cationic uncoupler C4R1 is an effective treatment for combating obesity in mice. Biochemistry Moscow 80, 620–628 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915050156
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915050156