Abstract
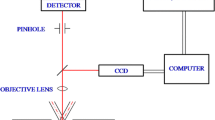
Dynamic phase microscopy was used to study the dynamic events of formation of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in interphase-arrested Xenopus egg extract. We have shown that the ER periodically oscillated in an ATP-dependent manner in the frequency range of 1.6–2.2 Hz, while the tubular membrane network formed in vitro. The spectral density, i.e. the pattern of a given frequency component in the Fourier spectrum, was strongly correlated with the dynamic events during microtubule-dependent and microtubule-independent ER network formation observed by video-enhanced contrast differential interference contrast and fluorescence microscopy. Because the 1.6–2.2 Hz frequency of oscillation during the network formation was detected both in the presence and absence of microtubules, it appears to be an intrinsic ATP-dependent ER membrane property. Several characteristic active and inactive stages of ER network formation were observed both in the presence and absence of microtubules. However, data analysis of these stages indicated that microtubules and dynein motor activity have a strong influence and a cooperative effect on the kinetics of ER formation by controlled fusion reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DP microscopy:
-
dynamic phase microscopy
- ER:
-
endoplasmic reticulum
- OPD:
-
optical path difference
- VEC-DIC microscopy:
-
video-enhanced contrast differential interference contrast microscopy
References
Terasaki, M., Chen, L. B., and Fujiwara, K. (1986) Microtubules and the endoplasmic reticulum are highly interdependent structures, J. Cell Biol., 103, 1557–1568.
Lee, C., and Chen, L. B. (1988) Dynamic behavior of endoplasmic reticulum in living cells, Cell, 54, 37–46.
Allan, V., and Vale, R. (1991) Cell cycle control of microtubule-based membrane transport and tubule formation in vitro, J. Cell Biol., 113, 347–359.
Allan, V., and Vale, R. (1994) Movement of membrane tubules along microtubules in vitro: evidence for specialized sites of motor attachment, J. Cell Sci., 107, 1885–1897.
Steffen, W., Karki, S., Vaughan, K. T., Vallee, R. B., Holzbaur, E. L. F., Weiss, D. G., and Kuznetsov, S. A. (1997) The involvement of the intermediate chain of cytoplasmic dynein in binding the motor complex to membranous organelle of Xenopus oocytes, Mol. Biol. Cell, 8, 2077–2088.
Dreier, L., and Rapoport, T. A. (2000) In vitro formation of the endoplasmic reticulum occurs independently of microtubules by a controlled fusion reaction, J. Cell Biol., 148, 883–898.
Wang, S., Romano, F. B., Field, C. M., Mitchison, T. J., and Rapoport, T. A. (2013) Multiple mechanisms determine ER network morphology during the cell cycle in Xenopus egg extracts, J. Cell Biol., 203, 801–814.
Wollert, T., Weiss, D. G., Gerdes, H.-H., and Kuznetsov, S. A. (2002) Activation of myosin V-based motility and F-actin-dependent network formation of endoplasmic reticulum during mitosis, J. Cell Biol., 159, 571–577.
Tychinsky, V. P., Weiss, D. G., Vyshenskaya, T. V., Yaguzhinskii, L. S., and Nikandrov, S. L. (2000) Cooperative processes in mitochondria: observation by dynamic phase microscopy, Biophysics, 45, 844–851.
Tychinsky, V. P. (2001) Coherent phase microscopy of intracellular processes, Physics-Uspekhi, 44, 649–662.
Weiss, D. G., Tychinsky, V. P., Steffen, W., and Budde, A. (2001) Digital light microscopy techniques for the study of living cytoplasm, in Image Analysis in Biology: Methods and Application (Hader, D. P., ed.) CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 209–239.
Tychinsky, V. P., Kufal, G., Odintsov, A., and Vyshenskaya, T. V. (1997) The measurements of submicrometer structures with the Airyscan laser phase microscope, Quantum Electronics, 27, 735–739.
Allen, R. D., Allen, N. S., and Travis, J. L. (1981) Videoenhanced contrast, differential interference contrast (AVEC-DIC) microscopy: a new method capable of analyzing microtubule-related motility in the reticulopodial network of Allogromia laticollaris, Cell Motil. Cytoskel., 1, 291–302.
Allen, R. D., Weiss, D. G., Hayden, J., Brown, D. T., Fujiwake, H., and Simpson, M. (1985) Gliding movement of bidirectional transport along single native microtubules from squid axoplasm: evidence for an active role of microtubules in cytoplasmic transport, J. Cell Biol., 100, 1736–1752.
Weiss, D. G., Maile, W., Wick, R. A., and Steffen, W. (1999) Video microscopy, in Light Microscopy in Biology. A Practical Approach (Lacey, A. J., ed.) IRL Press, Oxford, pp. 73–149.
Allan, V. (1995) Protein phosphatase 1 regulates the cytoplasmic dynein-driven formation of endoplasmic reticulum networks in vitro, J. Cell Biol., 128, 879–891.
Levin, S., and Korenstein, R. (1991) Membrane fluctuations in erythrocytes are linked to MgATP-dependent dynamic assembly of the membrane skeleton, Biophys. J., 60, 733–737.
Mittelman, L., Levin, S., Verschueren, H., De Baetselier, P., and Korenstein, R. (1994) Direct correlation between cell membrane fluctuations, cell filterability and the metastatic potential of lymphoid cell lines, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 203, 899–906.
Krol, A. Y., Grinfeldt, M. G., Levin, S. V., and Smilgavichus, A. D. (1990) Local mechanical oscillations of the cell surface within the range 0.2–30 Hz, Eur. Biophys. J., 19, 93–99.
Tuvia, S., Levin, S., Bitler, A., and Korenstein, R. (1998) Mechanical fluctuations of the membrane-skeleton are dependent on F-actin ATPase in human erythrocytes, J. Cell Biol., 141, 1551–1561.
Vladimir, P., Tychinsky, V. P., and Tikhonov, A. N. (2010) Interference microscopy in cell biophysics. 2. Visualization of individual cells and energy-transducing organelles, Cell Biochem. Biophys., 58, 117–128.
Waterman-Storer, C. M., Gregory, J., Parsons, S. F., and Salmon, E. D. (1995) Membrane/microtubule tip attachment complexes (TACs) allow the assembly dynamics of plus ends to push and pull membranes into tubulovesicular networks in interphase Xenopus egg extracts, J. Cell Biol., 130, 1161–1169.
Gard, D. L., Hafezi, S., Zhang, T., and Doxsey, S. J. (1990) Centrosome duplication continues in cycloheximide-treated Xenopus blastulae in the absence of a detectable cell cycle, J. Cell Biol., 110, 2033–2042.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2014, Vol. 79, No. 9, pp. 1124–1134.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vyshenskaya, T.V., Tychinsky, V.P., Weiss, D.G. et al. Dynamic phase microscopy reveals periodic oscillations of endoplasmic reticulum during network formation. Biochemistry Moscow 79, 907–916 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297914090077
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297914090077