Abstract
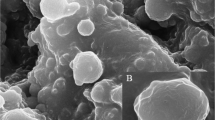
The aim of present study was to prepare liposomes containing vancomycin (Lipo-VAN) formulation, and to evaluate the anti-biofilm effect of Lipo-VAN on the expression of icaA genes in clinical strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Lipo-VAN was synthesized using thin-layer hydration method. Formulation no. 3 (F3) with the lowest size of 178.1 nm and polydispersity index value of 0.163 and with the highest efficiency for entrapping drug (65.49%) was selected as an optimal formulation. The formulations were tested for bactericidal and antibiofilm effects against S. aureus strains. The MIC and MBC obtained for the Lipo-VAN against clinical strains were 7.81–62.5 and 15.62–125 µg/mL, respectively. In addition, the reduction in biofilm formation in strains treated with Lipo-VAN was more significant rather than in the VAN-treated and control groups, which was demonstrated with down-regulation of icaA gene expression. Lipo-VAN formulation exhibited elevated antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activity against clinical S. aureus strains.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Falagas, M.E., Karageorgopoulos, D.E., Leptidis, J. and Korbila, I. P., PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, no. 7, p. e68024.
Bonesso, M.F., Yeh, A.J., Villaruz, A.E., Joo, H.-S. McCausland, J., Fortaleza, C.M., et al., Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 2016, vol. 193, no. 2, pp. 217–220.
Cheung, G.Y., Bae, J.S., and Otto, M., Virulence, 2021, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 547–569.
Oogai, Y., Matsuo, M., Hashimoto, M., Kato, F., Sugai, M., and Komatsuzawa, H., Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 77, no. 22, pp. 8097–8105.
Kaplan, J.B., Mlynek, K.D., Hettiarachchi, H., Alamneh, Y.A., Biggemann, L., Zurawski, D.V., et al., PLoS One, 2018, vol. 13, no. 10, p. e0205526.
Sauer, K., Genome Biol., 2003, vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 1–5.
Arciola, C.R., Baldassarri, L., and Montanaro, L., J. Clin. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 39, no. 6, pp. 2151–2156.
Now, M.M. and Common, B., Clevel. Clin. J. Med., 2012, vol. 79, no. 1, p. 57.
Boswihi, S.S. and Udo, E.E., Cur. Med. Res. Pract., 2018, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 18–24.
Bruniera, F., Ferreira, F., Saviolli, L., Bacci, M., Feder, D., da Luz Gonçalves, et al., Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci., 2015, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 694–700.
Hajiahmadi, F., Alikhani, M.Y., Shariatifar, H., Arabestani, M.R., and Ahmadvand, D., Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran, 2019, vol. 33, p. 153.
Drulis-Kawa, Z. and Dorotkiewicz-Jach, A., Int. J. Pharm., 2010, vol. 387, no. 1–2, pp. 187–198.
Huh, A.J. and Kwon, Y.J., J. Controlled Release, 2011, vol. 156, no. 2, pp. 128–145.
Alipour, M., Halwani, M., Omri, A., and Suntres, Z.E., Int. J. Pharm., 2008, vol. 355, nos. 1–2, pp. 293–298.
Liu, J., Wang, Z., Li, F., Gao, J., Wang, L., and Huang, G., Asian J. Pharm. Sci., 2015, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 212–222.
Panwar, P., Pandey, B., Lakhera, P., and Singh, K., Int. J. Nanomed., 2010, vol. 5, p. 101.
Miao, Z.L., Deng, Y. J., Du, H.Y., Suo, X. B., Wang, X.Y., Wang, X., et al., Exp. Ther. Med., 2015, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 941–946.
Barakat, H.S., Kassem, M.A., El-Khordagui, L.K., and Khalafallah, N.M., AAPS Pharm. Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 15, no. 5, pp. 1263–1274.
Stepanović, S., Vuković, D., Dakić, I., Savić, B., and Švabić-Vlahović, M., J. Microbiol. Methods, 2000, vol. 40, no. 2, pp. 175–179.
Cafiso, V., Bertuccio, T., Santagati, M., Campanile, F., Amicosante, G., Perilli, M., et al., Clin. Microbiol. Infect., 2004, vol. 10, no. 12, pp. 1081–1088.
Bian, Y., Gao, D., Liu, Y., Li, N., Zhang, X., Zheng, R.Y.; et al., RSC Adv., 2015, vol. 5, no. 24, pp. 18725–18732.
Yalcin, T.E., Ilbasmis–Tamer, S., Ibisoglu, B., Özdemir, A., Ark, M., and Takka, S., Pharm. Dev. Technol., 2018, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 76–86.
Ta, T. and Porter, T.M., J. Control Release 2013, vol. 169, nos. 1–2, pp. 112–125.
Hua, S., Int. J.Nanomed., 2014, vol. 9, p. 735.
Bhattacharyya, S., Sudheer, P., Das, K., and Ray, S., Adv. Pharm. Bull., 2021, vol. 11, no. 4, p. 651.
Cong, Y., Yang, S., and Rao, X., J. Adv. Res., 2020, vol. 21, pp. 169–176.
Ferreira, M., Ogren, M., Dias, J.N., Silva, M., Gil, S.,Tavares, L., et al., Molecules, 2021, vol. 26, no. 7, p. 2047.
Sande, L., Sanchez, M., Montes, J., Wolf, A.J., Morgan, M.A., Omri, A., et al., J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 2012, vol. 67, no. 9, pp. 2191–2194.
Vishwasrao, K., Surti, A., and Radha, S., arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.04824, 2018.
Scriboni, A.B., Couto, V.M., Ribeiro, L.N.M., Freires, I.A. Groppo, F.C., De Paula, E. et al., Front. Pharmacol., 2019, vol. 10, p. 1401.
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
This work does not contain any studies involving human and animal subjects.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors of this work declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note.
Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiri, M., Ashrafi, F. The Bactericidal and Antibiofilm Effects of New Liposomes Containing Vancomycin Formulation Against Clinical Biofilm Positive Staphylococcus aureus Isolates. Appl Biochem Microbiol 59, 824–832 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683823060157
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683823060157