Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the role of genetic variants including single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and copy number variants (CNVs) of TBX21, GATA3, Rorc and Foxp3 genes in Behcet's disease (BD) and Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) syndrome in a Chinese Han population. Genotyping of 25 SNPs was performed by iPLEX system (Sequenom) or polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP). TaqMan real time PCR was used to assess CNVs. The expression of Rorc and Foxp3 were examined by real-time PCR and cytokine production was measured by ELISA. High Rorc CNV was associated with the susceptibility to BD (P = 8.99 × 10−8, OR = 3.0) and low Foxp3 CNV predisposed to BD in female patients (P = 1.92 × 10−5, OR = 3.1). CNVs for the investigated genes were not altered in VKH syndrome. Further functional studies demonstrated that the relative mRNA expression levels of Rorc were increased in individuals with high Rorc copy number, but not for Foxp3. Increased production of IL-1β and IL-6 was found in individuals carrying a high CNV of Rorc. Our study showed that high CNVs of Rorc and low CNVs of Foxp3 confer risk for BD but not for VKH syndrome. The tested 25 SNPs in TBX21, GATA3, Rorc and Foxp3 did not associate with BD and VKH syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Inflammation of the uvea, a highly vascularized and pigmented area, is called uveitis. It is a relatively common eye disease1 as well as one of the main causes of blindness in the world2. Behcet's disease (BD) and Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) syndrome are two uveitis entities commonly seen in Asia3,4. However, these diseases display marked differences in their pathogenesis and clinical features. BD appears as a chronic systemic inflammatory disorder with a diverse spectrum of clinical manifestations including recurrent uveitis, oral aphthae, genital ulcers and skin lesions5. VKH syndrome on the other hand is a multi-systemic autoimmune disease featuring bilateral granulomatous panuveitis associated with poliosis, vitiligo, alopecia, auditory and central nervous system signs6. Although the etiology of uveitis remains unclear, genetic variants of immune related genes are considered to be important contributors to this disease as evidenced by a strong association with immune genes including genes encoding for the HLA system and various non-HLA genes such as IL23R and IL107,8.
The immune system is poised in a state of equilibrium. Immune or inflammatory disorders are characterized by a critical imbalance in T lymphocyte function and CD4+ T cells are central for the homeostasis9,10. CD4+ T cells are generally considered as having a pre-defined role as helper T cells within the immune system. Accumulative data showed that pathogenic CD4+ T cells are recognized as critical contributors to the development of Behcet's disease and VKH syndrome as evidenced by the aberrant production of Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cytokines and the aberrant frequency of these four T cell subsets11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19. TBX21, GATA3, Rorc and Foxp3 are key transcription factors for CD4+ T cell subsets including Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells, respectively. Previous studies found the dysregulations of TBX21/GATA3 and Rorc/Foxp3 ratios in uveitis patients with neuro-BD20, suggesting that a dysregulated function of these T cell subsets may lead to immune imbalance, proliferation and activation of pathogenic CD4+ T cells subsequently leading to uveitis.
Foxp3 polymorphisms were found to be associated with multiple autoimmune disorders such as type 1 diabetes, Graves' disease and psoriasis21,22,23,24. Additionally, certain SNPs in Foxp3 were found to significantly enhance transcription activity and lead to higher mRNA levels of Foxp3, suggesting that the SNP in the Foxp3 gene may have functional effects on immune tolerance mediated by Treg cells25. Previous studies also showed the association of genetic polymorphisms in TBX21 with systemic lupus erythematosus, type 1 diabetes, systemic sclerosis and Graves' disease26,27,28,29.
However, the association of these four transcriptional factors with BD and VKH syndrome has not yet been addressed and was therefore the aim of our study whereby we explored the association of two genetic variants including CNVs as well as SNPs of TBX21, GATA3, Rorc and Foxp3 in the pathogenesis of uveitis via a two-stage case control study. The results showed that a high CNV of Rorc and a low CNV for Foxp3 were associated with the susceptibility with BD but not with VKH syndrome in a Chinese Han population. No association was found for the tested 25 SNPs of the four genes with BD and VKH syndrome.
Results
Clinical Features of BD and VKH Syndrome Patients
The clinical findings of the BD and VKH patients enrolled in our study are shown in Supplementary Table 1–2.
Allele and Genotype Frequencies of Selected SNPs in Patients and Normal Controls
We applied the iPLEX system (Sequenom) and PCR-RFLP measurements to successfully evaluate 25 SNPs at TBX21, GATA3, Rorc and Foxp3 genes in an independent cohort containing 406 BD patients, 401 VKH syndrome patients and 613 healthy controls. The frequencies of genotype and allele of 22 SNPs at TBX21, GATA3, Rorc genes didn't show a significant difference among BD patients, VKH syndrome patients and healthy controls (Supplementary Table 3). Considering that Foxp3 is X-linked, we split each study colony into two groups by gender. After stratification by gender, no association was found for three SNPs in the Foxp3 gene with BD or VKH syndrome (Supplementary Tables 4 and 5).
First Stage Study for Copy Number Variations of TBX21, GATA3, Rorc and Foxp3 in Behcet's Disease and VKH Syndrome
A total of 406 BD patients, 401 VKH syndrome patients and 613 healthy controls were enrolled in the first stage CNV study. An increased frequency of high Rorc copy number was observed in patients with BD, but not in VKH patients (P = 0.001, OR = 2.7, 95% CI 1.5–5.1) (Table 1). A reduced Foxp3 CNV was found in female BD patients (P = 9.85 × 10−4, OR = 4.1, 95% CI 1.7–10.1) (Table 2). The result showed that no association of Foxp3 CNVs with VKH syndrome. Additionally, no significant difference was found for the CNVs of TBX21 and GATA3.
The Replication and Combining Studies for Copy Number Variants of Rorc and Foxp3 in Behcet's Patients and Controls
To further verify the association of Rorc and Foxp3 with BD, an additional set of 642 BD patients and 1623 healthy controls were evaluated for Rorc and Foxp3 CNVs (second stage or replication study). The replication results showed that a high Rorc CNV was consistently linked to the susceptibility to BD (P = 1.44 × 10−4, OR = 2.9, 95% CI 1.6–5.1) (Table 1). Reduced Foxp3 CNV again predisposed to BD in females (P = 2.36 × 10−3, OR = 2.7, 95% CI 1.4–5.4) (Table 2). Combining the two stage data showed that a high Rorc CNV (>2) was associated with the susceptibility to BD (P = 8.99 × 10−8, OR = 3.0, 95% CI 2.0–4.6) (Table 1). A low Foxp3 CNV (<2) predisposed to BD in females (p = 1.92 × 10−5, OR = 3.1, 95% CI 1.8–5.2) (Table 2) and a high Foxp3 (>2) CNV was a protective factor for BD in males (P = 5.84 × 10−4, OR = 0.5, 95% CI 0.3–0.7) (Table 3).
Association between Rorc/Foxp3 Copy Number Variants and mRNA Levels
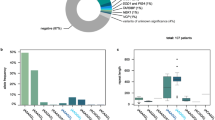
Because a gene dosage effect may be one of the mechanisms of action for CNVs, we investigated the association between Rorc/Foxp3 copy number variations and mRNA expression levels in healthy individuals. The expression studies of Rorc and Foxp3 were performed using samples from healthy controls (cDNA bank), since the patients enrolled in this study represented a heterogeneous group of individuals with marked differences in the degree of immunosuppressive therapy received and inflammation response. The relative mRNA expression levels of Rorc were increased in individuals with high Rorc copy number (Fig. 1a). For Rorc, the population specific median copy number (PMN) is two. The PMN of Foxp3 in female is two while the PMN of Foxp3 in male is one. A significantly up-regulated expression of Rorc was found in the high copy group (Rorc > PMN) when compared to the low copy number group (Rorc ≤ PMN) (P = 7.40 × 10−5). To further determine the relationship between Rorc mRNA expression and its CNV, correlation analysis was performed. The results showed a positive association between Rorc mRNA expression with its CNV (P = 0.04, r2 = 0.349) (Supplementary Fig. 1). However, no significant difference was found between Foxp3 copy number variations and mRNA levels (Fig. 1b).
The Influence of CNVs in Rorc/Foxp3 on the mRNA Levels.
(a) The mRNA expression of Rorc in PBMCs from controls carrying different copies of gene (Rorc ≤ PMN: n = 26, Rorc > PMN: n = 9). (b) The mRNA expression of Foxp3 in PBMCs from controls carrying different copies of gene (Foxp3 ≤ PMN: n = 30, Foxp3 > PMN: n = 19). Significance was examined using SPSS's two independent samples Nonparametric test. PMN represents the population specific median copy number.
The Influence of Rorc Copy Number Variants on Cytokine Production
The results of RT-PCR showed that CNVs of Rorc had an effect on its transcriptional regulation. IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17 and TNF-α-were shown to be involved in the development of Behcet's disease30,31,32,33,34. Further experiments were therefore performed to investigate whether Rorc CNVs affected the production of these four cytokines. As IL-1β is produced by activated macrophages, rather than specific subsets of T cells35,36, we tested the production of these cytokines using PBMCs that generally include a certain number of macrophages. The results showed that an increased production of IL-1β (P = 0.002) and IL-6 (P = 0.001) by stimulated PBMCs was discovered in individuals carrying a high CNV of Rorc (Fig. 2a–b). No significant association was found between IL-17 and TNF-α by stimulated PBMCs and CNV of Rorc (Fig. 2c–d).
The Influence of CNVs in Rorc on Cytokine Production.
The production of IL-1β(a), IL-6 (b), IL-17(c) and TNF-α(d) by stimulated PBMCs from healthy controls carrying different copy number of Rorc (Rorc ≤ 2: n = 88, Rorc > 2: n = 4). Significance was examined using SPSS's two independent samples Nonparametric test.
Discussion
In this study we show that the frequency of high Rorc CNV was significantly increased in BD, while an increased frequency of low Foxp3 CNV was found in female BD patients. Further functional studies demonstrated that the relative mRNA expression levels of Rorc were increased in individuals with high Rorc copy number.
Our data suggest a ratio dysregulation of Rorc/Foxp3 in BD patients which is in accordance with a previous report in neuro-BD patients20. Previous studies have investigated the association of CNVs at C4, IL17F, IL23A and DEFA1 with BD37,38,39. The present study identified two additional risk CNVs with BD including Rorc and Foxp3. The present study also examined the association of CNVs of Rorc and Foxp3 with another uveitis entity, VKH syndrome. However, no association was found for this syndrome. The discrepancy between Rorc and Foxp3 CNVs and susceptibility to these two uveitis entities may be due to the different features of these two diseases. Behcet's disease is considered as a non-granulomatous inflammation40, whereas VKH syndrome is in fact a granulomatous inflammation41,42, suggesting that Rorc and Foxp3 may be involved in these two diseases via different mechanisms.
TBX21, GATA3, Rorc and Fxop3 are classical master regulators of CD4+ helper T cell polarization and function. Our results showed that the genetic variants at Rorc and Foxp3, rather than TBX21, GATA3, are involved in the development of BD, suggesting CD4+ helper T cell subgroups contribute to this disease via a different pathway. Rorc and Foxp3 are key transcription factors for Th17 and Treg cells which have inverse impacts on autoimmunity. Th17 cells mainly regulated by Rorc produce IL-17, TNF-α and IL-6 to promote the development of autoimmunity and allergic reactions43. However, Treg cells mainly regulated by Foxp3 express anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β1, suggesting that they play an anti-inflammatory role and maintain immunologic tolerance to self-antigens44. The absence of Treg cells in Foxp3 mutant individuals could result in a breakdown of immunologic tolerance and uncontrolled inflammatory responses45. The Th17/Treg balance thus contributes to maintain a proper immune homeostasis. Our results also showed an increased production of IL-1β and IL-6 by stimulated PBMCs in individuals carrying a high CNV of Rorc. IL-6 and IL-1β are critical regulators of Th17 differentiation and are seen as inflammatory markers. Th17 cells are characterized by the secretion of IL-17 in addition to other pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α46. Increased expression of Rorc, IL-6 and IL-1β in psoriatic skin has been reported indicating their participation in the pathogenesis of immune disease47. Moreover, a higher increase of IL-6 has been previously reported in active BD patients48.
As one type of the most common genetic variations in the human genome, SNPs are concerned with human phenotypic differences and the susceptibility to disease49. In the present study, we selected 25 tagSNPs of TBX21, GATA3, Rorc and Foxp3. Contrary to previous studies that showed evidence of disease association in Caucasian populations21,22,23,24, no association was found between these 25 SNPs and the susceptibility to BD or VKH syndrome in Han Chinese. Composite analysis of our genotype data and HapMap data for Caucasian population showed that 18 out of 25 tested SNPs in this present study were significantly different concerning their allele frequency when comparing Han Chinese with Caucasians (Supplementary Table 6). Moreover, our recent Genome-wide association study didn't show an association between these 25 SNPs and risk of Behcet's disease and VKH syndrome50,51, suggesting that the SNPs at these four genes may be not involved in these two uveitis entities in Chinese Han. The inconsistent results between Caucasian and Han Chinese populations indicate a genetic heterogeneity towards disease susceptibility.
Our data suggest that a high gene copy number of Rorc may play a role in BD pathogenesis via the transcriptional regulation as well as a change in protein activity/expression. Further analysis of the biological function in individuals carrying a high CNV of Rorc is hampered by the fact that the frequency is as low as 1.70% and therefore only 4 samples with Rorc > 2 were enrolled in this study. We furthermore failed to find how the CNVs of Foxp3 exactly affect the development of BD. Further functional studies are therefore needed to elucidate the exact role of Rorc and Foxp3 genes in the development of BD. The role of gender in the predisposition to BD and the fact that a low Foxp3 CNV predisposed to BD in females requires further analysis. Other limitations of our study include the fact that patients were recruited from ophthalmic centers and may thus represent a selected population of patients. Further confirmation is needed by investigating BD patients from other medical specialties such as rheumatology or dermatology departments.
In conclusion, high Rorc CNV and low Foxp3 CNV were associated with the susceptibility to BD in a Chinese Han population. No association was found for the 25 SNPs at TBX21, GATA3, Rorc and Foxp3 genes with BD and VKH syndrome.
Methods
Study Population
The study group comprised 1048 BD patients and 401VKH syndrome patients who all belong to Chinese Han descent and were recruited from the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University (Chongqing, China) or the Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center of Sun Yat-sen University (Guangzhou, China) between October 2005 and January 2014. A total of 2236 unrelated, unselected normal controls were age-, ethnicity- and geography-matched with the patients. The criteria of the International Study Group for BD and First International Workshop for VKH were set as the diagnostic criteria for the diagnosis of BD and VKH syndrome respectively52,53. If there was any doubt in the diagnosis, the patients were excluded from the study.
Ethics Statement
All venous blood samples were collected after approval from the relevant research ethics committees and written informed consent was obtained from all the participants. The tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki were upheld during all procedures of this study. The present study was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University (Permit Number: 2009-201008). All methods were performed in accordance with the approved guidelines.
SNPs Selection
The SNPs examined in this study were tagSNPs chosen from HapMap data using Chinese Han Beijing data (MAF ≥ 0.05). As a result, a total of 25 SNPs were genotyped and analyzed in this study (Supplementary Table 3–5).
SNP Genotyping
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood of patients and controls using the QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit (QIAGEN Inc., Hilden, Germany) strictly following the manufacturer's instructions. Genotyping of 19 SNPs was determined by using the iPLEX system (Sequenom) in MassARRAY® platform according to the manufacturer's instructions. The primers to genotype these 19 SNPs were designed by MassARRAY Assay design software (Sequenom) (Supplementary Table 7). Genotyping of another 6 SNPs was performed by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP). The primers and restriction enzymes for PCR-RFLP were seen on Supplementary Table 8. Direct sequencing was performed in 5% of the total samples randomly chosen in order to validate the method employed in this study. All SNPs tested in this study had a genotyping success rate >95% and accuracy >99% in all subjects.
Copy Number Genotyping
For accurate quantification of each CNV, we have developed a corresponding TaqMan real time PCR assay performed in 96-well optical plates on a 7500 real-time PCR system following the manufacturer's protocols (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). TaqMan assays labeled with FAM were used to detect TBX21 (Hs06419992-cn), GATA3 (Hs02236731-cn), RORC (Hs00427550-cn) and Foxp3 (Hs02146785-cn) respectively (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). TaqMan® RNaseP assay labeled with VIC was used as an internal copy number reference (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). The amplification conditions were: 10 min at 95°C and 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 sec and 60°C for 1 min. In a model experiment, the method was shown to accurately quantify targets that vary in the range from 0 to 5 copies per genome. All samples were analyzed in triplicate.
Cell Culture and Cytokine Measurements
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from venous blood using Ficoll-Hypaque density-gradient centrifugation. Cell culture medium consisted of RPMI 1640 complete medium, 10% fetal calf serum, 2 mML-glutamine and 100 U/ml penicillin/streptomycin(Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). PBMCs were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml, Sigma, Missouri, USA) for 24 h to detect TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 at a density of 1 × 106 cells/mL. For IL-17 detection, PBMCs were stimulated with anti-CD3 (OKT3, 0.5 μg/ml) plus anti-CD28 antibodies (15E8, 0.1 μg/ml) (Miltenyi Biotec, Palo Alto, CA) for 72 h. The concentration of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-17 in cell culture supernatants was examined with DuosetELISA development kits (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN).
Real-time Quantitative PCR Analysis
Total RNA was isolated with Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and reverse transcribed with the Prime Script RT reagent Kit (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) strictly following the manufacturer's instructions. The real-time quantitative PCR (RT-PCR) was performed using the ABI7500 Fast System(Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA).The primers used for β-actin, Rorc and Foxp3 mRNA detection were as follows: β-actinF: 5′GGATGCAGAAGGAGATCACTG3′ and β-actinR: 5′CGATCCACACGGAGTACTT3′; RorcF: 5′AGAAGACCCACACCTCACAA3′ and RorcR: 5′CCTCACAGGTGATAACCCCG3′; Foxp3F: 5′ATTCCCTGAGCCCTGATCCA3′ and Foxp3R: 5′TGGGGAGCTCGGCTG3′. The relative expression levels of target genes were normalized to the expression of internal reference gene β-actin using the 2−CT method.
Statistical Analysis
For SNP analysis, Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) was tested using the Chi-square test. Genotype frequencies were estimated by direct counting. Allele and genotype frequencies were compared between patients and controls by the chi-square test using SPSS version 17.0. As to the CNV analysis, relative quantitation analysis was performed using CopyCaller, v2.0 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA).Statistical comparison between the patients and controls was performed by Chi-square test using SPSS. The P values were corrected (Pc) for multiple comparisons with the Bonferroni correction. Cytokine expression and RT-PCR data were analyzed by two independent samples nonparametric test. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
References
Gritz, D. C. & Wong, I. G. Incidence and prevalence of uveitis in Northern California; the Northern California Epidemiology of Uveitis Study. Ophthalmology. 111, 491–500; discussion 500 (2004).
Suttorp-Schulten, M. S. & Rothova, A. The possible impact of uveitis in blindness: a literature survey. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 80, 844–848 (1996).
Ohguro, N., Sonoda, K. H., Takeuchi, M., Matsumura, M. & Mochizuki, M. The 2009 prospective multi-center epidemiologic survey of uveitis in Japan. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 56, 432–435 (2012).
Yang, P. et al. Clinical patterns and characteristics of uveitis in a tertiary center for uveitis in China. Curr. Eye. Res. 30, 943–948 (2005).
Chi, W. et al. Upregulated IL-23 and IL-17 in Behcet patients with active uveitis. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 49, 3058–3064 (2008).
Yang, P. et al. Clinical characteristics of Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome in Chinese patients. Ophthalmology. 114, 606–614 (2007).
Mizuki, N. et al. Genome-wide association studies identify IL23R-IL12RB2 and IL10 as Behcet's disease susceptibility loci. Nat. Genet. 42, 703–706 (2010).
Meguro, A. et al. Genetics of Behcet disease inside and outside the MHC. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 69, 747–754 (2010).
Hirahara, K. et al. Mechanisms underlying helper T-cell plasticity: implications for immune-mediated disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 131, 1276–1287 (2013).
Talaat, R. M., Elmaghraby, A. M., Barakat, S. S. & El-Shahat, M. Alterations in immune cell subsets and their cytokine secretion profile in childhood idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). Clin. Exp. Immunol. 176, 291–300 (2014).
Melikoglu, M., Kural-Seyahi, E., Tascilar, K. & Yazici, H. The unique features of vasculitis in Behcet's syndrome. Clin. Rev. Allerg Immu. 35, 40–46 (2008).
Mantas, C., Direskeneli, H., Eksioglu-Demiralp, E. & Akoglu, T. Serum levels of Th2 cytokines IL-4 and IL-10 in Behcet's disease. J. Rheumatol. 26, 510–512 (1999).
Li, B. et al. Upregulation of T-bet expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells during Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 89, 1410–1412 (2005).
Kim, J. et al. Imbalance of Th17 to Th1 cells in Behcet's disease. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 28, S16–19 (2010).
Chi, W. et al. IL-23 promotes CD4+ T cells to produce IL-17 in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 119, 1218–1224 (2007).
Chen, W. et al. Discrepant expression of cytokines in inflammation- and age-related cataract patients. PLoS One. 9, e109647 (2014).
Chen, L. et al. Diminished frequency and function of CD4+CD25 high regulatory T cells associated with active uveitis in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 49, 3475–3482 (2008).
Amadi-Obi, A. et al. TH17 cells contribute to uveitis and scleritis and are expanded by IL-2 and inhibited by IL-27/STAT1. Nat. Med. 13, 711–718 (2007).
Raziuddin, S., al-Dalaan, A., Bahabri, S., Siraj, A. K. & al-Sedairy, S. Divergent cytokine production profile in Behcet's disease. Altered Th1/Th2 cell cytokine pattern. J. Rheumatol. 25, 329–333 (1998).
Hamzaoui, K., Borhani Haghighi, A., Ghorbel, I. B. & Houman, H. RORC and Foxp3 axis in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neuro-Behcet's disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 233, 249–253 (2011).
Noorafshan, A. & Ashkani-Esfahani, S. A Review of Therapeutic Effects of Curcumin. Curr. Pharm. Design. 19, 2032–2046 (2013).
Bassuny, W. M. et al. A functional polymorphism in the promoter/enhancer region of the FOXP3/Scurfin gene associated with type 1 diabetes. Immunogenetics. 55, 149–156 (2003).
Inoue, N. et al. Association of functional polymorphisms related to the transcriptional level of FOXP3 with prognosis of autoimmune thyroid diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 162, 402–406 (2010).
Shen, Z., Chen, L., Hao, F., Wang, G. & Liu, Y. Intron-1 rs3761548 is related to the defective transcription of Foxp3 in psoriasis through abrogating E47/c-Myb binding. J. Cell Mol. Med. 14, 226–241 (2010).
Zheng, J. et al. Heterozygous genetic variations of FOXP3 in Xp11.23 elevate breast cancer risk in Chinese population via skewed X-chromosome inactivation. Hum. Mutat. 34, 619–628 (2013).
Yu, B. et al. Copy number variations of Interleukin-12B and T-bet are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 50, 1201–1205 (2011).
Sasaki, Y. et al. Identification of a novel type 1 diabetes susceptibility gene, T-bet. Hum. Genet. 115, 177–184 (2004).
Gourh, P. et al. Polymorphisms in TBX21 and STAT4 increase the risk of systemic sclerosis: evidence of possible gene-gene interaction and alterations in Th1/Th2 cytokines. Arthritis Rheum. 60, 3794–3806 (2009).
Morita, M. et al. Functional polymorphisms in TBX21 and HLX are associated with development and prognosis of Graves' disease. Autoimmunity. 45, 129–136 (2012).
Liang, L. et al. IL-1beta triggered by peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide through TLR2/4 and ROS-NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pathways is involved in ocular Behcet's disease. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 54, 402–414 (2013).
Gul, A. et al. Interleukin-1beta-regulating antibody XOMA 052 (gevokizumab) in the treatment of acute exacerbations of resistant uveitis of Behcet's disease: an open-label pilot study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 71, 563–566 (2012).
Sugita, S. et al. Inhibition of Th17 differentiation by anti-TNF-alpha therapy in uveitis patients with Behcet's disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 14, R99 (2012).
Akman-Demir, G. et al. Interleukin-6 in neuro-Behcet's disease: association with disease subsets and long-term outcome. Cytokine. 44, 373–376 (2008).
Hamzaoui, K. Th17 cells in Behcet's disease: a new immunoregulatory axis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 29, S71–76 (2011).
Cheng, Y. L. et al. Effect of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7-Specific Enterohemolysin on Interleukin-1beta Production Differs between Human and Mouse Macrophages due to the Different Sensitivity of NLRP3 Activation. Immunology. 10.1111/imm.12442.(2015).
Martinez-Micaelo, N., Gonzalez-Abuin, N., Pinent, M., Ardevol, A. & Blay, M. Procyanidin B inhibits inflammasome-mediated IL-1beta production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 59, 262–269 (2015).
Ahn, J. K., Cha, H. S., Lee, J., Jeon, C. H. & Koh, E. M. Correlation of DEFA1 gene copy number variation with intestinal involvement in Behcet's disease. J. Korean Med. Sci. 27, 107–109 (2012).
Hou, S. et al. Copy number variations of complement component C4 are associated with Behcet's disease but not with ankylosing spondylitis associated with acute anterior uveitis. Arthritis Rheum. 65, 2963–2970 (2013).
Hou, S. et al. Genetic Variations of IL17F and IL23A Show Associations with Behcet's Disease and Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Syndrome. Ophthalmology. 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.09.025(2014).
Evereklioglu, C. Current concepts in the etiology and treatment of Behcet disease. Surv. Ophthalmol. 50, 297–350 (2005).
Rao, N. A. Mechanisms of inflammatory response in sympathetic ophthalmia and VKH syndrome. Eye (Lond) 11 (Pt 2), 213–216 (1997).
Moorthy, R. S., Inomata, H. & Rao, N. A. Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome. Surv. Ophthalmol. 39, 265–292 (1995).
Bettelli, E., Oukka, M. & Kuchroo, V. K. T(H)-17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 8, 345–350 (2007).
Sakaguchi, S. et al. Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ natural regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune disease. Immunol. Rev. 212, 8–27 (2006).
Littman, D. R. & Rudensky, A. Y. Th17 and regulatory T cells in mediating and restraining inflammation. Cell. 140, 845–858 (2010).
Tesmer, L. A., Lundy, S. K., Sarkar, S. & Fox, D. A. Th17 cells in human disease. Immunol. Rev. 223, 87–113 (2008).
Wilson, N. J. et al. Development, cytokine profile and function of human interleukin 17-producing helper T cells. Nat. Immunol. 8, 950–957 (2007).
Hamzaoui, K. et al. Cytokine profile in Behcet's disease patients. Relationship with disease activity. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 31, 205–210 (2002).
Frazer, K. A., Murray, S. S., Schork, N. J. & Topol, E. J. Human genetic variation and its contribution to complex traits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 241–251 (2009).
Hou, S. et al. Genome-wide association analysis of Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome identifies two new susceptibility loci at 1p31.2 and 10q21.3. Nat. Genet. 46, 1007–1011 (2014).
Hou, S. et al. Identification of a susceptibility locus in STAT4 for Behcet's disease in Han Chinese in a genome-wide association study. Arthritis Rheum. 64, 4104–4113 (2012).
Criteria for diagnosis of Behcet's disease. . International Study Group for Behcet's Disease. Lancet. 335, 1078–1080 (1990).
Read, R. W. et al. Revised diagnostic criteria for Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease: report of an international committee on nomenclature. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 131, 647–652 (2001).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation Major International (Regional) Joint Research Project (81320108009), National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (2011CB510200), Key Project of Natural Science Foundation (81130019), National Natural Science Foundation Project (31370893, 81270990), Basic Research program of Chongqing (cstc2013jcyjC10001), Chongqing Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology (CSTC, 2008CA5003), National Key Clinical Specialties Construction Program of China, Key Project of Health Bureau of Chongqing(2012-1-003), Chongqing Outstanding Youth Grant (cstc2014jcyjjq10005), Chongqing Science&Technology Platform and Base Construction Program (cstc2014pt-sy10002), The Youth Top-notch Support Plan of Chongqing and Fund for PAR-EU Scholars Program. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. We thank Lu Yang for helping with the ELISA experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.L., S.H. and P.Y. conceived the idea. D.L. and S.H. designed the experiments, J.Z., Y.L. and L.B. performed the experiments, J.F. and Q.C. analyzed the data. D.L., A.K. and P.Y. wrote the manuscript. S.H. prepared figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder in order to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, D., Hou, S., Zhang, J. et al. Copy Number Variants and Genetic Polymorphisms in TBX21, GATA3, Rorc, Foxp3 and Susceptibility to Behcet's Disease and Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Syndrome. Sci Rep 5, 9511 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09511
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09511
- Springer Nature Limited