Abstract
Recent discoveries of extant and fossilized communities indicate that eukaryotes, including fungi, inhabit energy-poor and anoxic environments deep within the fractured igneous crust. This subterranean biosphere may constitute the largest fungal habitat on our planet, but knowledge of abyssal fungi and their syntrophic interactions with prokaryotes and their concomitant metabolisms is scarce. Here we report findings of fossilized, chitin-bearing fungal hyphae at ~540 m depth in fractured bedrock of the Siljan impact structure, the largest crater in Europe. Strong 13C-enrichment of calcite precipitated with and on the fungi suggests formation following methanogenesis, and that the anaerobic fungi decomposed dispersed organic matter producing for example H2 that may have fueled autotrophic methanogens. An Eocene age determined for the calcite infers the first timing constraint of fossilized fungi in the continental igneous crust. Fungi may be widespread decomposers of organic matter and overlooked providers of H2 to autotrophs in the vast rock-hosted deep biosphere.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The deep biosphere is the largest microbial habitat on Earth by volume1,2,3,4. The subsurface encompasses diverse environments and ecosystems, including severely energy limited deep biosphere ecosystems, inhabited by ancient evolutionary microbial lineages, adapted to subsurface conditions1,5,6. Knowledge of these lifeforms and processes has important implications for life in extreme environments and evolution on Earth, as well as significance for the quest for life on other planets and icy moons7. Estimates of the total biomass in the continental deep biosphere range from a couple of percent to almost 20% of Earth’s total4,8. Research on active communities in the deep biosphere has so far focused on prokaryotes. Recent studies have, however, shown that microorganisms of all three domains of life are abundant and active in deep aquifers in Precambrian crystalline rocks9, which make up the largest volumes of the continental crust10. Eukaryotes have been detected at several kilometers depth11, but the general trend is increased proportion of prokaryotes with declination12. Of the eukaryotes, organisms of the kingdom Fungi have been detected in several studies of deep present-day fracture waters13,14. Deep remnants of ancient fungi have been found in fractured igneous rock in Sweden15,16. Fungi are evidently inhabiting the deep igneous biosphere, but knowledge about their ecological role, and how long they have dwelled in this environment is far from resolved. From other settings, ancient remains of fungi or fungus-like structures have been detected in cavities and/or beddings of Neoproterozoic sedimentary rocks17,18 and in vesicular basalt of Devonian19 and Paleoproterozoic age20. The most convincing fungal fossils are Phanerozoic in age21.
The shift to anoxic conditions generally occurs within the upper tens of meters in continental igneous aquifers22 suggesting that the majority of deep biosphere microorganisms, including fungi, have adapted to an anaerobic lifestyle. Most studies of obligate anaerobic fungi, and hence most well-established metabolic models, are of the phylum Neocallimastigomycota living in the rumens of herbivores. Neocallimastigomycota possess redox organelles called hydrogenosomes instead of mitochondria that produce H2 (as well as CO2, lactate, and formate) as a metabolic waste product23,24,25. In the rumen, fungi consort symbiotically with prokaryotes, such as methanogens26,27, and symbiotic relationships between gut fungi and methanogens in relation to changing diets have been reported28. For the deep biosphere, anaerobic fungi have been shown to have distinct survival strategies to adapt to anaerobic ecosystems (e.g., ethanol fermentation and production of amino acids by Schizophyllum commune 20R-7-F01 in sediments at 2 km below the seafloor29) and a similar type of syntrophic consortium as in rumens has been proposed, where fungi produce H2 that can be used by indigenous autotrophic prokaryotes, such as sulfate reducers16,30,31. The hypothesis includes degradation of prokaryotic biofilms by heterotrophic fungi and production of H2 as a waste product that then fuels the autotrophic communities, marking a potentially key ecological role for fungi in the deep biosphere31. When anaerobic fungi are enriched together with methanogens, they are able to degrade lignocellulose and produce more methane than bacteria and methanogens do32. This suggests that consortia of anaerobic fungi and methanogens in the deep subsurface hold the potential for methane production, not only from lignocellulose, but also from other sources of organic matter that may be more recalcitrant to degradation by bacteria and methanogens. This opens up a unique niche and new role for subsurface, fungal-methanogen consortia to fill, but in situ evidence of such consortia has not yet been reported form the deep subsurface.
Here, we explore the late Devonian (Frasnian) Siljan impact structure in Sweden for fossil fungi in anoxic environments and use imaging techniques, staining and biomarkers to identify and describe the fossilized fungal remains. Stable isotopes and organic molecular remains of coeval secondary minerals are used to link the fungi to prokaryotic metabolisms, such as methanogenesis. Microbial methane has formed in this impact structure at least since the Late Cretaceous33, making it an optimal site for exploration of potential ancient fungi–methanogen relationships. Our findings suggest a link between anaerobic fungi and methanogens at several hundred meters depth in the impact crater, in a putative process where fungi fueled methanogenesis via H2 production during degradation of organic matter infiltrated from black shales33. This complements H2 from other sources such as abiotic and prokaryotic fermentation, and manifests a potentially widespread and long-term ecological influence of fungi for methane formation in the vast deep biosphere environment. This may be of great importance, since methane is a very potent greenhouse gas34. We also establish the first timing constraints of anaerobic fungi in the continental deep biosphere, by linking it to previously reported U-Pb dating of coeval calcite33 and, in addition, detect a tetrahymanol biodegradation product in the form of 30nor-gammacerane in the fungal remnants.
Results
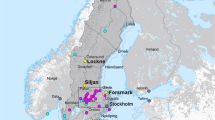
The eroded Siljan crater has an age of 380.9 ± 4.6 Ma35 and has down-faulted Devonian and Silurian sedimentary rocks with thicknesses of up to 400–500 m36,37 in a circular crater rim depression (Fig. 1). Cored boreholes of up to 700 m depth penetrate the rim zone38. Open fractures in seven of these drill cores representing both the sedimentary units and the underlying Paleoproterozoic felsic host rock were screened for the presence of fossilized microorganisms. A methane-dominated gas was encountered at several depths during borehole drilling, both in the sedimentary units and in the deeper basement33. Bituminous material and seep oil of shale origin are scattered in the pore space and fractures of both sedimentary rocks39,40 and the deeper igneous rocks33. A highly fractured and porous core section in granite-rhyolite at depths between 534 and 542 m in borehole CC1 contained scattered filamentous carbonaceous material resembling fungal hyphae. Five fractures in this section were sampled for detailed analysis. This rock section is >125 m below the contact to the Paleozoic sedimentary units and represents a sub-vertically dipping fracture network structure. The fractures are partly sealed by mineral infillings, but abundant open cavities with euhedral crystals remain, providing open pore space for colonization by microorganisms (Fig. 1c, d). The open cavities were exposed in the laboratory by opening the fractures physically with a chisel. The exposed fracture surfaces contain carbonaceous material, euhedral crystals of calcite, pyrite, and clay minerals grown on older euhedral quartz that lines the host rock contact (Fig. 1e). The morphology of the calcite crystals reveals more than one generation; an older core and an overgrowth (Calcite-1 and Calcite-OG, Fig. 1e).
a Map of Sweden with Siljan impact crater indicated (Adobe Illustrator drawing made by the authors). b Geological map of Siljan with location and simplified geology of cored borehole CC1 shown (no detailed mapping of the sedimentary units is available), including the fractured section at 534–542 m sampled for detailed studies. The map, excluding the drill core log, is modified from33 and is a electronically re-drawn in Adobe Illustrator after a map originally presented in the ref. 87. c Drill core section with partly open fractures and cavities in rhyolitic rock. d Exposed surface of the walls of mechanically opened cavities from c. e Back-scattered ESEM-image of minerals and carbonaceous and mineralized filaments (arrows “Hypha” and “Mineralized hypha”) on the surface of the exposed fracture. Minerals are quartz (Qz), pyrite, clay minerals, and calcite. The calcite crystals show an older core (“Calcite-1”) and a younger overgrowth (“Calcite-OG”, borders marked in one of the crystals by a gray line).
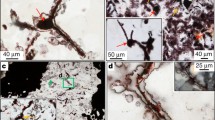
The carbonaceous material occurs as thin films resembling extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) biofilms on the fracture surface, preferentially on quartz (Fig. 2a) but also on the euhedral calcite crystals (Fig. 1e). From this presumed biofilm, filamentous structures protrude into the open cavity as single filaments or as intertwined mycelium-like networks (Fig. 2b, c) that are intergrown with the outermost parts of the calcite overgrowths. The filaments have diameters of ~10 ± 5 µm, and extend as undulating features of more than a millimeter (Fig. 3a) from the onset at the biofilm (Fig. 3b). At contact with mineral surfaces the filaments widen in a tapered fashion similar to so called hyphal bridges known from fungal hyphae38 (Fig. 3b). The filaments have septa at regular distances of around 50–60 µm (Fig. 3c), and branch frequently (Fig. 2c). Mineralization to dominantly clay minerals is a common feature and is partial (Fig. 2d) to complete (Fig. 2e). Fluorescence microscopy confirmed that the filaments were positively stained with Calcofluor White, which indicates the presence of chitin in some parts of the filaments (Fig. 4f). Parts of the filaments did not show a positive reaction, presumably due to degradation and mineralization.
a A thin carbonaceous biofilm covers older quartz crystals in fracture cavities. b Fungal hypha growth has started from the biofilm towards the open cavity where a mycelium of branching hyphae has started to form. c Close-up of the branching features of the hyphal network. d Partial mineralization by clay minerals and e complete mineralization by clay minerals. Back-scattered ESEM-images of uncoated samples.
a Back-scattered ESEM-image of a calcite crystal intergrown with the calcite overgrowth (Calcite-OG). b SRXTM orthoslice showing mineralized filaments existing within a euhedral calcite crystal, overgrown with the latest calcite overgrowth (Calcite-OG). c Close-up ESEM-image of a filament (arrow “Hypha”), featuring tiny precipitates of clay minerals and euhedral calcite crystals (<5 µm in size, composition in Supplementary Fig. 4) and filamentous carbonaceous material on the surface of the main filament (arrow “EPS”, carbonaceous composition documented in Supplementary Fig. 5). The EPS grades from carbonaceous to completely mineralized. d Back-scattered ESEM-image of microcrystalline pyrite aggregates on mineralized mycelium together with organically preserved filaments (arrows “Hypha”). e SRXTM surface-rendering of the mycelium (orange) together with fine-grained pyrite (bright yellow) and calcite (dark purple) on the older calcite fracture coating in the cavity. f Staining of a filament. The filament parts are either showing positive reaction for chitin, or no reaction due to mineralization. The hypha was detached from the fracture surface and background is glass vial and staining fluid. CFW Calcofluor White.
The outermost growth zone of the euhedral calcite crystals is intergrown and partly overgrown with filaments (Figs. 1e, and 4a). Synchrotron radiation X-ray tomographic microscopy (SRXTM) shows that mineralized filaments exist within the euhedral calcite crystals, and that the calcite overgrowth has completely covered the suggested organisms in places (Fig. 4b). Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy (ESEM) reveals that the individual filaments feature <5 µm sized precipitates of clay minerals and euhedral calcite crystals on the surface of the filaments (Fig. 4c). Carbonaceous material appears as small filamentous-like ridges with widths of ~1 µm and length of a few tens of micrometers, on the surfaces of the main filaments (Fig. 4c). These smaller filamentous-like features appear to form networks that transform into carbonaceous biofilm-like material interpreted as remnants of EPS, which contains calcite mineralization.
Microcrystalline aggregates of pyrite and late-stage calcite occur within the carbonaceous mycelium-like network, and are physically separated from the fracture wall and older euhedral pyrite and calcite (Calcite-1) coating (Fig. 4d, e and Supplementary Fig. 1). Spheres with diameters ranging between 5 and 15 µm occur on the tip of the hyphae (Fig. 3d) and as individual features on the fracture surface (Supplementary Fig. 2). Spheres within the smaller diameter range occur as connected pairs which resemble budding cell division (binary division). Orbs within the larger diameter range are usually singular. The morphology of the spheres and filaments is intact in the SEM and their chemical composition is close to identical (Supplementary Fig. 3).
The organic extracts of the fracture minerals including parts of the fungal biofilm contained predominantly highly degraded organic matter in an unresolved complex mixture, in common with bitumen-rich coatings in the fracture network33. Hydrocarbons C16–C35 detected with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) show a bimodal distribution with maxima at C19 and C25. Intriguingly, 30nor-gammacerane is detected, along with a number of hopanoids ranging from C27 to C35, but no steranes (Fig. 5a). This 30nor-gammacerane is most concentrated in the organic extract of permineralized hyphae together with elemental sulfur (Fig. 5b). In contrast to the mineral-dominated sample, the permineralized hyphae sample also contains fatty acids between C14 and C22, dominated by C16 and C18 (full chromatogram not shown). Minor but distinct peaks of unsaturated C16:1 and C18:1 occur. Odd-chain fatty acids, especially C15; C15i and C15ai, and C17; C17i and C17ai are also detected.
Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) microanalysis transects through calcite crystal cross-sections (Fig. 6) show a shift from relatively isotopically light δ13C values in the inner part of the calcite crystals (Calcite-1) to isotopically heavy in the outermost overgrowth that embeds the filaments (Calcite-OG). The δ13Ccalcite values are as high as +8.1 ± 0.4‰ (nSIMS = 14, median +6.0‰ in Calcite-OG, Supplementary Data 1). Pyrite occurring within the mycelium-like network (Fig. 4d, e) has isotopically light and relatively homogenous δ34S values of −40 ± 1‰ (nSIMS = 37) as presented previously33.
Discussion
The size and septation of the filaments as well as their occurrence in mycelium-like networks with frequent branching is in agreement with a fungal, rather than a prokaryotic, interpretation41. The mineralization to clay minerals is also a common fungal feature42,43 and the chemistry derived by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS, Supplementary Fig. 4) resembles previous findings of smectite/montmorillonite-dominated clay–mineralization of fungal hyphae42. Such mineralization of organic matter prevents further degradation and so explains the exceptional preservation of the mycelial network44. The detection of chitin further strengthens a fungal interpretation and excludes a prokaryotic affinity. Chitin can be resistant to degradation and diagenesis for long periods of time, and has previously been detected in fossilized fungi from the oceanic crust of Miocene age45, in 2 Ma old fungal fossils from a paleo-hydrothermal system46, as well as in fungal fossils of an alleged Neoproterozoic age in dolomitic shale of the Mbuji-Mayi Supergroup, Democratic Republic of Congo17. The behavior of hyphae originating from a basal film corresponds to previously described fossilized hyphae of the deep biosphere16,21. The hyphal size and morphology, including repetitive septa suggests an affinity to Dikarya (ascomycetes or basidiomycetes), but a conclusive affinity of the fungal fossils is challenging to determine. The spheres of small diameter exhibit likely cell division, and the single spheres of larger diameter correspond well with budding yeast and subsequent growth of single yeast cells. Yeasts have previously been reported from ~400 m depth in an anaerobic crystalline bedrock aquifer at Äspö, Sweden13. We suggest the spheres in our material represent fossil yeast-like organisms, although the interpretation is uncertain as it is merely based on morphology. Yeasts are facultative anaerobes and can survive under anoxic conditions throughout their lifecycle47. We posit that the contemporaneous occurrence of filaments and spheres, combined with their identical composition and preservation, indicates mold-like and yeast-like growth stages of a dimorphic fungus, rather than two different fungal taxa. Dimorphic fungi can exist as a yeast-like or a filamentous phase and can switch between these two during their lifecycle48. We hypothesize that the ability to grow and switch between a multicellular hyphal stage and a unicellular yeast confers a selective advantage for survival and colonization in the oligotrophic deep subsurface biome. Hyphal growth facilitates the exploration for nutrients and carbon, whilst the yeast form enables rapid reproduction and widespread dissemination of cells via fluids in rock fracture systems.
The findings of the fungal fossils at depths well below the redox front22,49, together with the associated unaltered sulfide minerals, indicate fungal growth under strictly anoxic conditions. Facultative anaerobic fungi are known from all major fungal divisions and are frequently found in extreme environments including the deep subsurface14. Obligate anaerobic fungi, however, are largely from the phylum Neocallimastigomycota and are best known from the rumen of mammalian herbivores but have been reported from the gut and coelomic fluid of the coastal sediment dwelling sea urchin Echinocardium cordatum50. They also occur in the guts of the algae-grazing marine iguana Amblyrhynchus cristatus51. They have been reported from environmental sites such as landfill soils52 as well as lacustrine53, estuarine54, and marine sediments55. Thus, a growing number of observations indicate that Neocallimastigomycota exist not only as endosymbionts in ruminants but also in marine animals. It still remains unclear however, whether the findings of free-living Neocallimastigomycota in anoxic sediments and soils, which are based on molecular data alone, are due to contamination, as no free-living example organisms have been enriched or isolated yet. The growing literature of extant and fossil fungi from strictly anoxic environments indicates a gap in our understanding of anaerobic fungi across the fungal taxonomic tree, and that the abundance and diversity of obligate anaerobic fungi are far from well understood.
The detection of 30nor-gammacerane exclusively in the hyphae and not in the other carbonaceous materials is interesting considering the isolated and strictly anoxic nature of the samples in which the fossil fungi are found. Nor-gammacerane is the decomposition product of tetrahymanol, a key molecule in anaerobic metabolism in various micro-eukaryotes including fungi56,57. Even though the precursor of tetrahymanol may be unclear, this lipid is only produced under anaerobic conditions, and thus in the geological record, gammacerane is a useful ecosystem biomarker and proxy for anoxic settings. Sterols play essential roles in cell physiology, especially in cell membranes, in most eukaryotes. Sterols requires molecular oxygen at multiple steps of biosynthesis. Even though the enzymes responsible can function at extremely low levels of oxygen, eukaryotes need additional strategies to survive in the absence of oxygen58. Possible strategies for anaerobic eukaryotes are either to acquire sterols from the environment, or use alternative molecules. Sterols, or the diagenetically degraded forms, steranes, can be stable for long periods of time as the primary degradation pathways are oxygen dependent59. Steranes can be detected at substantial quantities in various environments throughout the geologic record, and therefore act as available substrates for scavenged by other eukaryotes60. Most eukaryotes have transporters for acquisition of sterols from the environment. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, responsible for production of wine or beer is an example. Oxygen depletion prior to alcohol fermentation makes the yeasts unable to produce sterols. Instead they acquire sterols from the environment using Aus1 and Pdr11 transporters, which have homologs in many other fungi. Presence of either transporter is enough for growth during fermentation, but loss of both is lethal61. In isolated and strictly anoxic environments, eukaryotes can neither produce sterols nor scavenge off other steroid-bearing eukaryotes. Instead, they use a sterol-like molecule that can be produced in the absence of oxygen—tetrahymanol or other hopanoids—as an alternative62. Neocalligmastigomycota produce tetrahymanol as a characteristic membrane-reinforcing lipid instead of sterols as an adaptation to oxygen-free environments58,63. The rumen fungus Piromyces communis provides such an example, and lacks both sterols and homologs of the transporter Aus1 in its genome, but has tetrahymanol in the cell membranes63. Piromyces, as well as some other eukaryotes living in anoxic environments, can synthesize this molecule owing to a laterally transferred gene from bacteria64. This suggests that such fungi may have unique strategies for survival in environments permanently lacking oxygen29. Discoveries of actively anaerobic and facultatively anaerobic fungi in the deep biosphere, belonging mainly to the Ascomycota phylum14, suggest that this adaptation may be more widespread, but the tetrahymanol pathway has not been confirmed among deep biosphere fungi previously.
The traces of bitumen have infiltrated down into the crystalline basement fractures33 from the organic-rich Upper Ordovician Fjäcka shale existing in the sedimentary successions of the crater rim40. The bitumen has undergone substantial thermal maturation and biodegradation39,40. Seep-oil and solid bitumen in limestone fractures have carbon numbers of steranes and diasteranes, which might indicate predominantly terrigenous higher plant input deposited in oxidizing environments40,65. Investigations of bitumen in deeper fractures of the crystalline basement, however, indicate an absence of steranes33,65. Because of the molecular structure it is likely that steranes in the seep oils were incorporated in locally fixed kerogen structures and did not migrate through the fracture network. As the fungus lived in an anoxic part deep within the fracture network, where sterols could neither be readily acquired from the environment nor produced, it would have been necessary to find alternative ways to build sterol-like molecules to maintain cell wall stability. Although hopanoids synthesized via oxygen-independent pathways could also substitute position and function of the sterols in the membrane, the only known pathway for sterol substitution in anaerobic fungi is via tetrahymanol. The latter is in line with our findings of 30nor-gammacerane (Fig. 5). 30nor-gammacerane may thus be an important biomarker for anaerobic fungi in the rock record.
The fungal hyphae are succeeded by, and intergrown with, calcite overgrowths (Figs. 4 and 6). The outermost growth zone of the euhedral calcite crystals has been dated with high spatial resolution U-Pb geochronology to an age of 39.2 ± 1.4 Ma33. This marks the age of the fungi embedded in this calcite growth zone. However, partly organically preserved hyphae in the cavities are likely of younger age. Sampling of the drill core immediately after drilling assures that the fungi are not modern contaminants. The ancient nature of the fungal hyphae is supported by several lines of evidence, including 1) the partly to completely mineralized and degraded nature of the hyphae, as well as absence of any recent functionalized molecules in the extracted organic matter (e.g., intact lipids, or sugars and amino acids common in EPS), 2) presence of sulfides on the hyphae confirming formation under anaerobic conditions and not at oxic, atmospheric conditions after core retrieval, and 3) no collapsing of the filaments or spheres under vacuum in the SEM.
Relatively isotopically light, 12C-rich, methane is produced during microbial methanogenesis, and because of this isotopic discrimination against 13C, the residual CO2 becomes 13C-rich66. Incorporation of the residual carbon in authigenic carbonate minerals inherits the 13C-rich signature and can therefore be used as a marker for methanogenesis67. The significantly 13C-enriched calcite observed in the fungus-related calcite overgrowth (δ13Ccalcite values as heavy as +8.1‰, Fig. 6) is therefore proposed to reflect precipitation following microbial methanogenesis in situ. This is in agreement with previous widespread findings of isotopically heavy calcite in this fracture system, with δ13Ccalcite values up to +21.5‰33. The older calcite (Calcite-1) with lighter δ13Ccalcite values is, however, not linked to methanogenesis based on the C isotope values (Fig. 6). Instead, onset of methanogenesis occurred in temporal relation with the appearance of fungi. The significantly 13C enriched calcite values point to methanogenesis through the carbonate reduction pathway35,68, the dominant terminal process in petroleum biodegradation in the subsurface69. The in situ formation of microbial methane through the carbonate reduction pathway is further supported by isotopically light methane (δ13CCH4: −64 ± 2‰) and isotopically heavy carbon dioxide (δ13CCO2: +5–9‰) sampled in boreholes nearby33. As this is an active gas prospecting site with ongoing production well tests, no sampling for active microbial communities in the water has been possible, and hence the presence of active methanogenic communities has not been possible to determine.
The supply of the electron donor H2 needed for microbial methanogenesis through CO2 reduction may originate from fermentation of hydrocarbon related organic matter, in addition to geological sources (hydrolysis) in a first step and utilization of H2 by autotrophic methanogens in a second step (CO2 + 4H2 = CH4 + 2H2O)69. Based on the spatial link between 13C-rich calcite and fungal hyphae, we propose that anaerobic fungi that produce H2 as a metabolic waste product23,24,25 have facilitated autotrophic methanogenesis through degradation of organic matter, in addition to H2 originating from prokaryotic fermentation degradation. The significance of fungal derived H2 versus prokaryotic derived H2 for methanogenesis cannot be assessed in this fossil system, but the presence of 13C-rich calcite on the hyphae suggests a close connection between the fungi and methanogenesis. The available data do not suggest the presence of prokaryotic fermenters, but the possibility cannot be ruled out since they are known from subsurface settings70,71. Culture-dependent evidence of fungi–methanogen relationship has, so far, only been established in gut biomes and not in environmental samples72,73. However, fungi have been largely neglected in microbial ecology, not least in the deep biosphere, and anaerobic fungi as possible key players in anoxic systems is a relatively new concept30,31. Isolation and culture-dependent investigations of deep biosphere biota will hopefully be more frequently used in the future and shed more light on subsurface ecosystems. An in vitro approach using “synthetic” co-cultures of various candidate filamentous fungi and methanogens is of particular interest, as well as the enrichment, isolation, and co-culturing of native subsurface fungal-prokaryote community members. The organic matter may be remnants of bitumen that the fungi can degrade, and/or prokaryotic metabolites and mats16, the main constituent of dissolved organic matter at large depth within this type of setting74. It has been shown that soil-derived fungi are able to produce methane through biodegradation in relationship with methanogens75, but also without76. In the latter case, methane was produced by saprotrophic aerobic fungi, but so far, no anaerobic fungi are known to produce methane.
Microbial sulfate reduction (MSR) can also be involved, both in the oxidative degradation of organic matter of sedimentary origin, but also by autotrophic utilization of H273. Pyrite formed by MSR is typically strongly depleted in 34S77,78. The very low δ34Spyrite values (−40 ± 1‰, V-CDT)33 of pyrite precipitated in the mineralized mycelium (Fig. 4d, e) are thus proposed to reflect MSR, in similarity with findings of fungal hyphae with 34S-depleted pyrite at 740 m depth at Laxemar, Sweden16. The sulfate reducers were either feeding on the H2 or other fungal waste products, or scavenging the fungal biomass as a direct energy source. The sulfate reducers and methanogens were probably not completely coeval as the former outcompete methanogens for H2 and other substrates when sulfate concentrations are elevated79. Exhaustion of sulfate by MSR, or infiltration of fresh water may have resulted in temporal fluctuation of conditions in favor of methanogenesis.
The smaller filamentous EPS structures on the larger fungal hyphae are closely connected to calcite with methanogenesis signals (13C-rich). EPS formation is common in mixed fungal–bacterial biofilms80, but in the case presented here, neither body fossils resembling archaea, nor diagnostic biomarkers of methanogens remain in the fossilized biofilm on the fracture surface. This is in line with previous observations of ancient deep igneous-rock hosted microbial communities16.
The upper crystalline continental crust environment makes up one of the largest, but yet least explored, deep biosphere habitats on Earth. Considering the vastness of this biome, it is reasonable to assume that these microbial processes affect the energy cycles of our planet, but to what degree remains largely elusive. Of particular interest is the in situ microbial formation of methane, which if/when released to the atmosphere is a potent greenhouse gas34. The extent, continuity and physicochemical prerequisites for methane accumulation require more attention in order to assess the significance of this underexplored greenhouse gas source on a global scale. Autotrophic methanogenesis requires a supply of H2 as electron donor. In specific environments, such as serpentinized systems and at subduction zones, the flux of abiotic H2 may be large and can therefore provide enough energy for autotrophic communities such as methanogens81. In granitoid-hosted aquifers of Precambrian cratons, several different processes have been proposed for the origin of H2, including abiotic radiolysis82 that may build up in the waters over the long residence times recorded for deep brine fluids at kilometers depths83. Igneous-rock hosted groundwaters from the Fennoscandian shield show scattered elevated H2 concentrations, of up to ~0.2 mL/L84, that are neither correlated with depth nor with residence times. The residence times of these waters, in the order of a couple of thousand years85, are too short for build-up of significant H2 concentrations by radiolysis (cf.82). Instead, our results suggest that anaerobic fungi may be a neglected source of H2, that fuels autotrophic methanogens in the deep continental subsurface and complement potential prokaryotic degradation pathways of organic matter involved in H2 formation, such as fermentation. The heterotrophic fungal metabolism can be sustained either by scavenging of descended organic matter33,41, or feeding off of indigenous organic prokaryotic metabolites suspended in the water74 or available in microbial mats16, and we propose future co-culturing studies to gain more knowledge about the syntrophic relationships of fungi and methanogens in these deep environments. Our results also suggest that impact craters enable deep colonization by eukaryotes in the pore space and connected conductivity that result from deep crustal fracturing during meteorite bombardments, partly by introducing surficial organics to great depth. Impact events may thus have enabled intermittent eukaryotic propagation into new ecological niches in the deep biosphere throughout Earth’s history.
Methods
Materials
Open fractures from a drill core CC-1 at Mora, Sweden (Fig. 1) were sampled for carbonaceous filaments and coeval secondary fracture-coating minerals. Samples are from 534 to 542 m vertical depth from the ground-surface, in igneous rock fractures. Calcite mainly occurs as euhedral crystals of short c-axis type (Fig. 1e). Polished cross sections reveal growth zonation in several calcite crystals (Fig. 6a). The paragenesis includes pyrite, clay minerals, harmotome, apophyllite, sphalerite, galena, and quartz but most of these minerals are related to the oldest growth phases of calcite (exceptions are pyrite and clay minerals). Carbonaceous material resembling fragments of solid bitumen are present. The borehole was drilled at the crater rim zone through an upper layer of depressed Paleozoic sedimentary rocks into the deeper, fractured Proterozoic crystalline bedrock. The interface between the rock units is at 406 m in the studied borehole. The mineralogy and appearance of the fracture coatings were examined using a Hitachi S-3400N Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) equipped with an integrated EDS system and an Environmental SEM (ESEM) with a FEI QUANTA FEG 650 (Oxford Instruments, UK) EDS and an Oxford T-Max 80 detector. The analyses were performed in low vacuum to minimize surficial charging effects. This enables the use of uncoated samples and, thus, EDS analyses of the C content. The acceleration voltage was 20 or 15 kV depending on the nature of the sample, and the instrument was calibrated with a cobalt standard. Peak and element analyses were done using INCA Suite 4.11 software and normalized to 100 wt%. Element mapping was done using Aztec software. The calcite crystals were handpicked under the microscope for stable isotope analysis and carbonaceous filaments were hand-picked for staining and biomarker analysis. Larger fragments of the mycelium-like structures and mineral coatings were detached from the drill core sample for SRXTM.
SIMS
Calcite crystals related to hyphae were mounted in epoxy, polished to expose cross-sections and examined with SEM to trace zonation and impurities prior to SIMS analysis. SIMS-analysis (10 μm lateral beam dimension, 1–2 μm depth dimension) of carbon isotopes in calcite was performed on a Cameca IMS1280 ion microprobe following the analytical settings and tuning reported previously86. Analyses were performed in automated sequences, with each analysis comprising a 70 s pre-sputter to remove the gold coating over a rastered 15 × 15 µm area, centering of the secondary beam in the field aperture to correct for small variations in surface relief and data acquisition in sixteen four second integration cycles. The magnetic field was locked at the beginning of the session using an NMR field sensor. Secondary ion signals were detected simultaneously using a Faraday detector/Electron Multiplier combination with mass resolution 2500 on the 12C peak and 4000 on the 13C peak to resolve it from 12C1H. Results are reported as per mil (‰) δ13C based on the Pee Dee Belemnite (V-PDB) reference value. Data were normalized for instrumental mass fractionation (IMF) using matrix matched reference materials mounted together with the sample mounts and analyzed after every sixth sample analysis. The calcite reference material, S0161 from a granulite facies marble in the Adirondack Mountains, was kindly provided by R.A. Stern (Univ. of Alberta). The values used for IMF correction were determined by conventional stable isotope mass spectrometry at Stockholm University on ten separate pieces, yielding δ13C = −0.22 ± 0.11‰V-PDB (1 std. dev.). Precision was ±0.3–0.5‰. Values of the reference material measurements are listed together with the samples in Supplementary Data 1.
GC-MS
The fungi sample and a sample with calcite and fungi were gently acetone flushed to remove surface contaminations and then ground with an agate pistil. The sample powders (30 mg) were extracted in Teflon-capped glass vials using 2 mL of pre-distilled dichloromethane/methanol (ultrasonication, 15 min, 40 °C) and the supernatant was decanted after centrifuging. Extraction was repeated twice, with dichloromethane and hexane as solvents. Once evaporated, the combined extracts and re-dissolution in pure dichloromethane, the solvents were dried with N2. The total organic extract was derivatized by addition of 50 μL BSTFA (50 °C, overnight). After the sample was dried with N2, it was mobilized with 20 µL n-hexane and stored frozen at −18 °C. The sample remnants were dissolved and demineralized by adding 5 mL of TMCS/methanol (1 + 9) for 12 h and then derivatized for 90 min (80 °C). After cooling, the samples were mixed with n-hexane and the decanted supernatants collected separately. This procedure was repeated three times. The combined supernatants were dried with nitrogen and remobilized with 50 µL n-hexane. Each sample extract (1 µL) was analyzed via on-column injection into a Varian CP-3800 GC/1200-quadrupole MS (70 keV) equipped with a fused silica column (Phenomenex ZB-5; 30 m length, 0.32 µm inner diameter, 0.25 μm film thickness). The GC oven programming was from 80 °C (held 3 min) to 325 °C (held 40 min) at 6 °C min−1. Carrier gas was He, at 1.4 mL min−1. Compounds were assigned by comparison with spectral databases and published mass spectral data.
SRXTM
The tomographic measurements were carried out on the TOMCAT beamline at the Swiss Light Source, Paul Scherrer Institute, Villigen, Switzerland. Projections were acquired equiangularly over 180°, post-processed online and rearranged into flat-corrected and darkfield-corrected sinograms. The beam energy used for the five aliquots was respectively 20 (n = 2), 23 (2), and 25 (1) keV, for maximum absorption contrast. Specimens were scanned with objectives 10× (n = 2, exposure time 300 ms) and 20× (n = 3, exposure time 1300 ms) at two different sessions. During the scanning process a LuAg:Ce 20 µm scintillator was used. Visualization has been done using Avizo 9.5.0 (FEI Company). With the 20× lens used, the resulting voxel size was 0.325 μm and, respectively, 0.65 µm with 10×.
Staining
Samples were treated with sterile stainless steel forceps and not touched by ungloved hands prior to staining to reduce introduction of fluorescence particles. A few single fungal hyphae were detached from the fracture surface under the microscope, and investigated under fluorescence microscopy using a Olympus BX51 microscope connected to an external Lumen Dynamics X-CITE series 120 Q, prior to staining to exclude autoflourescence. The samples were stained with Calcofluor White (ordered from VWR) for ten minutes and investigated with fluorescence light illumination under the microscope.
Data availability
All relevant data are included in the Supplementary Information of this article and stored publically available in the archive at Swedish National Data Service (doris.snd.gu.se)
References
Hoehler, T. M. & Jorgensen, B. B. Microbial life under extreme energy limitation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 11, 83–94 (2013).
Whitman, W. B., Coleman, D. C. & Wiebe, W. J. Prokaryotes: the unseen majority. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 95, 6578 (1998).
Kallmeyer, J., Pockalny, R., Adhikari, R. R., Smith, D. C. & D’Hondt, S. Global distribution of microbial abundance and biomass in subseafloor sediment. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 109, 16213 (2012).
Magnabosco, C. et al. The biomass and biodiversity of the continental subsurface. Nat. Geosci. 11, 707–717 (2018).
Wu, X. et al. Microbial metagenomes from three aquifers in the Fennoscandian shield terrestrial deep biosphere reveal metabolic partitioning among populations. ISME J. 10, 1192–1203 (2016).
Eme, L., Spang, A., Lombard, J., Stairs, C. W. & Ettema, T. J. G. Archaea and the origin of eukaryotes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 15, 711–723 (2017).
Onstott, T. C. et al. Paleo-Rock-hosted life on earth and the search on mars: a review and strategy for exploration. Astrobiology 19, 1230–1262 (2019).
McMahon, S. & Parnell, J. Weighing the deep continental biosphere. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 87, 113–120 (2014).
Lopez-Fernandez, M. et al. Metatranscriptomes reveal that all three domains of life are active but are dominated by bacteria in the fennoscandian crystalline granitic Continental Deep biosphere. mBio 9, e01792–01718 (2018).
Sherwood Lollar, B., Onstott, T. C., Lacrampe-Couloume, G. & Ballentine, C. J. The contribution of the Precambrian continental lithosphere to global H2 production. Nature 516, 379–382 (2014).
Borgonie, G. et al. Nematoda from the terrestrial deep subsurface of South Africa. Nature 474, 79–82 (2011).
Purkamo, L., Kietäväinen, R., Nuppunen-Puputti, M., Bomberg, M. & Cousins, C. Ultradeep microbial communities at 4.4 km within crystalline bedrock: implications for habitability in a planetary context. Life 10, 2 (2020).
Ekendahl, S., O’Neill, H. A., Thomsson, E. & Pedersen, K. Characterisation of yeasts isolated from deep igneous rock aquifers of the Fennoscandian shield. Microb. Ecol. 46, 416–428 (2003).
Sohlberg, E. et al. Revealing the unexplored fungal communities in deep groundwater of crystalline bedrock fracture zones in Olkiluoto, Finland. Front. Microbiol. 6, 573 (2015).
Ivarsson, M. et al. Fungal colonization of an Ordovician impact-induced hydrothermal system. Sci. Rep. 3, 3487 (2013).
Drake, H. et al. Anaerobic consortia of fungi and sulfate reducing bacteria in deep granite fractures. Nat. Commun. 8, 55 (2017).
Bonneville, S. et al. Molecular identification of fungi microfossils in a neoproterozoic shale rock. Sci. Adv. 6, eaax7599 (2020).
Loron, C. C. et al. Early fungi from the Proterozoic era in Arctic Canada. Nature 570, 232–235 (2019).
Peckmann, J., Bach, W., Behrens, K. & Reitner, J. Putative cryptoendolithic life in Devonian pillow basalt, Rheinisches Schiefergebirge, Germany. Geobiology 6, 125–135 (2008).
Bengtson, S. et al. Fungus-like mycelial fossils in 2.4-billion-year-old vesicular basalt. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 1, 0141 (2017).
Ivarsson, M., Drake, H., Bengtson, S. & Rasmussen, B. A cryptic alternative for the evolution of hyphae. BioEssays 42, 1900183 (2020).
Drake, H., Tullborg, E.-L. & Mackenzie, A. B. Detecting the near-surface redox front in crystalline bedrock using fracture mineral distribution, geochemistry and U-series disequilibrium. Appl. Geochem. 24, 1023–1039 (2009).
Yarlett, N., Orpin, C. G., Munn, E. A., Yarlett, N. C. & Greenwood, C. A. Hydrogenosomes in the rumen fungus Neocallimastix patriciarum. Biochem. J. 236, 729–739 (1986).
O’Fallon, J. V., Wright, R. W. & Calza, R. E. Glucose metabolic pathways in the anaerobic rumen fungus Neocallimastix frontalis EB188. Biochem. J. 274, 595–599 (1991).
Brul, S. & Stumm, C. K. Symbionts and organelles in ancrobic protozoa and fungi. Trends Ecol. Evol. 9, 319–324 (1994).
Khejornsart, P. & Wanapat, M. Diversity of rumen anaerobic fungi and methanogenic archaea in swamp buffalo influenced by various diets. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 9, 3062–3069 (2010).
Gruninger, R. J. et al. Anaerobic fungi (phylum Neocallimastigomycota): advances in understanding their taxonomy, life cycle, ecology, role and biotechnological potential. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 90, 1–17 (2014).
Kumar, S., Indugu, N., Vecchiarelli, B. & Pitta, D. W. Associative patterns among anaerobic fungi, methanogenic archaea, and bacterial communities in response to changes in diet and age in the rumen of dairy cows. Front. Microbiol. 6, 781 (2015).
Zain Ul Arifeen, M. et al. The anaerobic survival mechanism of Schizophyllum commune 20R-7-F01, isolated from deep sediment 2 km below the seafloor. Environ. Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15332 (2020).
Ivarsson, M., Schnürer, A., Bengtson, S. & Neubeck, A. Anaerobic fungi: a potential source of biological H2 in the oceanic crust. Front. Microbiol. 7, 674 (2016).
Drake, H. & Ivarsson, M. The role of anaerobic fungi in fundamental biogeochemical cycles in the deep biosphere. Fung. Biol. Rev. 32, 20–25 (2018).
Ma, Y., Li, Y., Li, Y., Cheng, Y. & Zhu, W. The enrichment of anaerobic fungi and methanogens showed higher lignocellulose degrading and methane producing ability than that of bacteria and methanogens. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 36, 125 (2020).
Drake, H. et al. Timing and origin of natural gas accumulation in the Siljan impact structure, Sweden. Nat. Commun. 10, 4736 (2019).
Hmiel, B. et al. Preindustrial 14CH4 indicates greater anthropogenic fossil CH4 emissions. Nature 578, 409–412 (2020).
Jourdan, F., Reimold, W. U. & Deutsch, A. Dating terrestrial impact structures. Elements 8, 49 (2012).
Muhamad, H. et al. Analysis of borehole geophysical data from the Mora area of the Siljan Ring impact structure, central Sweden. J. Appl. Geophys. 115, 183–196 (2015).
Juhlin, C. et al. A new interpretation of the sedimentary cover in the western Siljan Ring area, central Sweden, based on seismic data. Tectonophysics 580, 88–99 (2012).
Lehnert, O. et al. New Ordovician–Silurian drill cores from the Siljan impact structure in central Sweden: an integral part of the Swedish Deep Drilling Program. GFF 134, 87–98 (2012).
Vlierboom, F. W., Collini, B. & Zumberge, J. E. The occurrence of petroleum in sedimentary rocks of the meteor impact crater at Lake Siljan, Sweden. Org. Geochem. 10, 153–161 (1986).
Ahmed, M., Lehnert, O., Fuentes, D. & Meinhold, G. Origin of oil and bitumen in the Late Devonian Siljan impact structure, central Sweden. Org. Geochem. 68, 13–26 (2014).
Webster, J. & Weber, R. W. S. Introduction to Fungi 3rd edn (Cambridge University Press, 2007).
Sallstedt, T., Ivarsson, M., Drake, H. & Skogby, H. Instant attraction: clay authigenesis in fossil fungal biofilms. Geosciences 9, 369 (2019).
Fomina, M., Burford, E. P., Hillier, S., Kierans, M. & Gadd, G. M. Rock-building fungi. Geomicrobiol. J. 27, 624–629 (2010).
Wattel-Koekkoek, E. J. W., van Genuchten, P. P. L., Buurman, P. & van Lagen, B. Amount and composition of clay-associated soil organic matter in a range of kaolinitic and smectitic soils. Geoderma 99, 27–49 (2001).
Ivarsson, M. et al. Fossilized fungi in subseafloor Eocene basalts. Geology 40, 163–166 (2012).
Ivarsson, M. et al. Exceptional preservation of fungi as H2-bearing fluid inclusions in an early quaternary paleo-hydrothermal system at Cape Vani, Milos, Greece. Minerals 9, 749 (2019).
Andreasen, A. A. & Stier, T. J. B. Anaerobic nutrition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Ergosterol requirement for growth in a defined medium. J. Cell. Comp. Physiol. 41, 23–36 (1953).
Boyce, K. J. & Andrianopoulos, A. Fungal dimorphism: the switch from hyphae to yeast is a specialized morphogenetic adaptation allowing colonization of a host. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 39, 797–811 (2015).
Yu, C. et al. A combined X-ray absorption and Mössbauer spectroscopy study on Fe valence and secondary mineralogy in granitoid fracture networks: implications for geological disposal of spent nuclear fuels. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 2832–2842 (2020).
Thorsen, M. S. Abundance and biomass of the gut-living microorganisms (bacteria, protozoa and fungi) in the irregular sea urchin Echinocardium cordatum (Spatangoida: Echinodermata). Mar. Biol. 133, 353–360 (1999).
Mackie, R. I., Rycyk, M., Ruemmler, R. L., Aminov, R. I. & Wikelski, M. Biochemical and microbiological evidence for fermentative digestion in free-living land iguanas (Conolophus pallidus) and marine iguanas (Amblyrhynchus cristatus) on the Galapagos archipelago. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 77, 127–138 (2004).
Lockhart, R. J., Van Dyke, M. I., Beadle, I. R., Humphreys, P. & McCarthy, A. J. Molecular biological detection of anaerobic gut fungi (Neocallimastigales) from landfill sites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 5659–5661 (2006).
Wurzbacher, C. et al. High habitat-specificity in fungal communities in oligo-mesotrophic, temperate Lake Stechlin (North-East Germany). MycoKeys 16, 17–44 (2016).
Mohamed, D. J. & Martiny, J. B. Patterns of fungal diversity and composition along a salinity gradient. ISME J. 5, 379–388 (2011).
Picard, K. T. Coastal marine habitats harbor novel early-diverging fungal diversity. Fung. Ecol. 25, 1–13 (2017).
Harvey, H. R. & McManus, G. B. Marine ciliates as a widespread source of tetrahymanol and hopan-3β-ol in sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 55, 3387–3390 (1991).
Venkatesan, M. I., Ruth, E. & Kaplan, I. R. Triterpenols from sediments of Santa Monica Basin, Southern California Bight, USA. Org. Geochem. 16, 1015–1024 (1990).
Waldbauer, J. R., Newman, D. K. & Summons, R. E. Microaerobic steroid biosynthesis and the molecular fossil record of Archean life. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 108, 13409 (2011).
Kreit, J. & Sampson, N. S. Cholesterol oxidase: physiological functions. FEBS J. 276, 6844–6856 (2009).
Summons, R. E., Bradley, A. S., Jahnke, L. L. & Waldbauer, J. R. Steroids, triterpenoids and molecular oxygen. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 361, 951–968 (2006).
Wilcox, L. J. et al. Transcriptional profiling identifies two members of the ATP-binding cassette transporter superfamily required for sterol uptake in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 32466–32472 (2002).
Siedenburg, G. & Jendrossek, D. Squalene-hopene cyclases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 3905–3915 (2011).
Kemp, P., Lander, D. J. & Orpin, C. G. The lipids of the Rumen fungus piromonas communis. Microbiology 130, 27 (1984).
Takishita, K. et al. Lateral transfer of tetrahymanol-synthesizing genes has allowed multiple diverse eukaryote lineages to independently adapt to environments without oxygen. Biol. Direct 7, 5 (2012).
Siljeström, S. et al. Analysis of hopanes and steranes in single oil-bearing fluid inclusions using time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS). Geobiology 8, 37–44 (2010).
Whiticar, M. J. Carbon and hydrogen isotope systematics of bacterial formation and oxidation of methane. Chem. Geol. 161, 291–314 (1999).
Budai, J. M., Martini, A. M., Walter, L. M. & Ku, T. C. W. Fracture-fill calcite as a record of microbial methanogenesis and fluid migration; a case study from the Devonian Antrim Shale. Michigan Basin. Geofluids 2, 163–183 (2002).
Meister, P. & Reyes, C. The carbon-isotope record of the sub-seafloor biosphere. Geosciences 9, 507 (2019).
Head, I. M., Jones, D. M. & Larter, S. R. Biological activity in the deep subsurface and the origin of heavy oil. Nature 426, 344–352 (2003).
Lee, D.-J., Show, K.-Y. & Su, A. Dark fermentation on biohydrogen production: pure culture. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 8393–8402 (2011).
Das, D. & Veziroǧlu, T. N. Hydrogen production by biological processes: a survey of literature. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 26, 13–28 (2001).
Marvin-Sikkema, F. D., Richardson, A. J., Stewart, C. S., Gottschal, J. C. & Prins, R. A. Influence of hydrogen-consuming bacteria on cellulose degradation by anaerobic fungi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56, 3793 (1990).
Edwards, J. E. et al. PCR and omics based techniques to study the diversity, ecology and biology of anaerobic fungi: insights, challenges and opportunities. Front. Microbiol. 8, 1657 (2017).
Kieft, T. L. et al. Dissolved organic matter compositions in 0.6–3.4 km deep fracture waters, Kaapvaal Craton, South Africa. Org. Geochem. 118, 116–131 (2018).
Guo, H. et al. Important role of fungi in the production of secondary biogenic coalbed methane in China’s Southern Qinshui Basin. Energy Fuels 31, 7197–7207 (2017).
Lenhart, K. et al. Evidence for methane production by saprotrophic fungi. Nat. Commun. 3, 1046 (2012).
Sim, M. S., Bosak, T. & Ono, S. Large sulfur isotope fractionation does not require disproportionation. Science 333, 74–77 (2011).
Kohn, M. J., Riciputi, L. R., Stakes, D. & Orange, D. L. Sulfur isotope variability in biogenic pyrite; reflections of heterogeneous bacterial colonization? Am. Mineral. 83, 1454–1468 (1998).
Muyzer, G. & Stams, A. J. M. The ecology and biotechnology of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 441 (2008).
Ramírez Granillo, A. et al. Antibiosis interaction of Staphylococccus aureus on Aspergillus fumigatus assessed in vitro by mixed biofilm formation. BMC Microbiol. 15, 33–33 (2015).
Vitale Brovarone, A. et al. Subduction hides high-pressure sources of energy that may feed the deep subsurface biosphere. Nat. Commun. 11, 3880 (2020).
Lin, L.-H., Slater, G. F., Sherwood Lollar, B., Lacrampe-Couloume, G. & Onstott, T. C. The yield and isotopic composition of radiolytic H2, a potential energy source for the deep subsurface biosphere. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 69, 893–903 (2005).
Warr, O. et al. Tracing ancient hydrogeological fracture network age and compartmentalisation using noble gases. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 222, 340–362 (2018).
Hallbeck, L. & Pedersen, K. Culture-dependent comparison of microbial diversity in deep granitic groundwater from two sites considered for a Swedish final repository of spent nuclear fuel. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 81, 66–77 (2012).
Laaksoharju, M. et al. Hydrogeochemical evaluation and modelling performed within the Swedish site investigation programme. Appl. Geochem. 23, 1761–1795 (2008).
Drake, H. et al. Extreme 13C-depletion of carbonates formed during oxidation of biogenic methane in fractured granite. Nat. Commun. 6, 7020 (2015).
Högström, A. E. S., Sturkell, E., Ebbestad, J. O. R., Lindström, M. & Ormö, J. Concentric impact structures in the Palaeozoic of Sweden—the Lockne and Siljan craters. GFF 132, 65–70 (2010).
Acknowledgements
Swedish research council (contract 2017-05186 to H.D., 2017-04129 to M.I.) and Formas (contracts 2017-00766, 2020-01577 to H.D. and M.W.) are thanked for financial support. K. Lindén is thanked for sample preparation assistance and F, Marone for TOMCAT beamline assistance. Thanks to AB Igrene for access to the drill core, drilling logs and gas data and to University of Gothenburg for access to SEM. This is NordSIM publication 665.
Funding
Open Access funding provided by Linnaeus University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.D. and M.I. conceived the study. H.D. and M.I. carried out SEM investigations, microscopy and staining. S.B. and V.B. carried out SRXTM, M.W. and H.D. carried out SIMS analysis. C.H. carried out GC-MS investigations. H.D., M.I., C.H. and O.S.-W. wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and revised the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Primary handling editors: Mojtaba Fakhraee, Joe Aslin.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Drake, H., Ivarsson, M., Heim, C. et al. Fossilized anaerobic and possibly methanogenesis-fueling fungi identified deep within the Siljan impact structure, Sweden. Commun Earth Environ 2, 34 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-021-00107-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-021-00107-9
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Sterane and hopane biomarkers capture microbial transformations of complex hydrocarbons in young hydrothermal Guaymas Basin sediments
Communications Earth & Environment (2022)
-
Biosignatures of ancient microbial life are present across the igneous crust of the Fennoscandian shield
Communications Earth & Environment (2021)