Abstract
Wolbachia, an endosymbiotic alpha-proteobacterium commonly found in insects, can inhibit the transmission of human pathogens by mosquitoes. Biocontrol programs are underway using Aedes aegypti mosquitoes trans-infected with a non-natural Wolbachia strain to reduce dengue virus transmission. Less is known about the impact of Wolbachia on the biology and vectorial capacity of Anopheles mosquitoes, the vectors of malaria parasites. A naturally occurring strain of Wolbachia, wAnga, infects populations of the major malaria vectors Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles coluzzii in Burkina Faso. Previous studies found wAnga infection was negatively correlated with Plasmodium infection in the mosquito and wAnga influenced mosquito egg-laying behavior. Here, we investigate wAnga in natural populations of An. coluzzii and its interactions with other resident microbiota using targeted 16S sequencing. Though we find no major differences in microbiota composition associated with wAnga infection, we do find several taxa that correlate with the presence or absence of wAnga in female mosquitoes following oviposition, with the caveat that we could not rule out batch effects due to the unanticipated impact of wAnga on oviposition timing. These data suggest wAnga may influence or interact with the Anopheles microbiota, which may contribute to the impact of wAnga on Anopheles biology and vectorial capacity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Despite progress in control efforts over the past decade, malaria remains a major global health problem, with over 200 million reported cases each year1. The most lethal form of malaria is caused by the parasite Plasmodium falciparum, which remains endemic across much of sub-Saharan Africa. Vector control has been the most important contributor to reduction in global mortality and morbidity2,3,4,5,6. A recent stall in the decline of malaria1,6, and the increasingly widespread observations of insecticide resistance in mosquito populations7, however, highlight the need for novel approaches to malaria vector control.
Manipulation of mosquito microbiota, and in particular the introduction of the alphaproteobacterial endosymbiont Wolbachia, is an example of a promising new avenue of vector control8,9. Wolbachia infection reduces the capacity of Aedes mosquitoes to transmit dengue virus and other arboviruses through mechanisms that are incompletely understood, but which may include manipulation of the mosquito innate immune response, nutrient competition, and life-shortening of the mosquito10,11,12. In Ae. aegypti, transinfected Wolbachia has been shown to significantly alter the mosquito microbiome, suggesting the existence of complex interactions between resident microbes that may also influence vectorial capacity13. Wolbachia can be vertically transmitted from mother to offspring through infection of the germ line, thus allowing it to persist across generations once introduced. In Aedes and many other arthropod hosts, the spread of Wolbachia is enhanced through a phenomenon termed cytoplasmic incompatibility (CI), in which uninfected females that mate with infected males produce sterile broods, giving a strong reproductive advantage to infected females4,14.
Wolbachia has recently been detected with PCR-based and whole-genome sequencing approaches in several important African malaria vector species, Anopheles coluzzii, Anopheles gambiae, and An. arabiensis15,16,17,18,19,20,21. These findings, although called into question by a recent study22, have challenged the notion that anopheline mosquitoes do not harbor natural Wolbachia infections. The Wolbachia strain identified in Burkina Faso, named wAnga, has been found to exhibit very low infection intensity in An. gambiae and An. coluzzii15,16. Moreover, wAnga is present at low to intermediate frequencies in wild populations, most likely because it does not induce CI16. Wolbachia infections are negatively correlated with P. falciparum in An. coluzzii16,19, raising interest in understanding the mechanism by which these bacteria affect the capacity of Anopheles mosquitoes to transmit malaria parasites.
To aid in understanding the biological effects of wAnga infection on An. coluzzii, and the potential avenues by which it could be impacting malaria vectorial capacity, we collected blood-fed adult female mosquitoes in Burkina Faso. Using 16S-based assays on DNA extracted from mosquito carcasses, we found that while there are no major differences in the microbiome composition between mosquitoes with vs. without wAnga, certain bacterial taxa appear to be positively or negatively associated with this Wolbachia strain. This could suggest that some residents of the Anopheles microbiota may promote the ability of wAnga to colonize the mosquito host, while others may disrupt it. Interpretation of these associations between wAnga and other microbes is complicated by the biological effects of wAnga infection on An. coluzzii oviposition timing16, motivating further studies to explore the interaction of these effects on microbiome profile.
Results
The An. coluzzii microbiota
We analysed 171 mosquitoes (Fig. 1), 102 of which were determined to be infected with wAnga by 16S PCR16, by targeted 16S rRNA sequencing and obtained a mean of 72,656 reads per sample (Supplementary Fig. 1a); 144 samples exhibited at least 10,000 reads and were retained for further analysis. We observed a total of 3,189 operational taxonomic units (OTUs) at 97% identity; filtering to remove low abundance and rare OTUs (defined by those seen in only one sample or fewer than 50 reads across all samples) reduced this number to 916 OTUs. (Supplementary Fig. 1a). Only four OTUs were “core” (i.e. present in every one of the 144 mosquitoes), three of which were assigned to Acinetobacter and one to Comamonadaceae, all of which were within Proteobacteria. These core OTUs ranged in relative abundance within individual mosquitoes, sometimes as high as 80% of all bacteria (Supplementary Fig. 1b). Alpha rarefaction analyses indicated that we sequenced to a sufficient depth such that we are accurately estimating the diversity of the microbiota of the mosquitoes, and that the presence or absence of a given OTU is not likely due to insufficient sequencing depth (Supplementary Fig. 1c).
Breakdown of samples collected. A total of 171 samples were captured and then collected for DNA extraction after up to 3 days in captivity (top row, numbers indicate samples collected on each given day). Mosquitoes were collected for extraction after oviposition (second row, in beige), upon death in captivity regardless of oviposition (mortality, third row, in red), or at the end of 3 days in captivity regardless of oviposition or death. Due to study design, virtually all samples collected early (i.e., one and 2 days in captivity) underwent DNA extraction in Burkina Faso (BF, yellow circles), while the rest were extracted at a later date in the United States (US, blue circles). wAnga infection status was performed using a nested PCR, with the infection rate signified by the size of the bright blue and yellow arcs in the last row. The fraction of wAnga-positive samples for each bottom pie chart are specified by the numbers in the bottom row. Due to the accelerated oviposition impact of wAnga, wAnga infection correlated with days in captivity (p = 8.4 × 10–9), oviposition (p = 7.2 × 10–10), whether the mosquito was collected still alive or dead (p = 0.0094), and DNA extraction location (p < 10–15). p-values reported are from Fisher’s Exact Tests and have been corrected for multiple hypothesis testing using Benjamini-Hochberg.
Overall, our study confirmed previous reports showing that the An. coluzzii microbiome is diverse and composed of many phyla15,23,24,25,26. It is dominated by Proteobacteria, while Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, and Bacteroidetes are abundant secondary phyla (Fig. 2a). Greater diversity is apparent at the family level. Mosquito microbiomes were dominated by bacteria from Comamonadaceae, Moraxellaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, and occasionally Enterobacteriaceae (Fig. 2b). At the genus level, we observed Acinetobacter, Pseudomonas, and Variovorax as the most abundant genera (Fig. 2c), consistent with core OTU-level analysis (Supplementary Fig. 1b) and also detected Comamonas and Elizabethkingia. We observed significant variation among individual mosquitoes at each of these levels of taxonomy, again consistent with previous reports that indicated individual mosquito microbial compositions can vary widely24,25,27,28,29,30. To note, we were able to detect one OTU assigned to Wolbachia, which was observed in only a single mosquito sample (42 reads; 0.04% relative abundance).
The bacterial composition of the An. coluzzii microbiota. Per sample distributions of phyla (a), families (b), and genera (c) are shown. X axis represents individual mosquitoes and Y axis indicates the relative abundance of each taxon, which are colour-coded. For each, samples have been sorted on the abundance of the most dominant taxon. Only the most abundant taxa are displayed for clarity. The microbiome is dominated by Proteobacteria in the majority of mosquitoes analysed, though there was substantial variation between individuals. At the family and genus level, there is increased diversity, though in many of the samples Moraxellaceae and the genus Acinetobacter were dominant. These results are consistent with previously published reports on Anopheles.
wAnga infection has limited effects on overall microbiota composition
We next explored the relationship between several sample features (see Fig. 1) and microbiota diversity. Alpha diversity, as measured by the metric Chao1, indicating the richness of the bacterial community, did not differ significantly between mosquitoes with respect to wAnga infection status (Kruskal–Wallis; H = 0.1, p = 0.75) (Fig. 3a). In addition, Chao1 values did not differ significantly according to whether they were alive or dead at time of collection for DNA extraction (referred to as ‘mortality’ here) (Kruskal–Wallis, p > 0.5) (Supplementary Fig. 2a). The location in which the sample was extracted (either Burkina Faso or our laboratory in Boston, USA) also had no significant effect on Chao1 values (Kruskal–Wallis, p > 0.5) (Supplementary Fig. 2b). However, the day mosquitoes were collected had a significant effect on alpha diversity (Kruskal–Wallis, H = 19.8, p = 5 × 10–5), with mosquitoes collected on the first day of collection exhibiting significantly more diversity than those collected on the second and third days (Kruskal–Wallis, p < 10–4) (Supplementary Fig. 2c). Notably, the sample features ‘wAnga infection status’, ‘mortality’, and ‘DNA extraction location’ were also correlated with each other to varying degrees (Fig. 1; Supplementary Fig. 3).
wAnga infection minimally alters overall composition of microbiota. Whether a mosquito was infected with wAnga did not alter the overall composition of the microbiota. Alpha diversity measurements using the Chao1 metric were not significantly different between infected and uninfected mosquitoes (a). Principal Coordinate Analysis indicates no clear visual distinction or clustering between wAnga infected (red) and uninfected (blue) mosquitoes (b). There was a very slight, but significant (PERMANOVA pseudo-F = 1.99, p = 0.023) increase in Bray–Curtis distances between uninfected and infected mosquitoes than distances within individual infected mosquitoes, indicating that infected mosquitoes are more similar to each other in composition than to uninfected mosquitoes (c). The reciprocal measure, in which uninfected mosquitoes were more similar to uninfected than infected mosquitoes, was also true (data not shown).
There was no clear visual clustering by Principal Coordinate Analysis of Bray–Curtis distances (i.e., beta diversity) of samples for the measured sample attributes, including wAnga infection status (Fig. 3b), indicating that neither technical nor biological factors appeared to affect the overall composition of the microbiome. We also tested for an association between alpha diversity and other variables: wAnga infection status, extraction location, and collection day. All three associations were significant by PERMANOVA of Bray–Curtis distances (corrected p < 0.05, 10,000 permutations), indicating that despite the absence of a clear visual pattern, samples from the same extraction batch, infection status and collection day were significantly more similar to each other (Fig. 3c). As all three variables were correlated to each other (Fig. 1; Supplementary Fig. 3), it is difficult to infer the source of causality for these observations.
Interactions between Wolbachia and individual OTUs
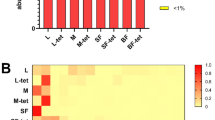
We sought to disentangle potential OTUs (i.e., individual bacterial species) that correlate with wAnga infection status, given that infection status is also correlated with several other biological and technical sample attributes, using multiple orthogonal approaches. The first approach was to use LDA Effect Size (LEfSe), which can find continuous features (i.e., taxonomy abundances) that vary based on categorical variables (e.g., wAnga infection status)31. Using LEfSe, we found multiple OTUs and associated taxonomies that differed between wAnga infection status (Fig. 4a). The strongest signal was an OTU assigned to the Variovorax genus, which was highly and significantly negatively associated with wAnga infection (p = 2.96e−11, logLDA = 4.5), with the majority of wAnga-positive mosquitoes containing little to no Variovorax, and the majority of wAnga-negative mosquitoes containing a high abundance of this OTU (Fig. 4b). Variovorax are Beta-Proteobacteria within the Comamonadaceae family, are gram-negative, and are found ubiquitously through many environments, including soil, plant rhizosphere, and many aquatic environments32,33,34,35. The most well-known member of the genus is the type species V. paradoxus, which has been extensively found in heavily-polluted environments as it can degrade a wide array of organic pollutants36. Variovorax has also been previously isolated from anopheline mosquitoes37.
wAnga infection may alter specific OTU abundances. We investigated potential OTUs that correlated with wAnga infection status using the tool LEfSe31. We observed many OTUs and their upper levels of taxonomies associated with wAnga, both infected (green) and uninfected (light blue). Here we plot their log10 LDA score for the top 5 scores from both infected and uninfected mosquitoes (a). Using the extraction location as a sub-class, we observed an unbalanced number of wAnga-positive samples from the samples that were extracted in Burkina Faso (BF, yellow) compared to the USA (blue). Here we plot Variovorax relative abundance in each sample, separated by both wAnga infection status and extraction location (b). Variovorax is no longer robustly correlated with wAnga uninfected samples as there were a very limited number of mosquitoes extracted in BF that were uninfected with wAnga. Upon reanalysing mosquitoes that were extracted only in the USA, we observed a number of OTUs and taxonomies positively associated with wAnga infection, including Proteobacteria as a whole. Here, we display the hierarchical tree based on taxonomy of these associated taxa highlighted in green (c). All figure panels were generated using LEfSe31.
LEfSe also takes a sub-class into account, which tests if the main class results are consistent between sub-classes (e.g., wAnga infection status compared across both extraction locations). However, when we opted to use extraction location as a sub-class, our power was significantly reduced due to having only six (out of 69) wAnga-negative mosquitoes extracted in Burkina Faso. Thus, using this approach, we did not have the power to statistically determine if our previous results were robust to different extraction locations.
We therefore took two alternative approaches to circumvent the possible confounding effect of extraction location. First, we used LEfSe to analyse only the subset of samples that were extracted in the USA, and excluding samples that were extracted in Burkina Faso. With the caveat that this dataset was unbalanced (with more mosquitoes that were wAnga negative than wAnga positive), we found four unique taxa that were all positively associated with wAnga infection (Fig. 4c). These taxa included the phylum Proteobacteria (p < 0.05, logLDA = 4.5), as well as three OTUs assigned to the genera Aquitalea, Phreatobacter, and Weissella (all p < 0.05, logLDA > 2). Aquitalea has been previously isolated from aquatic environments38,39. Phreatobacter has been isolated from water used for industrial purposes40. Weissella is a Firmicute that has been isolated mainly from fermentable foods, but some Weissella species have been found in the guts of various insects41,42. Aquitalea and Phreatobacter are within the phylum Proteobacteria, though the majority of OTUs within Proteobacteria were not significantly different (Fig. 4c). Proteobacteria levels appeared to be driven by certain non-infected mosquito samples that had much lower levels of Proteobacteria as a whole (Supplementary Fig. 4a).
Next, we employed MaAsLin, which uses multi-linear regression to take into account multiple sample variables in one model43. Many OTUs were associated with alive vs. dead at time of collection (n = 27), collection day (n = 107), and extraction location (n = 39) (Supplementary Table 1). Three OTUs were associated with wAnga infection status: OTU150 (Sphingomonas) and OTU232 (Bacteria) were negatively associated, while OTU271 (Bacillus) was positively associated (Supplementary Fig. 4b). To note, OTU232 and OTU271 were also concordant in the original LEfSe result including all samples, but OTU150 was not found. Sphingomonas are Alphaproteobacteria and have been known to have a wide array of biosynthetic and biodegradative properties and occasionally cause nosocomial infections in humans44,45, whereas Bacillus are ubiquitous gram-positive species found within the Firmicutes phylum, commonly found in soil and other natural habitats45.
As we discovered subsequent to sample collection for this study, wAnga influences Anopheles oviposition timing16, and therefore collection day in this experiment. We therefore opted to exclude the sample variable ‘day’ from MaAsLin analysis due to a real biological mechanism masking potential smaller, bona fide correlations16. Upon re-performing analysis, we found a different set of OTUs associated with wAnga infection status (Supplementary Table 2). OTU150 (Sphingomonas) again was negatively correlated with wAnga infection, while OTU148 (Pseudomonas), OTU196 (Lysinibacillus), and OTU2500 (Janthinobacterium) were all positively correlated with the presence of these bacteria (Supplementary Fig. 4b). To note, except for OTU150, these OTUs were concordantly found within the original LEfSe results as well. Pseudomonas has been previously reported as a member of the anopheline midgut microbiota25,26,28,46. One species of Lysinibacillus, L. sphaericus (previously Bacillus sphaericus), has been shown to have larvicidal properties against anophelines and has been used with some success as a pest control47,48. Janthinobacterium lividum, the type strain of the Janthinobacterium genus, is a gram-negative soil-dwelling beta-proteobacterium and has been shown to have antimicrobial properties49.
Previous reports have implicated Asaia as a competitive inhibitor of Wolbachia in Anopheles stephensi, where an individual mosquito can harbor either Asaia or Wolbachia, but not both at once18,50. We were able to detect one OTU assigned to the Asaia genus in 56 of 171 mosquitoes, with 28 (16%) mosquitoes having two or more counts. Contrary to previous results from these other reports, we found no negative correlation in our dataset between the abundance of Asaia and wAnga infection, as samples with higher levels of Asaia were evenly distributed between wAnga infected and uninfected mosquitoes (Supplementary Fig. 5).
Discussion
There have been multiple studies of mosquitoes associating attributes of their microbiome with developmental life stage25,26,29, ecological (e.g., geographic, seasonal) differences24,27,46,51, insecticide resistance52, and resistance to infection by Plasmodium and other human pathogens2,3,4,5,8,9,10,14,16,19,23,37,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60. There has been great interest and relevance for human health in the harnessing of the microbiome to block mosquito infection by human pathogens. In the An. gambiae species complex, several bacterial groups have been nominated for this task, including Asaia, Serratia, and the leading candidate Wolbachia2,4,10,14,15,16,18,19,51,55,61. To date, however, the relationship between Wolbachia and the rest of the microbiome of An. gambiae species complex has remained unstudied.
Here, using 16S rRNA sequencing to investigate the microbiome of wild-caught, blood-fed An. coluzzii female mosquitoes in Burkina Faso, we found microbiota in An. coluzzii similar to those described in previous studies and to the microbiome of other Anopheles mosquitoes, with a predominance of Proteobacteria and a smaller representation of other phyla25,28,62. At the family level, we also observed several previously reported families24,27,28,30,46,50,51,52, including a large fraction of Comamonadaceae and Moraxellaceae, Pseudomonadaceae, and rarely Enterobacteriaceae. We also found a large amount of variation between individual microbiomes at each of these levels, as previously observed25,27,28,29,46. Our samples had been previously divided into wAnga-positive or wAnga-negative status (using a Wolbachia-specific, highly sensitive PCR assay (Fig. 1)16,63. In our 16S rRNA sequence data, we were however able to detect sequence assigned to the Wolbachia genus in only one mosquito, which was likely due to a combination of limited sequencing depth and low infection intensity and is concordant with other anopheline microbiome studies23,24,25,27,28,46,51.
We investigated the potential interactions between wAnga infection and the An. coluzzii microbiota composition. We found no major differences between wAnga-infected vs. non- infected mosquitoes, as shown by both alpha and beta diversity measurements. This is in agreement with a previous report of the influence of Wolbachia infection in the related mosquito Aedes aegypti, where similar phylum-level profiles were observed irrespective of the presence of Wolbachia13. Upon closer investigation of finer-level details of the microbiota, we observed several OTUs and bacterial taxa that strongly correlated with wAnga infection status, including the strongest signal, an OTU assigned to the genus Variovorax. These results may indicate that these bacterial taxa may be promoting or disrupting the ability of wAnga to colonize the mosquito host, depending on whether they are positively or negatively correlated with wAnga infection, respectively. Alternatively, the presence of wAnga itself may instead influence the ability of these other microbes to colonize the mosquito, through either direct competition or potential stimulation of the host immune system13,58,60. However, due to the impact of wAnga infection on oviposition timing16 and the use of female mosquitoes collected following oviposition in this study, we cannot completely disentangle the potential for batch effects from bona fide signals. However, we feel that batch effects are unlikely to explain the observed OTU associations with Wolbachia, given that these mosquito samples had significant bacterial biomass and may therefore be less susceptible to contamination during DNA extraction64. More sophisticated bioinformatics approaches that attempt to account for stratification yielded several additional candidate OTUs associated with wAnga infection, motivating future studies employing randomized sample processing.
From this study, we predict that if a native wAnga strain were to be used for future vector control efforts the overall microbiota of the mosquito would be unlikely to change. Specific low-abundance bacterial taxa, such as Variovorax or Asaia may act as competitive inhibitors of Wolbachia infection18,50, and thus, could be impediments to Wolbachia-based disease transmission efforts in the absence of a strong CI phenotype. More studies are needed to validate our findings and to further explore how the full diversity of the An. coluzzii microbiome could be exploited for vector control.
Conclusion
Our previous findings that Wolbachia imparts phenotypic effects on An. coluzzii mosquitoes as well as P. falciparum parasites appear to not be driven by or associated with changes in the overall composition of the microbiota of the mosquito. We observe differences in the abundance of select species and taxa within the microbiota, though these differences are difficult to disentangle from potential batch effects deriving from the impact of Wolbachia infection on oviposition timing16. Future work using both laboratory and natural populations of An. coluzzii will further elucidate possible microbe-microbe interactions between wAnga and other members of the resident microbiota, and may inform future efforts to control Plasmodium malaria parasite transmission.
Materials and methods
Collection of samples and DNA extraction
Anopheles coluzzii were previously collected from the village of VK5 (11°23′N; 4°24′W) in the Vallée du Kou, 30 km northwest of Bobo-Dioulasso in Burkina Faso in September 201416. Blood-fed adult females were captured inside houses within the village, through a longstanding collaboration and with informed consent of the house owners, and maintained in an insectary on a 5% glucose diet for up to 3 days for observation. They were sacrificed immediately upon oviposition. The head was separated from the carcass, as insect heads have reported to contain PCR inhibitors that can give false negative results65,66, while the headless carcass was used for downstream DNA extraction. Though Wolbachia infections localize to reproductive organs, we profiled the whole (headless) carcass to explore potential impacts on other organs, including the midgut. Mosquitoes collected on day 1 (n = 29) and day 2 (n = 56) were extracted for DNA sequencing in Burkina Faso using the Qiagen Blood and Tissue kit as previously described16. The rest (n = 86) from day 1 (n = 21), day 2 (n = 22), and day 3 (n = 43) were stored in RNAlater (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and extracted using the Qiagen Blood and Tissue kit at a later date in the USA. This extracted DNA was used to assess Wolbachia via 16S, as previously described16,63. In brief, detection of wAnga in mosquito carcasses was performed by nested PCR amplification of the 16S rDNA region using Wolbachia-specific primers (W-Specf: 5′-CATACCTATTCGAAGGGATAG-3′, W-Specr: 5′-AGCTTCGAGTGAAACCAATTC-3′) and specific internal primers (16SNF: 5′-GAAGGGATAGGGTCGGTTCG-3′, 16SNR: 5′-CAATTCCCATGGCGTGACG-3′). For positive samples, the sequence of the resulting 412 bp fragment was determined by Sanger sequencing, and then both wAnga-infected and uninfected samples were submitted for 16S rRNA sequencing. Mosquito species was determined using PCR amplification of the extracted DNA with the S200 X6.1 locus (forward 5′-TCGCCTTAGACCTTGCGTTA-3′, reverse 5′-CGCTTCAAGAATTCGAGATAC-3′)67.
16S rRNA sequencing and analysis
Sequencing
Extracted DNA from mosquitoes was used to construct 16S rRNA sequencing libraries targeting ~ 250 bp in the V4 hypervariable region using 515F (5′-GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) PCR primers68. Then, libraries were sequenced using an Illumina MiSeq with paired end reads of 175 bp in length. Paired FASTQ files were generated and used in downstream analysis described below.
OTU table generation
A combination of QIIME (v1.4)69,70 and the UPARSE pipeline within the program usearch (v8.1.1861 64-bit)71,72 were used to generate Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) from the 16S rRNA sequences. In brief, using QIIME, paired reads from the V4 region were merged into one overlapping sequence for each read pair. Chimeric sequences were detected and filtered out. Then, unique sequences within the data were generated using usearch derep_fulllength. OTU clusters were generated from these unique sequences using usearch cluster_otus with a minsize of two, discarding singletons. Taxonomy was assigned to the OTU clusters using the utax algorithm within usearch with the RDP v16 database provided by the usearch author. Finally, an OTU table, tabulating read counts per OTU per sample, was created using usearch_global with an identity of 97% (-id 0.97).
Diversity analysis
The feature table73 and diversity modules from QIIME 2™ (version 2017.12.1 from qiime2.org)70,74 was used to filter and analyse the OTU table created above. First, the OTU table was filtered to remove OTUs present in only one sample, as well as present in fewer than 50 total counts across all 171 samples. This reduced the table from containing 3,189 to 916 OTUs, removing rare and ultra-low abundant OTUs.
This reduced table was then used as input for alpha rarefaction analysis with QIIME 2™, generating Chao1 measurements of down-sampled OTU tables from 1,000 to 20,000 counts per sample. Using this rarefaction curve, we determined 10,000 counts per sample was sufficient to measure the diversity within the majority of samples while retaining the majority of samples.
We thus down-sampled the OTU table to 10,000 counts per sample, which retained 11.6% of all counts and 144 (84%) samples, as samples containing fewer than 10,000 counts were excluded from the filtered table.
This filtered even-depth table was used to generate alpha diversity measurements (Chao175) as well as beta diversity measurements (Bray Curtis76) using QIIME 2™. The Kruskal–Wallis test was used to compare Chao1 values for different groups of samples (e.g., wAnga infected vs uninfected). Bray Curtis measurements were input for Principal Coordinate Analysis to visualize how similar pairwise samples were to each other in two dimensions using EMPeror77,78. In addition, PERMANOVA with 10,000 permutations was used to assess how similar groups were to each other using Bray Curtis distances.
OTU-level analysis
LDA Effect Size (LEfSe)31 was used to assess correlations between OTUs and higher levels of taxonomy with various phenotypes (e.g., wAnga infection status, day collected, mortality [i.e., collected alive or dead], DNA extraction location). Input for LEfSe was the downsampled to 10,000 count, rare OTU filtered OTU table. The Galaxy implementation from the Huttenhower group was used (https://huttenhower.sph.harvard.edu/galaxy/). Default parameters were used.
The Huttenhower group Galaxy implementation of Multivariate Association with Linear Models (MaAsLin)43 was used to investigate correlations of individual OTUs with multiple sample metadata at once, including those described above. Again, input for the tool was the downsampled, filtered OTU table. Default parameters were used.
Other statistics and graphing
All other statistics and plotting were performed in R (v3.4.3)79 using RStudio (v1.1.423)80.
Data availability
All raw sequence data from this work can be found at NCBI under BioProject PRJNA294068. Only a subset of samples from the BioProject were used in the analysis.
References
Global Malaria Programme, W. G. World malaria report 2019. https://www.who.int/publications-detail/world-malaria-report-2019 (2019).
Shaw, W. R. & Catteruccia, F. Vector biology meets disease control: Using basic research to fight vector-borne diseases. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 20–34 (2019).
Romoli, O. & Gendrin, M. The tripartite interactions between the mosquito, its microbiota and Plasmodium. Parasit. Vectors 11, 200 (2018).
Hoffmann, A. A., Ross, P. A. & Rašić, G. Wolbachia strains for disease control: Ecological and evolutionary considerations. Evol. Appl. 8, 751–768 (2015).
Ippolito, M. M., Denny, J. E., Langelier, C., Sears, C. L. & Schmidt, N. W. Malaria and the microbiome: A systematic review. Clin. Infect. Dis. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciy374 (2018).
Bhatt, S. et al. The effect of malaria control on Plasmodium falciparum in Africa between 2000 and 2015. Nature 526, 207–211 (2015).
Hemingway, J. et al. Averting a malaria disaster: Will insecticide resistance derail malaria control?. Lancet 387, 1785–1788 (2016).
Kotnis, B. & Kuri, J. Evaluating the usefulness of paratransgenesis for malaria control. Math. Biosci. 277, 117–125 (2016).
Wilke, A. B. B. & Marrelli, M. T. Paratransgenesis: A promising new strategy for mosquito vector control. Parasit. Vectors 8, 342 (2015).
Moreira, L. A. et al. A Wolbachia symbiont in Aedes aegypti limits infection with dengue, chikungunya, and Plasmodium. Cell 139, 1268–1278 (2009).
Kambris, Z., Cook, P. E., Phuc, H. K. & Sinkins, S. P. Immune activation by life-shortening Wolbachia and reduced filarial competence in mosquitoes. Science 326, 134–136 (2009).
McMeniman, C. J. et al. Stable introduction of a life-shortening Wolbachia infection into the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Science 323, 141–144 (2009).
Audsley, M. D. et al. Wolbachia infection alters the relative abundance of resident bacteria in adult Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, but not larvae. Mol. Ecol. 27, 297–309 (2018).
Slatko, B. E., Luck, A. N., Dobson, S. L. & Foster, J. M. Wolbachia endosymbionts and human disease control. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 195, 88–95 (2014).
Baldini, F. et al. Evidence of natural Wolbachia infections in field populations of Anopheles gambiae. Nat. Commun. 5, 3985 (2014).
Shaw, W. R. et al. Wolbachia infections in natural Anopheles populations affect egg laying and negatively correlate with Plasmodium development. Nat. Commun. 7, 1–7 (2016).
Niang, E. H. A. et al. First report of natural Wolbachia infection in wild Anopheles funestus population in Senegal. Malaria J. 17, 1–6 (2018).
Jeffries, C. L. et al. Novel Wolbachia strains in Anopheles malaria vectors from Sub-Saharan Africa. Wellcome Open Res. 3, 113 (2018).
Gomes, F. M., Hixson, B. L. & Tyner, M. D. W. Effect of naturally occurring Wolbachia in Anopheles gambiae sl mosquitoes from Mali on Plasmodium falciparum malaria transmission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114(47), 12566–12571 (2017).
Ayala, D. et al. Natural Wolbachia infections are common in the major malaria vectors in Central Africa. Evol. Appl. 12, 1583–1594 (2019).
Baldini, F. et al. First report of natural Wolbachia infection in the malaria mosquito Anopheles arabiensis in Tanzania. Parasit. Vectors 11, 635 (2018).
Chrostek, E. & Gerth, M. Is Anopheles gambiae a natural host of Wolbachia? mBio 10, (2019).
Boissière, A. et al. Midgut microbiota of the malaria mosquito vector Anopheles gambiae and interactions with Plasmodium falciparum infection. PLoS Pathog. 8, e1002742 (2012).
Buck, M. et al. Bacterial associations reveal spatial population dynamics in Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes. Sci. Rep. 6, 22806 (2016).
Gimonneau, G. et al. Composition of Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles gambiae microbiota from larval to adult stages. Infect. Genet. Evol. 28, 715–724 (2014).
Segata, N. et al. The reproductive tracts of two malaria vectors are populated by a core microbiome and by gender- and swarm-enriched microbial biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 6, 1 (2016).
Akorli, J. et al. Seasonality and locality affect the diversity of Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles coluzzii midgut microbiota from Ghana. PLoS ONE 11, e0157529 (2016).
Wang, Y., Gilbreath, T. M. 3rd., Kukutla, P., Yan, G. & Xu, J. Dynamic gut microbiome across life history of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae in Kenya. PLoS ONE 6, e24767 (2011).
Coon, K. L., Brown, M. R. & Strand, M. R. Mosquitoes host communities of bacteria that are essential for development but vary greatly between local habitats. Mol. Ecol. 25, 5806–5826 (2016).
Minard, G., Mavingui, P. & Moro, C. V. Diversity and function of bacterial microbiota in the mosquito holobiont. Parasit. Vectors 6, 146 (2013).
Segata, N. et al. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 12, R60 (2011).
Willems, A., De Ley, J., Gillis, M. & Kersters, K. Comamonadaceae, a new family encompassing the acidovorans rRNA complex, including Variovorax paradoxus gen. nov., comb. Nov., for Alcaligenes paradoxus (Davis 1969). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 41, 445–450 (1991).
Gao, W. et al. Characterization of Co(III) EDTA-reducing bacteria in metal- and radionuclide-contaminated groundwater. Geomicrobiol. J. 27, 93–100 (2010).
Haaijer, S. C. M. et al. Bacteria associated with iron seeps in a sulfur-rich, neutral pH, freshwater ecosystem. ISME J. 2, 1231–1242 (2008).
Lee, J., Lee, C. S., Hugunin, K. M., Maute, C. J. & Dysko, R. C. Bacteria from drinking water supply and their fate in gastrointestinal tracts of germ-free mice: A phylogenetic comparison study. Water Res. 44, 5050–5058 (2010).
Satola, B., Wübbeler, J. H. & Steinbüchel, A. Metabolic characteristics of the species Variovorax paradoxus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97, 541–560 (2013).
Chavshin, A. et al. Isolation and identification of culturable bacteria from wild Anopheles culicifacies, a first step in a paratransgenesis approach. Parasites Vectors 7, 419 (2014).
Lau, H.-T., Faryna, J. & Triplett, E. W. Aquitalea magnusonii gen. nov., sp. Nov., a novel Gram-negative bacterium isolated from a humic lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 867–871 (2006).
Lee, C.-M. et al. Aquitalea denitrificans sp. nov., isolated from a Korean wetland. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 1045–1048 (2009).
Tóth, E. M. et al. Phreatobacter oligotrophus gen. nov., sp. nov., an alphaproteobacterium isolated from ultrapure water of the water purification system of a power plant. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64, 839–845 (2014).
Fusco, V. et al. The genus Weissella: Taxonomy, ecology and biotechnological potential. Front. Microbiol. 6, 155 (2015).
Praet, J. et al. Novel lactic acid bacteria isolated from the bumble bee gut: Convivina intestini gen. nov., sp. nov., Lactobacillus bombicola sp. nov., and Weissella bombi sp. nov.. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 107, 1337–1349 (2015).
Morgan, X. C. et al. Dysfunction of the intestinal microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease and treatment. Genome Biol. 13, R79 (2012).
Ryan, M. P. & Adley, C. C. Sphingomonas paucimobilis: A persistent Gram-negative nosocomial infectious organism. J. Hosp. Infect. 75, 153–157 (2010).
Whitman, W. B. Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria (Wiley, New York, 2015).
Krajacich, B. J. et al. Investigation of the seasonal microbiome of Anopheles coluzzii mosquitoes in Mali. PLoS ONE 13, e0194899 (2018).
Berry, C. The bacterium, Lysinibacillus sphaericus, as an insect pathogen. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 109, 1–10 (2012).
Filha, M. H. N. L. S., Berry, C. & Regis, L. Lysinibacillus sphaericus: Toxins and mode of action, applications for mosquito control and resistance management. In Advances in Insect Physiology, Vol. 47, 89–176 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2014).
O’Sullivan, J. et al. Janthinocins A, B and C, novel peptide lactone antibiotics produced by Janthinobacterium lividum. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical and biological characterization. J. Antibiot. 43, 913–919 (1990).
Hughes, G. L. et al. Native microbiome impedes vertical transmission of Wolbachia in Anopheles mosquitoes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 111, 12498–12503 (2014).
Villegas, L. M. & Pimenta, P. F. P. Metagenomics, paratransgenesis and the Anopheles microbiome: A portrait of the geographical distribution of the anopheline microbiota based on a meta-analysis of reported taxa. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 109, 672–684 (2014).
Guégan, M. et al. The mosquito holobiont: Fresh insight into mosquito-microbiota interactions. Microbiome 6, 1–7 (2018).
Cirimotich, C. M. et al. Natural microbe-mediated refractoriness to Plasmodium infection in Anopheles gambiae. Science 332, 855–858 (2011).
Dong, Y., Manfredini, F. & Dimopoulos, G. Implication of the mosquito midgut microbiota in the defense against malaria parasites. PLoS Pathog. 5, e1000423 (2009).
Jayakrishnan, L., Sudhikumar, A. V. & Aneesh, E. M. Role of gut inhabitants on vectorial capacity of mosquitoes. J. Vector Borne Dis. 55, 69–78 (2018).
Jupatanakul, N., Sim, S. & Dimopoulos, G. The insect microbiome modulates vector competence for arboviruses. Viruses 6, 4294–4313 (2014).
Ramirez, J. L. et al. Chromobacterium Csp_P reduces malaria and dengue infection in vector mosquitoes and has entomopathogenic and in vitro anti-pathogen activities. PLoS Pathog. 10, e1004398 (2014).
Rancès, E., Ye, Y. H., Woolfit, M., McGraw, E. A. & O’Neill, S. L. The relative importance of innate immune priming in Wolbachia-mediated dengue interference. PLoS Pathog. 8, e1002548 (2012).
Tchioffo, M. T. et al. Modulation of malaria infection in Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes exposed to natural midgut bacteria. PLoS ONE 8, e81663 (2013).
Ye, Y. H., Woolfit, M., Rancès, E., O’Neill, S. L. & McGraw, E. A. Wolbachia-associated bacterial protection in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 7, e2362 (2013).
Zélé, F., Denoyelle, J., Duron, O. & Rivero, A. Can Wolbachia modulate the fecundity costs of Plasmodium in mosquitoes?. Parasitology 145, 775–782 (2018).
Muturi, E. J., Ramirez, J. L., Rooney, A. P. & Kim, C.-H. Comparative analysis of gut microbiota of mosquito communities in central Illinois. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 11, e0005377 (2017).
Werren, J. H. & Windsor, D. M. Wolbachia infection frequencies in insects: Evidence of a global equilibrium?. Proc. Biol. Sci. 267, 1277–1285 (2000).
Salter, S. J. et al. Reagent and laboratory contamination can critically impact sequence-based microbiome analyses. BMC Biol. 12, 87 (2014).
Dowton, M. & Austin, A. D. Evolutionary dynamics of a mitochondrial rearrangement ‘hot spot’ in the Hymenoptera. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16, 298–309 (1999).
Beckmann, J. F. & Fallon, A. M. Decapitation improves detection of Wolbachia pipientis (Rickettsiales: Anaplasmataceae) in Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae) mosquitoes by the polymerase chain reaction. J. Med. Entomol. 49, 1103–1108 (2012).
Santolamazza, F. et al. Insertion polymorphisms of SINE200 retrotransposons within speciation islands of Anopheles gambiae molecular forms. Malar. J. 7, 163 (2008).
Caporaso, J. G. et al. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 108(Suppl 1), 4516–4522 (2011).
Caporaso, J. G. et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 6, 1621–1624 (2012).
Caporaso, J. G. et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 7, 335–336 (2010).
Edgar, R. C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26, 2460–2461 (2010).
Edgar, R. C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 10, 996–998 (2013).
McDonald, D. et al. The Biological Observation Matrix (BIOM) format or: How I learned to stop worrying and love the ome-ome. Gigascience 1, 7 (2012).
Kuczynski, J. et al. Using QIIME to analyze 16S rRNA gene sequences from microbial communities. Curr. Protocols Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780471729259.mc01e05s27 (2012).
Chao, A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. Stat. Theory Appl. 11, 265–270 (1984).
Bray, J. R. & Curtis, J. T. An Ordination Of The Upland Forest Communities Of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 27, 25 (1957).
Vázquez-Baeza, Y. et al. Bringing the dynamic microbiome to life with animations. Cell Host Microbe 21, 7–10 (2017).
Vázquez-Baeza, Y., Pirrung, M., Gonzalez, A. & Knight, R. EMPeror: A tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. Gigascience 2, 16 (2013).
Team, R. C. & Others. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. (2013).
Team, R. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R [Internet], Vol. 626. (Team, R. RStudio, Boston, 2015).
Acknowledgements
This project has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services, under Grant Number U19AI110818 to the Broad Institute. Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number R21AI117313 and by a Faculty Research Scholar Award by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) (Grant ID: OPP1158190) to FC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.R.S., P.M., and F.C. conceived of and designed the study. W.R.S., P.M., S.P.S., R.K.D., and A.D. collected and coordinated the processing of samples. W.R.S., P.M., and D.E.N. coordinated delivery of samples to the Broad for sequencing. T.J.S. and D.E.N. processed and analysed sequence data. F.C. and D.E.N. provided project oversight. T.J.S., W.R.S., P.M., F.C., and D.E.N. drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Straub, T.J., Shaw, W.R., Marcenac, P. et al. The Anopheles coluzzii microbiome and its interaction with the intracellular parasite Wolbachia. Sci Rep 10, 13847 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70745-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70745-0
- Springer Nature Limited