Abstract
Background
Hospitalized children with acute kidney injury (AKI) have not been extensively studied for clinical outcomes including hospital stay, the need for mechanical ventilation, mortality rates, and healthcare utilization. We hypothesize significant financial costs and increased morbidity and mortality associated with pediatric AKI.
Methods
This is a retrospective study of pediatric patients (age ≤18 years) included in the Kids’ Inpatient Database (KID) between January 1, 2016, and December 31, 2021. The results of the data analysis were utilized for comparative testing between the AKI and non-AKI cohorts.
Results
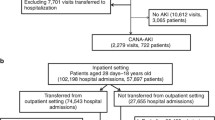
The study included 4842 children [with AKI (n = 2424) and without AKI (n = 2418)]. The odds of mortality (p = 0.004) and mechanical ventilation (p < 0.001) were observed to be significantly higher among those with AKI as compared to those without AKI. Additionally, the median (IQR) duration of stay in the hospital (p < 0.001) and total cost (p < 0.001) were significantly higher among those with AKI vs. those without AKI.
Conclusions
AKI in children was associated with higher odds of mortality, longer duration of hospital stay, increased requirement of mechanical ventilation, and increased hospital expenditure. The scientific community can utilize this information to better understand the outcomes associated with this disease process in this patient population.
Impact
-
This article has thoroughly evaluated epidemiologic data associated with pediatric acute kidney injury (AKI) in hospitalized patients
-
This study assesses mortality, hospital expenditure, and other factors to strengthen single-center and few multi-center studies and provides novel data regarding insurance and cost associated with pediatric AKI
-
With increased knowledge of current epidemiology and risk factors, the scientific community can better understand prevention and outcomes in hospitalized children with AKI.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Raina, R. et al. Treatment of AKI in developing and developed countries: an international survey of pediatric dialysis modalities. PLoS ONE 12, e0178233 (2017).
Raina, R., Chakraborty, R., Tibrewal, A., Sethi, S. K. & Bunchman, T. Advances in pediatric acute kidney injury. Pediatr. Res. 91, 44–55 (2022).
Basu, R. K. et al. Assessment of Worldwide Acute Kidney Injury, Renal Angina and Epidemiology in critically ill children (AWARE): study protocol for a prospective observational study. BMC Nephrol. 16, 24 (2015).
Askenazi, D. J., Feig, D. I., Graham, N. M., Hui-Stickle, S. & Goldstein, S. L. 3-5 year longitudinal follow-up of pediatric patients after acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 69, 184–189 (2006).
Almeida, J. P., Valente, I. F. & da Rocha Lordelo, M. Association between pediatric Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss and End Stage Renal Disease score and mortality in a pediatric intensive care unit: a retrospective study. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiv. 30, 429–435 (2018).
Mammen, C. et al. Long-term risk of CKD in children surviving episodes of acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit: a prospective cohort study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 59, 523–530 (2012).
Sutherland, S. M. et al. AKI in hospitalized children: epidemiology and clinical associations in a national cohort. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 8, 1661–1669 (2013).
Pavkov, M. E., Harding, J. L. & Burrows, N. R. Trends in hospitalizations for acute kidney injury-United States, 2000-2014. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 67, 289–293 (2018).
Xue, J. L. et al. Incidence and mortality of acute renal failure in Medicare beneficiaries, 1992 to 2001. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 17, 1135–1142 (2006).
Brown, J. R., Rezaee, M. E., Marshall, E. J. & Matheny, M. E. Hospital Mortality in the United States following Acute Kidney Injury. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 4278579 (2016).
Kaddourah, A., Basu, R. K., Bagshaw, S. M. & Goldstein, S. L., AWARE Investigators. Epidemiology of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Children and Young Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 376, 11–20 (2017).
Schneider, J., Khemani, R., Grushkin, C. & Bart, R. Serum creatinine as stratified in the RIFLE score for acute kidney injury is associated with mortality and length of stay for children in the pediatric intensive care unit. Crit. Care Med. 38, 933–939 (2010).
Ball, E. F. & Kara, T. Epidemiology and outcome of acute kidney injury in New Zealand children. J. Paediatr. Child Health 44, 642–646 (2008).
Hui-Stickle, S., Brewer, E. D. & Goldstein, S. L. Pediatric ARF epidemiology at a tertiary care center from 1999 to 2001. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 45, 96–101 (2005).
Williams, D. M., Sreedhar, S. S., Mickell, J. J. & Chan, J. C. M. Acute kidney failure: a pediatric experience over 20 years. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 156, 893–900 (2002).
HCUP-US KID Overview. https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/kidoverview.jsp (2016).
Alkandari, O. et al. Acute kidney injury is an independent risk factor for pediatric intensive care unit mortality, longer length of stay and prolonged mechanical ventilation in critically ill children: a two-center retrospective cohort study. Crit. Care 15, R146 (2011).
Agras, P. I. et al. Acute renal failure in the neonatal period. Ren. Fail. 26, 305–309 (2004).
Jetton, J. G. et al. Incidence and outcomes of neonatal acute kidney injury (AWAKEN): a multicentre, multinational, observational cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 1, 184–194 (2017).
Uber, A. M. & Sutherland, S. M. Acute kidney injury in hospitalized children: consequences and outcomes. Pediatr. Nephrol. 35, 213–220 (2020).
Sutherland, S. M. et al. AKI in hospitalized children: comparing the pRIFLE, AKIN, and KDIGO definitions. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10, 554–561 (2015).
Fan, Y. et al. Risk factors and outcomes of acute kidney injury in ventilated newborns. Ren. Fail. 41, 995–1000 (2019).
Selewski, D. T. et al. Validation of the KDIGO acute kidney injury criteria in a pediatric critical care population. Intensive Care Med. 40, 1481–1488 (2014).
Li, S. et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective multicenter study. Crit. Care Med. 39, 1493–1499 (2011).
Chertow, G. M., Burdick, E., Honour, M., Bonventre, J. V. & Bates, D. W. Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 16, 3365–3370 (2005).
Carmody, J. B., Swanson, J. R., Rhone, E. T. & Charlton, J. R. Recognition and reporting of AKI in very low birth weight infants. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 9, 2036–2043 (2014).
Rheault, M. N. et al. AKI in Children Hospitalized with Nephrotic Syndrome. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10, 2110–2118 (2015).
Akcan-Arikan, A. et al. Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 71, 1028–1035 (2007).
Zappitelli, M., Moffett, B. S., Hyder, A. & Goldstein, S. L. Acute kidney injury in non-critically ill children treated with aminoglycoside antibiotics in a tertiary healthcare centre: a retrospective cohort study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 26, 144–150 (2011).
Perico, N. & Remuzzi, G. Acute kidney injury in low-income and middle-income countries: no longer a death sentence. Lancet Glob. Health 4, e216–e217 (2016).
Susantitaphong, P. et al. World incidence of AKI: a meta-analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 8, 1482–1493 (2013).
Hoste, E. A. J. et al. Global epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 14, 607–625 (2018).
Chen, Z. et al. Exploring reasons for state-level variation in incidence of dialysis-requiring acute kidney injury (AKI-D) in the United States. BMC Nephrol. 21, 336 (2020).
Jefferies, J. L. & Devarajan, P. Early detection of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery. Prog. Pediatr. Cardiol. 41, 9–16 (2016).
Hirano, D. et al. Independent risk factors and 2-year outcomes of acute kidney injury after surgery for congenital heart disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 46, 204–209 (2017).
Park, P. G. et al. Acute kidney injury in pediatric cancer patients. J. Pediatr. 208, 243–250.e3 (2019).
Xiong, M. et al. Acute kidney injury among hospitalized children with cancer. Pediatr. Nephrol. 36, 171–179 (2021).
Kizilbash, S. J., Kashtan, C. E., Chavers, B. M., Cao, Q. & Smith, A. R. Acute kidney injury and the risk of mortality in children undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 22, 1264–1270 (2016).
Koh, K.-N. et al. Acute kidney injury in pediatric patients receiving allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: incidence, risk factors, and outcomes. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 24, 758–764 (2018).
Hamada, M., Matsukawa, S., Shimizu, S., Kai, S. & Mizota, T. Acute kidney injury after pediatric liver transplantation: incidence, risk factors, and association with outcome. J. Anesth. 31, 758–763 (2017).
Baddam, S. et al. Acute kidney injury during a pediatric sickle cell vaso-occlusive pain crisis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 32, 1451–1456 (2017).
Hursh, B. E., Ronsley, R., Islam, N., Mammen, C. & Panagiotopoulos, C. Acute kidney injury in children with type 1 diabetes hospitalized for diabetic ketoacidosis. JAMA Pediatr. 171, e170020 (2017).
Steflik, H. J. et al. Correction to: costs associated with acute kidney injury in critically Ill neonates with patent Ductus arteriosus: pediatric health information system (PHIS) analysis. J. Perinatol. 42, 1714 (2022).
Elsabbagh, E. M. & Hashmat, S. Acute kidney injury in childhood cancer: an insight from Kids’ inpatient database. J. Clin. Oncol. 37, e18379–e18379 (2019).
Silver, S. A., Long, J., Zheng, Y. & Chertow, G. M. Cost of acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients. J. Hosp. Med. 12, 70–76 (2017).
Collister, D. et al. Health care costs associated with AKI. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 12, 1733–1743 (2017).
Bates, D. W. et al. Mortality and costs of acute renal failure associated with amphotericin B therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32, 686–693 (2001).
McCormick, M., Richardson, T., Warady, B. A., Novelli, E. M. & Kalpatthi, R. Acute kidney injury in paediatric patients with sickle cell disease is associated with increased morbidity and resource utilization. Br. J. Haematol. 189, 559–565 (2020).
Rogowski, J. A. et al. Economic implications of neonatal intensive care unit collaborative quality improvement. Pediatrics 107, 23–29 (2001).
Sathe, N. A. et al. The costs of participating in a diabetes quality improvement collaborative: variation among five clinics. Jt. Comm. J. Qual. Patient Saf. 42, 18–25 (2016).
Acknowledgements
There are no funding sources to report for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data—R.R., S.S., and A.V. Drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content—V.A. and I.H.. Final approval of the version to be published—R.R.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Patient consent was obtained.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Raina, R., Sethi, S., Aitharaju, V. et al. Epidemiology data on the cost and outcomes associated with pediatric acute kidney injury. Pediatr Res 94, 1385–1391 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-023-02564-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-023-02564-8
- Springer Nature America, Inc.