Abstract
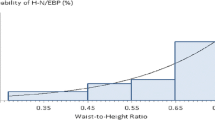
Excess body weight and fat mass levels in children have previously been associated with childhood hypertension. The aim of the current study was to identify anthropometric and body composition indices most strongly associated with hypertension and to propose relevant cut-off values for these indices, above which the likelihood of hypertension in schoolchildren aged 9–13 years old is increased. A sample of 2,665 children participated in a cross-sectional epidemiological study, the Healthy Growth Study. The current study enrolled 1,315 children with full data on blood pressure, anthropometric, and body composition indices. Increased blood pressure in children was associated with body mass index (BMI) (odds ratio (OR) 1.188), waist circumference (OR 1.062), waist-to-height ratio (OR 1.101), total body fat mass (OR 1.063), and trunk fat mass levels (OR 1.083). Also, BMI, waist circumference, waist-to-height ratio, trunk fat mass, and total body fat mass levels above the age-specific and gender-specific cut-off values identified in the present study were associated with a higher likelihood of hypertension. Anthropometric and body composition indices and the relevant cut-off values proposed by the current study can be used for identifying children with higher likelihood of presence of hypertension, as the available BMI thresholds for identifying overweight and obese children may underestimate those at increased risk of hypertension. It is essential for future studies to confirm these findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C. et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384:766–781.
Fox CS, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Pou KM, Maurovich-Horvat P, Liu CY, et al. Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments: association with metabolic risk factors in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2007;116:39–48.
Feber J, Ahmed M. Hypertension in children: new trends and challenges. Clin Sci. 2010;119:151–61.
Genovesi S, Antolini L, Giussani M, Pieruzzi F, Galbiati S, Valsecchi MG, et al. Usefulness of waist circumference for the identification of childhood hypertension. J Hypertens. 2008;26:1563–70.
Papalia T, Greco R, Lofaro D, Mollica A, Roberti R, Bonofiglio R. Anthropometric measures can better predict high blood pressure in adolescents. J Nephrol. 2013;26:899–905.
Moser DC, Giuliano Ide C, Titski AC, Gaya AR, Coelho-e-Silva MJ, Leite N. Anthropometric measures and blood pressure in school children. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2013;89:243–9.
Pausova Z, Mahboubi A, Abrahamowicz M, Leonard GT, Perron M, Richer L, et al. Sex differences in the contributions of visceral and total body fat to blood pressure in adolescence. Hypertension. 2012;59:572–9.
Moschonis G, Kaliora AC, Karatzi K, Michaletos A, Lambrinou CP, Karachaliou AK, et al. Perinatal, sociodemographic and lifestyle correlates of increased total and visceral fat mass levels in schoolchildren in Greece: the Healthy Growth Study. Public Health Nutr. 2017;20:660–70.
Moschonis G, Mavrogianni C, Karatzi K, Iatridi V, Chrousos GP, Lionis C, et al. Increased physical activity combined with more eating occasions is beneficial against dyslipidemias in children. The Healthy Growth Study. Eur J Nutr. 2013;52:1135–44.
Marshall WA, Tanner JM. Variations in the pattern of pubertal changes in boys. Arch Dis Child. 1970;45:13–23.
Marshall WA, Tanner JM. Variations in pattern of pubertal changes in girls. Arch Dis Child. 1969;44:291–303.
Manios Y, Karatzi K, Protogerou AD, Moschonis G, Tsirimiagou C, Androutsos O, et al. Prevalence of childhood hypertension and hypertension phenotypes by weight status and waist circumference: the Healthy Growth Study. Eur J Nutr. 2017.
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2004;114:555–76.
Moschonis G, Tanagra S, Vandorou A, Kyriakou AE, Dede V, Siatitsa PE, et al. Social, economic and demographic correlates of overweight and obesity in primary-school children: preliminary data from the Healthy Growth Study. Public Health Nutr. 2010;13:1693–700.
Mazicioglu MM, Yalcin BM, Ozturk A, Ustunbas HB, Kurtoglu S. Anthropometric risk factors for elevated blood pressure in adolescents in Turkey aged 11–17. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010;25:2327–34.
Kajale NA, Khadilkar AV, Chiplonkar SA, Khadilkar VV. Body fat indices for identifying risk of hypertension in Indian children. Indian Pediatr. 2014;51:555–60.
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ. 2000;320:1240–3.
International Obesity Task Force. Global prevalence of obesity; 2005.
Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Kaufman F, Tajima N, Silink M, Arslanian S, et al. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents—an IDF consensus report. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007;8:299–306.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the “Healthy Growth Study” group for the valuable contribution to the completion of the study.
Funding
This research has been co-financed by the European Union (European Social Fund—ESF) and Greek national funds through the Operational Program “Education and Lifelong Learning” of the National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF)—Research Funding Program: Heracleitus II. Investing in knowledge society through the European Social Fund.
Author contributions
GM conception and design of the study, collection of data, drafting and revision of the manuscript, and approved the final version of the manuscript. KK analysis and interpretation of data, drafting and revision of the manuscript, and approved the final version of the manuscript. O.A. collection and interpretation of data, drafting and revision of the manuscript, and approved the final version of the manuscript. CL interpretation of data, drafting and revision of the manuscript, and approved the final version of the manuscript. GPC interpretation of data, drafting and revision of the manuscript, and approved the final version of the manuscript. YM conception and design of the study, interpretation of data, drafting and revision of the manuscript, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moschonis, G., Karatzi, K., Androutsos, O. et al. Anthropometric cut-off values identifying Greek children at risk of hypertension: the Healthy Growth Study. J Hum Hypertens 32, 190–196 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0031-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0031-8
- Springer Nature Limited