Abstract
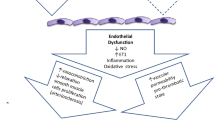
Hypertension is associated with microcirculatory impairment. Our objectives were to evaluate endothelial function and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with resistant (RH) and mild to moderate (MMH) arterial hypertension in comparison to normotensives (control group—CG). Three groups, 25 patients each, have been investigated, by anamnesis, venous occlusion plethysmography (VOP) and serum determination of adhesion molecules (VCAM, ICAM), adiponectin, endothelin and C-reactive protein (CRP). Patients not using statins and with or without blood pressure control were also analyzed. RH group showed smaller percentage increase of maximum forearm blood flow (FBF) (endothelial-dependent vasodilatation) than controls (p < 0.05), but no significant difference could be detected between MMH and CG groups on maximum FBF and minimum vascular resistance post-ischemia. RH and MMH groups showed higher resistance averages compared to controls (p < 0.05). Uncontrolled BP in hypertensive patients showed worse results for blood flow and resistance. Endothelial-independent vasodilatation was not affected. Endothelin levels were higher in RH and MMH groups (p < 0.05) not using statins. CRP was significantly higher only in RH compared to CG (p < 0.05). In conclusion patients with severe hypertension and lack of blood pressure control showed greater impairment of endothelial function with higher CRP and endothelin levels.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mortality GBD, Causes of Death C. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;385:117–71.
Sociedade Brasileira de C, Sociedade Brasileira de H, Sociedade Brasileira de N. [VI Brazilian Guidelines on Hypertension]. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2010;95(1 Suppl):1–51.
Ribeiro AL, Duncan BB, Brant LC, Lotufo PA, Mill JG, Barreto SM. Cardiovascular health in Brazil: trends and perspectives. Circulation. 2016;133:422–33.
National Center for Health Statistics. NHANES 2007–2008 public data general release file documentation. Hyattsville, MD (2009). Available from: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/ContinuousNhanes/Default.aspx?BeginYear=2007
Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN. US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988-2008. JAMA. 2010;303:2043–50.
Wright JD, Hughes JP, Ostchega Y, Yoon SS, Nwankwo T. Mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure in adults aged 18 and over in the United States, 2001-2008. Natl Health Stat Report. 2011;24: 1–22.
Panza JA, Quyyumi AA, Brush JE Jr, Epstein SE. Abnormal endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:22–7.
Ridker PM, Rifai N, Clearfield M, Downs JR, Weis SE, Miles JS, et al. Measurement of C-reactive protein for the targeting of statin therapy in the primary prevention of acute coronary events. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1959–65.
Harrison DG, Guzik TJ, Lob HE, Madhur MS, Marvar PJ, Thabet SR, et al. Inflammation, immunity, and hypertension. Hypertension. 2011;57:132–40.
Gupta V, Sachdeva S, Khan AS, Haque SF. Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation in different stages of essential hypertension. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2011;22:97–103.
Plotnikova IV, Kovalev IA, Suslova TE, Bezliak VV. Correlation of endothelial dysfunction with course of essential arterial hypertension in adolescence. Kardiologiia. 2015;55:21–6.
Martinez-Lemus LA, Aroor AR, Ramirez-Perez FI, Jia G, Habibi J, DeMarco VG, et al. Amiloride improves endothelial function and reduces vascular stiffness in female mice fed a western diet. Front Physiol. 2017;8:456.
da Silva Franco N, Lubaczeuski C, Guizoni DM, Victorio JA, Santos-Silva JC, Brum PC, et al. Propranolol treatment lowers blood pressure, reduces vascular inflammatory markers and improves endothelial function in obese mice. Pharmacol Res. 2017;122:35–45.
Joyner MJ, Dietz NM, Shepherd JT. From Belfast to Mayo and beyond: the use and future of plethysmography to study blood flow in human limbs. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2001;91:2431–41.
Lekakis J, Abraham P, Balbarini A, Blann A, Boulanger CM, Cockcroft J, et al. Methods for evaluating endothelial function: a position statement from the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Peripheral Circulation. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2011;18:775–89.
Wilkinson IB, Webb DJ. VOP in cardiovascular research: methodology and clinical applications. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2001;52: 631–46.
Anderson TJ, Charbonneau F, Title LM, Buithieu J, Rose MS, Conradson H, et al. Microvascular function predicts cardiovascular events in primary prevention: long-term results from the Firefighters and Their Endothelium (FATE) study. Circulation. 2011;123:163–9.
Cockcroft JR, Chowienczyk PJ, Benjamin N, Ritter JM. Preserved endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1036–40.
Panza JA, Casino PR, Badar DM, Quyyumi AA. Effect of increased availability of endothelium-derived nitric oxide precursor on endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in normal subjects and in patients with essential hypertension. Circulation. 1993;87:1475–81.
Panza JA, Casino PR, Kilcoyne CM, Quyyumi AA. Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in the abnormal endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation of patients with essential hypertension. Circulation. 1993;87:1468–74.
Engelke KA, Halliwill JR, Proctor DN, Dietz NM, Joyner MJ. Contribution of nitric oxide and prostaglandins to reactive hyperemia in human forearm. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1996;81: 1807–14.
Park JB, Schiffrin EL. Small artery remodeling is the most prevalent (earliest?) form of target organ damage in mild essential hypertension. J Hypertens. 2001;19:921–30.
Roman RJ, Van Dokkum RP. Commentary on the special issue on the impact of myogenic tone in health and disease. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2014;12:779.
Durand MJ, Gutterman DD. Diversity in mechanisms of endothelium-dependent vasodilation in health and disease. Microcirculation. 2013;20:239–47.
Reglin B, Pries AR. Metabolic control of microvascular networks: oxygen sensing and beyond. J Vasc Res. 2014;51:376–92.
Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists C, Sundstrom J, Arima H, Woodward M, Jackson R, Karmali K, et al. Blood pressure-lowering treatment based on cardiovascular risk: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet. 2014;384:591–8.
Weisbrod RM, Shiang T, Al Sayah L, Fry JL, Bajpai S, Reinhart-King CA, et al. Arterial stiffening precedes systolic hypertension in diet-induced obesity. Hypertension. 2013;62:1105–10.
Oberleithner H, Riethmuller C, Schillers H, MacGregor GA, de Wardener HE, Hausberg M. Plasma sodium stiffens vascular endothelium and reduces nitric oxide release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:16281–6.
Tsounis D, Bouras G, Giannopoulos G, Papadimitriou C, Alexopoulos D, Deftereos S. Inflammation markers in essential hypertension. Med Chem. 2014;10:672–81.
Stefanadi E, Tousoulis D, Androulakis ES, Papageorgiou N, Charakida M, Siasos G, et al. Inflammatory markers in essential hypertension: potential clinical implications. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2010;8:509–16.
Danesh J, Wheeler JG, Hirschfield GM, Eda S, Eiriksdottir G, Rumley A, et al. C-reactive protein and other circulating markers of inflammation in the prediction of coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1387–97.
Emerging Risk Factors C, Kaptoge S, Di Angelantonio E, Lowe G, Pepys MB, Thompson SG, et al. C-reactive protein concentration and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and mortality: an individual participant meta-analysis. Lancet. 2010;375:132–40..
Venugopal SK, Devaraj S, Yuhanna I, Shaul P, Jialal I. Demonstration that C-reactive protein decreases eNOS expression and bioactivity in human aortic endothelial cells. Circulation. 2002;106:1439–41.
Barbaro NR, Fontana V, Modolo R, De Faria AP, Sabbatini AR, Fonseca FH, et al. Increased arterial stiffness in resistant hypertension is associated with inflammatory biomarkers. Blood Press. 2015;24:7–13.
Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, Genest J, Gotto AM Jr., Kastelein JJ, et al. Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2195–207.
Glynn RJ, Koenig W, Nordestgaard BG, Shepherd J, Ridker PM. Rosuvastatin for primary prevention in older persons with elevated C-reactive protein and low to average low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels: exploratory analysis of a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152:488–96,W174.
Sahebkar A, Kotani K, Serban C, Ursoniu S, Mikhailidis DP, Jones SR, et al. Statin therapy reduces plasma endothelin-1 concentrations: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials. Atherosclerosis. 2015;241:433–42.
Struijker-Boudier HA, Rosei AE, Bruneval P, Camici PG, Christ F, Henrion D, et al. Evaluation of the microcirculation in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:2834–40.
Juncos LI, Juncos LA, Garcia NH. The antihypertensive actions of statins: modulation by salt intake. Am J Hypertens 2012;25:1140–8.
Levy BI, Ambrosio G, Pries AR, Struijker-Boudier HA. Microcirculation in hypertension: a new target for treatment? Circulation. 2001;104:735–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Junqueira, C.L., Magalhães, M.E.C., Brandão, A.A. et al. Evaluation of endothelial function by VOP and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with arterial hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 32, 105–113 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-017-0024-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-017-0024-z
- Springer Nature Limited