Abstract
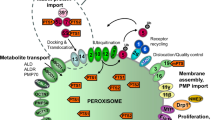
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi membrane system have major roles in cell signaling and regulation of the biosynthesis/transport of proteins and lipids in response to environmental cues such as amino acid and cholesterol levels. Rab1 is the founding member of the Rab small GTPase family, which is known to mediate dynamic membrane trafficking between ER and Golgi. Growing evidence indicate that Rab1 proteins have important functions beyond their classical vesicular transport functions, including nutrient sensing and signaling, cell migration and presentation of cell-surface receptors. Moreover, deregulation of RAB1 expression has been linked to a myriad of human diseases such as cancer, cardiomyopathy and Parkinson’s disease. Further investigating these new physiological and pathological functions of Rab1 should provide new opportunities for better understanding of the disease processes and may lead to more effective therapeutic interventions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmitt HD, Wagner P, Pfaff E, Gallwitz D . The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell 1986; 47: 401–412.
Touchot N, Chardin P, Tavitian A . Four additional members of the ras gene superfamily isolated by an oligonucleotide strategy: molecular cloning of YPT-related cDNAs from a rat brain library. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987; 84: 8210–8214.
Vielh E, Touchot N, Zahraoui A, Tavitian A . Nucleotide sequence of a rat cDNA: rab1B, encoding a rab1-YPT related protein. Nucleic Acids Res 1989; 17: 1770.
Hutagalung AH, Novick PJ . Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology. Physiol Rev 2011; 91: 119–149.
Touchot N, Zahraoui A, Vielh E, Tavitian A . Biochemical properties of the YPT-related rab1B protein: Comparison with rab1A. FEBS Lett 1989; 256: 79–84.
Plutner H, Cox AD, Pind S, Khosravi-Far R, Bourne JR, Schwaninger R et al. Rab1b regulates vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and successive Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol 1991; 115: 31–43.
Saraste J, Lahtinen U, Goud B . Localization of the small GTP-binding protein rab1p to early compartments of the secretory pathway. J Cell Sci 1995; 108: 1541–1552.
Wang C, Yoo Y, Fan H, Kim E, Guan KL, Guan JL . Regulation of Integrin beta 1 recycling to lipid rafts by Rab1a to promote cell migration. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 29398–29405.
Zoppino FC, Militello RD, Slavin I, Alvarez C, Colombo MI . Autophagosome formation depends on the small GTPase Rab1 and functional ER exit sites. Traffic 2010; 11: 1246–1261.
Bailly E, McCaffrey M, Touchot N, Zahraoui A, Goud B, Bornens M . Phosphorylation of two small GTP-binding proteins of the Rab family by p34cdc2. Nature 1991; 350: 715–718.
Mukherjee S, Liu X, Arasaki K, McDonough J, Galan JE, Roy CR . Modulation of Rab GTPase function by a protein phosphocholine transferase. Nature 2011; 477: 103–106.
Muller MP, Peters H, Blumer J, Blankenfeldt W, Goody RS, Itzen A . The Legionella effector protein DrrA AMPylates the membrane traffic regulator Rab1b. Science 2010; 329: 946–949.
Neunuebel MR, Chen Y, Gaspar AH, Backlund PS Jr, Yergey A, Machner MP . De-AMPylation of the small GTPase Rab1 by the pathogen Legionella pneumophila. Science 2011; 333: 453–456.
Cherfils J, Zeghouf M . Regulation of small GTPases by GEFs, GAPs, and GDIs. Physiol Rev 2013; 93: 269–309.
Barrowman J, Bhandari D, Reinisch K, Ferro-Novick S . TRAPP complexes in membrane traffic: convergence through a common Rab. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010; 11: 759–763.
Frasa MAM, Koessmeier KT, Ahmadian MR, VMM Braga . Illuminating the functional and structural repertoire of human TBC/RABGAPs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2012; 13: 67–73.
Lee MCS, Miller EA, Goldberg J, Orci L, Schekman R . Bi-directional protein transport between the ER and Golgi. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2004; 20: 87–123.
Allan BB, Moyer BD, Balch WE . Rab1 recruitment of p115 into a cis-SNARE complex: programming budding COPII vesicles for fusion. Science 2000; 289: 444–448.
Diao A, Rahman D, Pappin DJ, Lucocq J, Lowe M . The coiled-coil membrane protein golgin-84 is a novel rab effector required for Golgi ribbon formation. J Cell Biol 2003; 160: 201–212.
Satoh A, Wang Y, Malsam J, Beard MB, Warren G . Golgin-84 is a rab1 binding partner involved in Golgi structure. Traffic 2003; 4: 153–161.
Horton JD, Goldstein JL, Brown MS . SREBPs: activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest 2002; 109: 1125–1131.
Kim I, Xu W, Reed JC . Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2008; 7: 1013–1030.
Roberg KJ, Bickel S, Rowley N, Kaiser CA . Control of amino acid permease sorting in the late secretory pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by SEC13, LST4, LST7 and LST78. Genetics 1997; 147: 1569–1584.
Drenan RM, Liu X, Bertram PG, Zheng XFS . FKBP12-rapamycin-associated protein or mammalian target of rapamycin (FRAP/mTOR) localization in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 772–778.
Liu X, Zheng XFS . Endoplasmic reticulum and golgi localization sequences for mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Biol Cell 2007; 18: 1073–1082.
Puria R, Zurita-Martinez SA, Cardenas ME . Nuclear translocation of Gln3 in response to nutrient signals requires Golgi-to-endosome trafficking in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2008; 105: 7194–7199.
Demmel L, Beck M, Klose C, Schlaitz AL, Gloor Y, Hsu PP et al. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the Golgi phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase Pik1 is regulated by 14-3-3 proteins and coordinates Golgi function with cell growth. Mol Biol Cell 2008; 19: 1046–1061.
Han J, Li E, Chen L, Zhang Y, Wei F, Liu J et al. The CREB coactivator CRTC2 controls hepatic lipid metabolism by regulating SREBP1. Nature 2015; 524: 243–246.
Porstmann T, Santos CR, Griffiths B, Cully M, Wu M, Leevers S et al. SREBP activity is regulated by mTORC1 and contributes to akt-dependent cell growth. Cell Metab 2008; 8: 224–236.
Abraham RT . Making sense of amino acid sensing. Science 2015; 347: 128–129.
Sanchez-Gurmaches J, Guertin David A . mTORC1 gRABs the Golgi. Cancer Cell 2014; 26: 601–603.
Li L, Kim E, Yuan H, Inoki K, Goraksha-Hicks P, Schiesher RL et al. Regulation of mTORC1 by the Rab and Arf GTPases. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 19705–19709.
Thomas Janice D, Zhang Y-J, Wei Y-H, Cho J-H, Morris Laura E, Wang H-Y et al. Rab1A is an mTORC1 activator and a colorectal oncogene. Cancer Cell 2014; 26: 754–769.
Xu BH, Li XX, Yang Y, Zhang MY, Rao HL, Wang HY et al. Aberrant amino acid signaling promotes growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinomas through Rab1A-dependent activation of mTORC1 by Rab1A. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 20813–20828.
Efeyan A, Zoncu R, Sabatini DM . Amino acids and mTORC1: from lysosomes to disease. Trends Mol Med 2012; 18: 524–533.
Li H, Tsang C, Watkins M, Bertram P, Zheng X . Nutrient regulates Tor1 nuclear localization and association with rDNA promoter. Nature 2006; 442: 1058–1061.
Tsang C, Li H, Zheng X . Nutrient starvation promotes condensin loading to maintain rDNA stability. EMBO J 2007; 26: 448–458.
Kopan R . Notch signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2012; 4: a011213.
Charng WL, Yamamoto S, Jaiswal M, Bayat V, Xiong B, Zhang K et al. Drosophila Tempura, a novel protein prenyltransferase alpha subunit, regulates notch signaling via Rab1 and Rab11. PLoS Biol 2014; 12: e1001777.
Huttenlocher A, Horwitz AR . Integrins in cell migration. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2011; 3: a005074.
He C, Klionsky DJ . Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet 2009; 43: 67–93.
Meiling-Wesse K, Epple UD, Krick R, Barth H, Appelles A, Voss C et al. Trs85 (Gsg1), a component of the TRAPP complexes, is required for the organization of the preautophagosomal structure during selective autophagy via the Cvt pathway. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 33669–33678.
Wang J, Menon S, Yamasaki A, Chou HT, Walz T, Jiang Y et al. Ypt1 recruits the Atg1 kinase to the preautophagosomal structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 9800–9805.
Wang J, Davis S, Menon S, Zhang J, Ding J, Cervantes S et al. Ypt1/Rab1 regulates Hrr25/CK1delta kinase activity in ER-Golgi traffic and macroautophagy. J Cell Biol 2015; 210: 273–285.
Winslow AR, Chen CW, Corrochano S, Acevedo-Arozena A, Gordon DE, Peden AA et al. alpha-Synuclein impairs macroautophagy: implications for Parkinson's disease. J Cell Biol 2010; 190: 1023–1037.
Zhuang X, Adipietro KA, Datta S, Northup JK, Ray K . Rab1 small GTP-binding protein regulates cell surface trafficking of the human calcium-sensing receptor. Endocrinology 2010; 151: 5114–5123.
Wu G . regulation of the trafficking and function of g protein-coupled receptors by Rab1 GTPase in cardiomyocytes. Methods Enzymol 2008; 438: 227–238.
Bao ZS, Li MY, Wang JY, Zhang CB, Wang HJ, Yan W et al. Prognostic value of a nine-gene signature in glioma patients based on mRNA expression profiling. CNS Neurosci Ther 2014; 20: 112–118.
Abd Elmageed ZY, Yang Y, Thomas R, Ranjan M, Mondal D, Moroz K et al. Neoplastic reprogramming of patient-derived adipose stem cells by prostate cancer cell-associated exosomes. Stem Cells 2014; 32: 983–997.
Shimada K, Uzawa K, Kato M, Endo Y, Shiiba M, Bukawa H et al. Aberrant expression of RAB1A in human tongue cancer. Br J Cancer 2005; 92: 1915–1921.
Zhai H, Song B, Xu X, Zhu W, Ju J . Inhibition of autophagy and tumor growth in colon cancer by miR-502. Oncogene 2013; 32: 1570–1579.
He H, Dai F, Yu L, She X, Zhao Y, Jiang J et al. Identification and characterization of nine novel human small GTPases showing variable expressions in liver cancer tissues. Gene Expr 2002; 10: 231–242.
Nalesnik MA, Tseng G, Ding Y, Xiang G-S, Zheng ZL, Yu Y et al. Gene deletions and amplifications in human hepatocellular carcinomas: correlation with hepatocyte growth regulation. Am J Pathol 2012; 180: 1495–1508.
Nikoshkov A, Broliden K, Attarha S, Sviatoha V, Hellstrom AC, Mints M et al. Expression pattern of the PRDX2, RAB1A, RAB1B, RAB5A and RAB25 genes in normal and cancer cervical tissues. Int J Oncol 2015; 46: 107–112.
Sun T, Wang X, He HH, Sweeney CJ, Liu SX, Brown M et al. MiR-221 promotes the development of androgen independence in prostate cancer cells via downregulation of HECTD2 and RAB1A. Oncogene 2014; 33: 2790–2800.
Jiang HL, Sun HF, Gao SP, Li LD, Hu X, Wu J et al. Loss of RAB1B promotes triple-negative breast cancer metastasis by activating TGF-beta/SMAD signaling. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 16352–16365.
Yang Y, Hou N, Wang X, Wang L, Chang S, He K et al. miR-15b-5p induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma, both in vitro and in vivo, by suppressing Rab1A. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 16227–16238.
Wu G, Yussman MG, Barrett TJ, Hahn HS, Osinska H, Hilliard GM et al. Increased myocardial Rab GTPase expression: a consequence and cause of cardiomyopathy. Circ Res 2001; 89: 1130–1137.
Filipeanu CM, Zhou F, Wu G . Analysis of Rab1 function in cardiomyocyte growth. Methods Enzymol 2008; 438: 217–226.
Wei L, Yuan M, Zhou R, Bai Q, Zhang W, Zhang M et al. MicroRNA-101 inhibits rat cardiac hypertrophy by targeting Rab1a. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2015; 65: 357–363.
Sciarretta S, Volpe M, Sadoshima J . Mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in cardiac physiology and disease. Circ Res 2014; 114: 549–564.
Dehay B, Bourdenx M, Gorry P, Przedborski S, Vila M, Hunot S et al. Targeting α-synuclein for treatment of Parkinson's disease: mechanistic and therapeutic considerations. Lancet Neurol 2015; 14: 855–866.
Cooper AA, Gitler AD, Cashikar A, Haynes CM, Hill KJ, Bhullar B et al. α-Synuclein blocks ER-golgi traffic and Rab1 rescues neuron loss in Parkinson’s models. Science 2006; 313: 324–328.
Coune PG, Bensadoun JC, Aebischer P, Schneider BL . Rab1A over-expression prevents Golgi apparatus fragmentation and partially corrects motor deficits in an alpha-synuclein based rat model of Parkinson's disease. J Parkinsons Dis 2011; 1: 373–387.
Sherwood Racquel K, Roy Craig R . A Rab-centric perspective of bacterial pathogen-occupied vacuoles. Cell Host Microbe 2013; 14: 256–268.
Stein M-P, Müller MP, Wandinger-Ness A . Bacterial pathogens commandeer rab GTPases to establish intracellular niches. Traffic 2012; 13: 1565–1588.
Kumar A, Shetty J, Kumar B, Blanton SH . Confirmation of linkage and refinement of the RP28 locus for autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa on chromosome 2p14-p15 in an Indian family. Mol Vis 2004; 10: 399–402.
Huang W, Wu G, Wang GY . Cell type-specific and light-dependent expression of Rab1 and Rab6 GTPases in mammalian retinas. Vis Neurosci 2009; 26: 443–452.
Alexander KR, Fishman GA . Prolonged rod dark adaptation in retinitis pigmentosa. Br J Ophthalmol 1984; 68: 561–569.
Park JS, Heo JS, Chang HS, Choi IS, Kim MK, Lee JU et al. Association analysis of member RAS oncogene family gene polymorphisms with aspirin intolerance in asthmatic patients. DNA Cell Biol 2014; 33: 155–161.
Cervigne NK, Machado J, Goswami RS, Sadikovic B, Bradley G, Perez-Ordonez B et al. Recurrent genomic alterations in sequential progressive leukoplakia and oral cancer: drivers of oral tumorigenesis? Hum Mol Genet 2014; 23: 2618–2628.
Hwang YS, Park KK, Chung WY . Kalopanaxsaponin A inhibits the invasion of human oral squamous cell carcinoma by reducing metalloproteinase-9 mRNA stability and protein trafficking. Biol Pharm Bull 2012; 35: 289–300.
Acknowledgements
Related work in authors’ laboratories was supported by NIH R01 grants CA123391, CA166575 and CA173519, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant nos: 81171891, 81270035 and 81572440, the Recruitment Program of Global Experts, the Lead Talent of Guangdong Province, the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province for Distinguished Young Scholar (no: 2015A030306047), the Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, and Shanghai Pujiang Program 15PJ1404900.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, XZ., Li, XX., Zhang, YJ. et al. Rab1 in cell signaling, cancer and other diseases. Oncogene 35, 5699–5704 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.81
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.81
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Molecular characterization of Rab5A, and involvement in innate immunity in Yellow River Carp Cyprinus carpio
Aquaculture International (2024)
-
Water channel protein AQP1 in cytoplasm is a critical factor in breast cancer local invasion
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)
-
Gamma-glutamyltransferase 7 suppresses gastric cancer by cooperating with RAB7 to induce mitophagy
Oncogene (2022)
-
Endocytosis: a pivotal pathway for regulating metastasis
British Journal of Cancer (2021)
-
Novel insights into the interaction between long non-coding RNAs and microRNAs in glioma
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2021)