Abstract
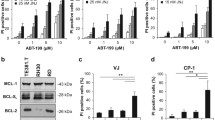
JNJ-26481585 is a second-generation histone deacetylase inhibitor with broad-range efficacy and improved pharmacodynamic properties. In the present study, we investigated the therapeutic potential of JNJ-26481585 and its molecular mechanisms of action in rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS). Here, we report that JNJ- 26481585’s anticancer activity critically depends on an intact mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. JNJ-26481585 induces apoptosis and also inhibits long-term clonogenic survival of several RMS cell lines at nanomolar concentrations that cause histone acetylation. Importantly, JNJ-26481585 significantly suppresses tumor growth in vivo in two preclinical RMS models, that is, the chorioallantoic membrane model and a xenograft mouse model. Mechanistically, we identify activation of the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis as a key event that is critically required for JNJ-26481585-mediated cell death. JNJ-26481585 upregulates expression levels of several BH3-only proteins including Bim, Puma and Noxa, which all contribute to JNJ-26481585-mediated apoptosis, as knockdown of Bim, Puma or Noxa significantly inhibits cell death. This shift toward proapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins promotes activation of Bax and Bak as a critical event, as genetic silencing of Bax or Bak protects against JNJ-26481585-induced apoptosis. Intriguingly, rescue experiments reveal that JNJ-26481585 triggers Bax/Bak activation independently of caspase activation and activates caspase-9 as the initiator caspase in the cascade, as Bcl-2 overexpression, but not the broad-range caspase inhibitor N-benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-fluoromethylketone (zVAD.fmk) blocks JNJ-26481585-induced Bax/Bak activation and caspase-9 cleavage. In conclusion, JNJ-26481585 exerts potent antitumor activity against RMS in vitro and in vivo by engaging mitochondrial apoptosis before caspase activation and represents a promising therapeutic for further investigation in RMS.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller RW, Young JL Jr, Novakovic B . Childhood cancer. Cancer 1995; 75: 395–405.
Dagher R, Helman L . Rhabdomyosarcoma: an overview. Oncologist 1999; 4: 34–44.
Hayes-Jordan A, Andrassy R . Rhabdomyosarcoma in children. Curr Opin Pediatr 2009; 21: 373–378.
Dantonello TM, Int-Veen C, Harms D, Leuschner I, Schmidt BF, Herbst M et al. Cooperative trial CWS-91 for localized soft tissue sarcoma in children, adolescents, and young adults. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 1446–1455.
Fulda S, Debatin KM . Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 2006; 25: 4798–4811.
Taylor RC, Cullen SP, Martin SJ . Apoptosis: controlled demolition at the cellular level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 231–241.
Fulda S, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G . Targeting mitochondria for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2010; 9: 447–464.
Adams JM, Cory S . The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 2007; 26: 1324–1337.
Ellis L, Atadja PW, Johnstone RW . Epigenetics in cancer: targeting chromatin modifications. Mol Cancer Ther 2009; 8: 1409–1420.
Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW . Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006; 5: 769–784.
Matthews GM, Newbold A, Johnstone RW . Intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathway signaling as determinants of histone deacetylase inhibitor antitumor activity. Adv Cancer Res 2012; 116: 165–197.
Arts J, King P, Marien A, Floren W, Belien A, Janssen L et al. JNJ-26481585, a novel "second-generation" oral histone deacetylase inhibitor, shows broad-spectrum preclinical antitumoral activity. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 6841–6851.
Deleu S, Lemaire M, Arts J, Menu E, Van Valckenborgh E, King P et al. The effects of JNJ-26481585, a novel hydroxamate-based histone deacetylase inhibitor, on the development of multiple myeloma in the 5T2MM and 5T33MM murine models. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1894–1903.
Venugopal B, Baird R, Kristeleit RS, Plummer R, Cowan R, Stewart A et al. A phase I study of quisinostat (JNJ-26481585), an oral hydroxamate histone deacetylase inhibitor with evidence of target modulation and antitumor activity, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2013; 19: 4262–4272.
Carol H, Gorlick R, Kolb EA, Morton CL, Manesh DM, Keir ST et al. Initial testing (stage 1) of the histone deacetylase inhibitor, quisinostat (JNJ-26481585), by the Pediatric Preclinical Testing Program. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2014; 61: 245–252.
Chen X, Stewart E, Shelat AA, Qu C, Bahrami A, Hatley M et al. Targeting oxidative stress in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Cell 2013; 24: 710–724.
Halkidou K, Gaughan L, Cook S, Leung HY, Neal DE, Robson CN . Upregulation and nuclear recruitment of HDAC1 in hormone refractory prostate cancer. Prostate 2004; 59: 177–189.
Vogler M, Walczak H, Stadel D, Haas TL, Genze F, Jovanovic M et al. Small molecule XIAP inhibitors enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis and antitumor activity in preclinical models of pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 2425–2434.
Stupack DG, Teitz T, Potter MD, Mikolon D, Houghton PJ, Kidd VJ et al. Potentiation of neuroblastoma metastasis by loss of caspase-8. Nature 2006; 439: 95–99.
Graab U, Hahn H, Fulda S . Identification of a novel synthetic lethality of combined inhibition of hedgehog and PI3K signaling in rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 8722–8735.
Sarosiek KA, Chi X, Bachman JA, Sims JJ, Montero J, Patel L et al. BID preferentially activates BAK while BIM preferentially activates BAX, affecting chemotherapy response. Mol Cell 2013; 51: 751–765.
Felix CA, Kappel CC, Mitsudomi T, Nau MM, Tsokos M, Crouch GD et al. Frequency and diversity of p53 mutations in childhood rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res 1992; 52: 2243–2247.
Taylor AC, Shu L, Danks MK, Poquette CA, Shetty S, Thayer MJ et al. P53 mutation and MDM2 amplification frequency in pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma tumors and cell lines. Med Pediatr Oncol 2000; 35: 96–103.
Happo L, Strasser A, Cory S . BH3-only proteins in apoptosis at a glance. J Cell Sci 2012; 125: 1081–1087.
Han Z, Hendrickson EA, Bremner TA, Wyche JH . A sequential two-step mechanism for the production of the mature p17:p12 form of caspase-3 in vitro. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 13432–13436.
Stuhmer T, Arts J, Chatterjee M, Borawski J, Wolff A, King P et al. Preclinical anti-myeloma activity of the novel HDAC-inhibitor JNJ-26481585. Br J Haematol 2010; 149: 529–536.
Inoue S, Riley J, Gant TW, Dyer MJ, Cohen GM . Apoptosis induced by histone deacetylase inhibitors in leukemic cells is mediated by Bim and Noxa. Leukemia 2007; 21: 1773–1782.
Wiegmans AP, Alsop AE, Bots M, Cluse LA, Williams SP, Banks KM et al. Deciphering the molecular events necessary for synergistic tumor cell apoptosis mediated by the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat and the BH3 mimetic ABT-737. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 3603–3615.
Xargay-Torrent S, Lopez-Guerra M, Saborit-Villarroya I, Rosich L, Campo E, Roue G et al. Vorinostat-induced apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma is mediated by acetylation of proapoptotic BH3-only gene promoters. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 3956–3968.
Labi V, Erlacher M, Kiessling S, Manzl C, Frenzel A, O'Reilly L et al. Loss of the BH3-only protein Bmf impairs B cell homeostasis and accelerates gamma irradiation-induced thymic lymphoma development. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 641–655.
Witt O, Milde T, Deubzer HE, Oehme I, Witt R, Kulozik A et al. Phase I/II intra-patient dose escalation study of vorinostat in children with relapsed solid tumor, lymphoma or leukemia. Klin Padiatr 2012; 224: 398–403.
Fulda S, Sieverts H, Friesen C, Herr I, Debatin KM . The CD95 (APO-1/Fas) system mediates drug-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 3823–3829.
Heinicke U, Fulda S . Chemosensitization of rhabdomyosarcoma cells by the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA. Cancer Lett 2014; 351: 50–58.
Hacker S, Dittrich A, Mohr A, Schweitzer T, Rutkowski S, Krauss J et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors cooperate with IFN-gamma to restore caspase-8 expression and overcome TRAIL resistance in cancers with silencing of caspase-8. Oncogene 2009; 28: 3097–3110.
Workman P, Aboagye EO, Balkwill F, Balmain A, Bruder G, Chaplin DJ et al. Guidelines for the welfare and use of animals in cancer research. Br J Cancer 2010; 102: 1555–1577.
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Hugenberg for expert secretarial assistance. This work has been partially supported by grants from the BMBF and the Deutsche Kinderkrebsstiftung (to SF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heinicke, U., Kupka, J., Fichter, I. et al. Critical role of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis for JNJ-26481585-induced antitumor activity in rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncogene 35, 3729–3741 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.440
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.440
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Staufen1 controls mitochondrial metabolism via HIF2α in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma and promotes tumorigenesis
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Evidence of a non-apoptotic mode of cell death in microglial BV-2 cells exposed to different concentrations of zinc oxide nanoparticles
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2021)
-
MEK inhibitors induce apoptosis via FoxO3a-dependent PUMA induction in colorectal cancer cells
Oncogenesis (2018)
-
BCL-2 selective inhibitor ABT-199 primes rhabdomyosarcoma cells to histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptosis
Oncogene (2018)
-
Concomitant epigenetic targeting of LSD1 and HDAC synergistically induces mitochondrial apoptosis in rhabdomyosarcoma cells
Cell Death & Disease (2017)