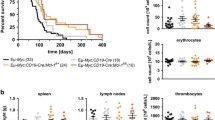
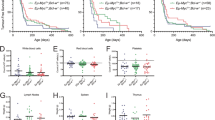
Abstract
Genomic analyses revealed that many cancers have acquired abnormalities in their expression of pro- or anti-apoptotic members of the BCL-2 protein family. It is, however, unknown whether changes in pro- or anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members have similar impact on tumorigenesis or whether changes in one subgroup have disproportionate impact. We compared the consequences of concomitant loss of anti-apoptotic Bclx and pro-apoptotic Bim on MYC-induced lymphomagenesis. Whereas only loss of both Bclx alleles markedly forestalled tumorigenesis, loss of a single Bim allele overcame this blockade. Conversely, loss of even a single Bim allele sufficed to substantially accelerate lymphomagenesis, and only loss of both but not loss of a single allele of Bclx could attenuate this acceleration. The evidence that modest (two-fold) monoallelic changes in the expression of at least some BH3-only proteins can profoundly impact tumorigenesis suggests that such aberrations, imposed by epigenetic or genetic changes, may expedite tumorigenesis more effectively than elevated expression of pro-survival BCL-2 family members. These findings further our understanding of the mechanisms of lymphomagenesis and possibly also cancer therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strasser A, Harris AW, Bath ML, Cory S . Novel primitive lymphoid tumours induced in transgenic mice by cooperation between myc and bcl-2. Nature 1990; 348: 331–333.
Strasser A, Cory S, Adams JM . Deciphering the rules of programmed cell death to improve therapy of cancer and other diseases. EMBO J 2011; 30: 3667–3683.
Motoyama N, Wang FP, Roth KA, Sawa H, Nakayama K, Nakayama K et al. Massive cell death of immature hematopoietic cells and neurons in Bcl-x deficient mice. Science 1995; 267: 1506–1510.
Egle A, Harris AW, Bouillet P, Cory S . Bim is a suppressor of Myc-induced mouse B cell leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 6164–6169.
Bouillet P, Metcalf D, Huang DCS, Tarlinton DM, Kay TWH, Köntgen F et al. Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science 1999; 286: 1735–1738.
Akhtar RS, Klocke BJ, Strasser A, Roth KA . Loss of BH3-only protein Bim inhibits apoptosis of hemopoietic cells in the fetal liver and male germ cells but not neuronal cells in bcl-x-deficient mice. J Histochem Cytochem 2008; 56: 921–927.
Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ, Fletcher JI, Hinds MG et al. Differential targeting of pro-survival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell 2005; 17: 393–403.
Tsujimoto Y, Yunis J, Onorato-Showe L, Erikson J, Nowell PC, Croce CM . Molecular cloning of the chromosomal breakpoint of B-cell lymphomas and leukemias with the t(11;14) chromosome translocation. Science 1984; 224: 1403–1406.
Beroukhim R, Mermel C, Porter D, Wei G, Raychaudhuri S, Donovan J et al. The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature 2010; 463: 899–905.
Tagawa H, Karnan S, Suzuki R, Matsuo K, Zhang X, Ota A et al. Genome-wide array-based CGH for mantle cell lymphoma: identification of homozygous deletions of the proapoptotic gene BIM. Oncogene 2005; 24: 1348–1358.
Mestre-Escorihuela C, Rubio-Moscardo F, Richter JA, Siebert R, Climent J, Fresquet V et al. Homozygous deletions localize novel tumor suppressor genes in B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2007; 109: 271–280.
Garrison SP, Jeffers JR, Yang C, Nilsson JA, Hall MA, Rehg JE et al. Selection against PUMA gene expression in Myc-driven B-cell lymphomagenesis. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 5391–5402.
Swanson PJ, Kuslak SL, Fang W, Tze L, Gaffney P, Selby S et al. Fatal acute lymphoblastic leukemia in mice transgenic for B cell-restricted bcl-xL and c-myc. J Immunol 2004; 172: 6684–6691.
Michalak EM, Jansen ES, Happo L, Cragg MS, Tai L, Smyth GK et al. Puma and to a lesser extent Noxa are suppressors of Myc-induced lymphomagenesis. Cell Death Differ 2009; 16: 684–696.
Adams JM, Harris AW, Pinkert CA, Corcoran LM, Alexander WS, Cory S et al. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature 1985; 318: 533–538.
Kelly PN, Grabow S, Delbridge ARD, Strasser A, Adams JM . Endogenous Bcl-xL is essential for Myc-driven lymphomagenesis in mice. Blood 2011; 118: 6380–6386.
Labi V, Erlacher M, Kiessling S, Manzl C, Frenzel A, O’Reilly L et al. Loss of the BH3-only protein Bmf impairs B cell homeostasis and accelerates gamma irradiation-induced thymic lymphoma development. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 641–655.
Michalak EM, Vandenberg CJ, Delbridge ARD, Wu L, Scott CL, Adams JM et al. Apoptosis-promoted tumorigenesis: gamma-irradiation-induced thymic lymphomagenesis requires Puma-driven leukocyte death. Genes Dev 2010; 24: 1608–1613.
Opferman J, Iwasaki H, Ong CC, Suh H, Mizuno S, Akashi K et al. Obligate role of anti-apoptotic MCL-1 in the survival of hematopoietic stem cells. Science 2005; 307: 1101–1104.
Kaplan HS . The Role of Radiation on Experimental Leukemogenesis. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 1964; 14: 207–220.
Delbridge AR, Valente LJ, Strasser A . The role of the apoptotic machinery in tumor suppression. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2012; 4: doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a008789.
Happo L, Cragg MS, Phipson B, Haga JM, Jansen ES, Herold MJ et al. Maximal killing of lymphoma cells by DNA-damage inducing therapy requires not only the p53 targets Puma and Noxa but also Bim. Blood 2010; 116: 5256–5267.
Cragg MS, Harris C, Strasser A, Scott CL . Unleashing the power of inhibitors of oncogenic kinases through BH3 mimetics. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 321–326.
Merino D, Khaw SL, Glaser SP, Anderson DJ, Belmont LD, Wong C et al. Bcl-2, Bcl-x(L), and Bcl-w are not equivalent targets of ABT-737 and navitoclax (ABT-263) in lymphoid and leukemic cells. Blood 2012; 119: 5807–5816.
Kelly PN, Grabow S, Delbridge AR, Adams JM, Strasser A . Prophylactic treatment with the BH3 mimetic ABT-737 impedes Myc-driven lymphomagenesis in mice. Cell Death Differ 2013; 20: 57–63.
Kelly PN, Puthalakath H, Adams JM, Strasser A . Endogenous bcl-2 is not required for the development of Eμ-myc-induced B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2007; 109: 4907–4913.
Print CG, Loveland KL, Gibson L, Meehan T, Stylianou A, Wreford N et al. Apoptosis regulator Bcl-w is essential for spermatogenesis but appears otherwise redundant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 12424–12431.
Acknowledgements
We thank PN Kelly (NIH) for previously published work that laid the foundation for the present study, G Siciliano and his team for animal husbandry, the FACS facility and the histology facility at The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute. Work in the authors’ laboratory was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (program grant 461221/1016701, Fellowship 1020363, NHMRC Project 1046010), the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (SCOR grant #7413; 7001-13), the Cancer Council Victoria (CCV grant 1052309), and fellowships from the Cancer Council of Victoria (SG), Lady Tata Postdoctoral Fellowship (SG), Melbourne International Research Scholarship (University of Melbourne, SG), Melbourne International Fee Remission Scholarship (University of Melbourne, SG), Australian Postgraduate Award (ARDD) and Cancer Therapeutics CRC Top-up Scholarship (SG and ARDD). This work was made possible by operational infrastructure grants through the Australian Government (IRISS) and the Victorian State Government (OIS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors are employed by The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute. The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute receives milestone payments from Genentech and AbbVie for the development of ABT-199 for cancer therapy.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delbridge, A., Grabow, S., Bouillet, P. et al. Functional antagonism between pro-apoptotic BIM and anti-apoptotic BCL-XL in MYC-induced lymphomagenesis. Oncogene 34, 1872–1876 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.132
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.132
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Betulin and betulinic acid: triterpenoids derivatives with a powerful biological potential
Phytochemistry Reviews (2019)
-
The BCL-2 protein family, BH3-mimetics and cancer therapy
Cell Death & Differentiation (2015)